The full name of DNS is “Domain Name System,” which is a fundamental service of the Internet that maps domain names to IP addresses, making it easier for people to access the Internet. However, sometimes custom DNS operations are needed to resolve certain network issues. This article demonstrates how to set up DNS optimization and traffic splitting on OpenWrt, along with an analysis of the underlying principles.
DNS Principles
Various services and software on the Internet actually use IP address patterns for networking, but the relevant IP addresses are not built into the client. Instead, they are obtained in real-time through domain name resolution. Domain names are easier to remember and can remain unchanged. Through DNS servers, network service administrators can change the IP addresses corresponding to domain names at any time for server changes, network traffic CDN splitting, etc., while users do not need to worry about changes in server IP addresses; they only need to remember the domain name.
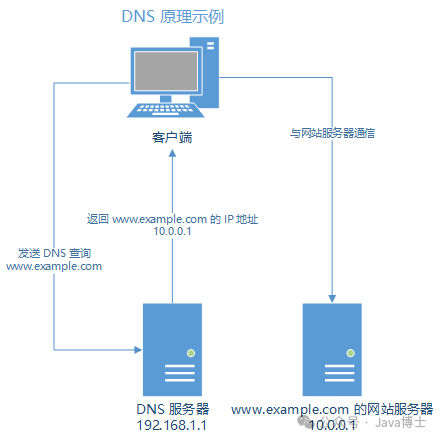
DNS servers are usually in the form of fixed IP addresses, and clients send DNS query requests directly to this IP address to obtain the corresponding IP address for the domain name.DNS servers are like the front desk of a hotel, while DNS queries are akin to asking the front desk for a guest’s room number.
For example, when a client browser wants to access a website, it first sends a domain name query request to the DNS server, which returns an IP address. The client’s browser then communicates with this IP address and subsequently displays the website’s content.
The Internet’s DNS system consists of many DNS servers, including those provided by local network operators and those provided by large Internet companies. The resolution effectiveness of these DNS servers varies.
DNS Pollution
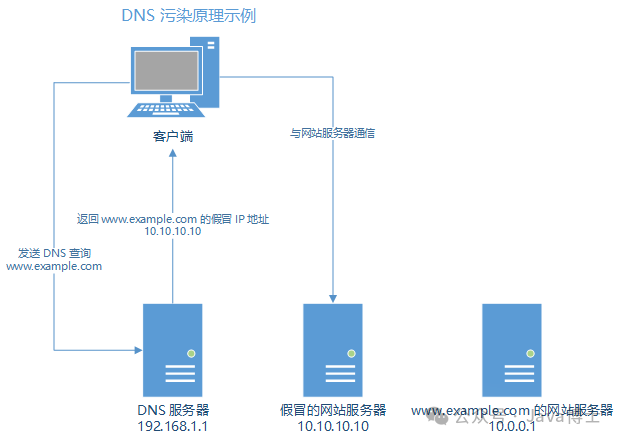
As a public basic Internet service, DNS servers should theoretically return the correct IP addresses fairly and reliably. However, since DNS servers are managed by people, under various interests or certain national policies, some public DNS servers may deliberately implement pollution strategies, mapping certain domain names to incorrect IP addresses, preventing users from accessing them or causing network failures.
These unreliable public DNS servers can also implement more functions, such as specifically resolving normal user requests to a particular IP address, thereby utilizing the massive user traffic for network attacks, such as detailed logging of users’ query requests and other privacy information.
Note: If you are surfing the Internet within China, you will inevitably encounter DNS pollution issues, as the Great Firewall (GFW) actively pollutes all authoritative DNS query results.
OpenWrt DNS Optimization and Traffic Splitting Setup
From the above DNS principles, it is clear that some public DNS servers are unreliable. To avoid the pollution strategies of public DNS servers, local DNS optimization settings must be made to resolve network failures or risks caused by DNS pollution.
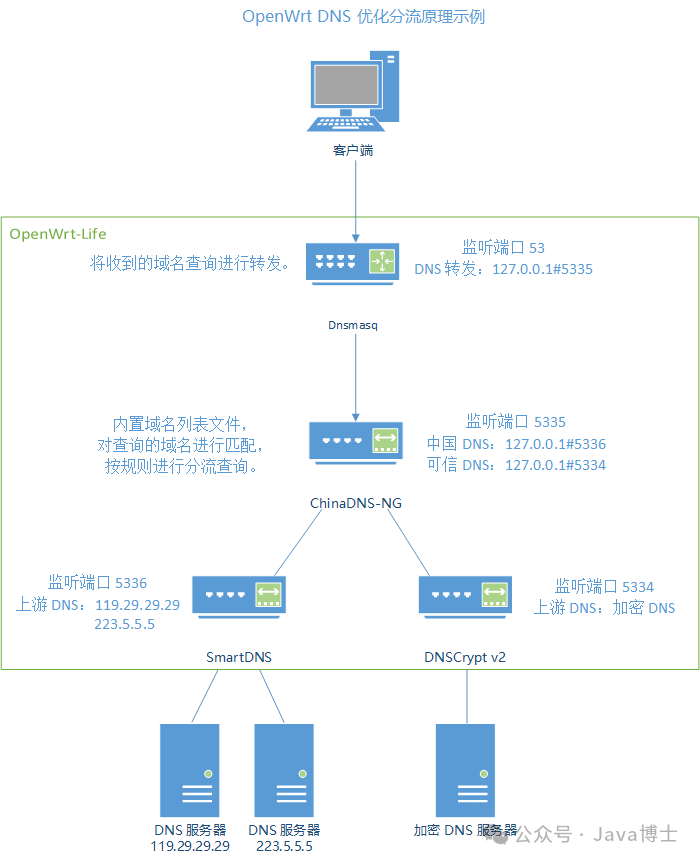
This example demonstrates DNS optimization settings on a typical single router, using the following solution: Dnsmasq + ChinaDNS-NG + SmartDNS + DNSCrypt v2.
Dnsmasq is the default DNS server for the OpenWrt system, responsible for providing DNS services to all LAN clients.ChinaDNS-NG has a built-in domain name list file that matches queried domain names and performs traffic splitting queries according to rules.SmartDNS is used to resolve domain names for Chinese websites.DNSCrypt v2 is used to resolve polluted domain names.
The effect of DNS optimization and traffic splitting: clients do not need additional settings; the gateway router proxies DNS queries, using Chinese DNS servers for Chinese domain names and trusted DNS servers for polluted domain names, thus obtaining correct DNS query results.
Note: Various clients typically use UDP port 53 or TCP port 53 for DNS queries, so the router must have a DNS server listening on port 53.
Clients can also set up another DNS server to bypass the router for DNS queries. If you do not want clients to use custom DNS, you need to add hijacking rules for port 53 on the gateway router.
Note: This optimization and traffic splitting scheme is only for demonstrating the principles of DNS splitting and does not guarantee the stability of this scheme or the performance of the related software.
Please configure various DNS software reasonably according to your needs to achieve your goals. Some DNS software can independently implement domain name splitting functions; please configure according to actual conditions. Different DNS software can also be deployed on different devices.
Note: Do not blindly configure overly complex DNS rules, as this may lead to negative impacts on the network.
Key points for Dnsmasq settings: In the “General Settings” tab, set “DNS Forwarding” to 127.0.0.1#5335.In the “HOSTS and Resolution Files” tab, check the “Ignore Resolution Files” option.

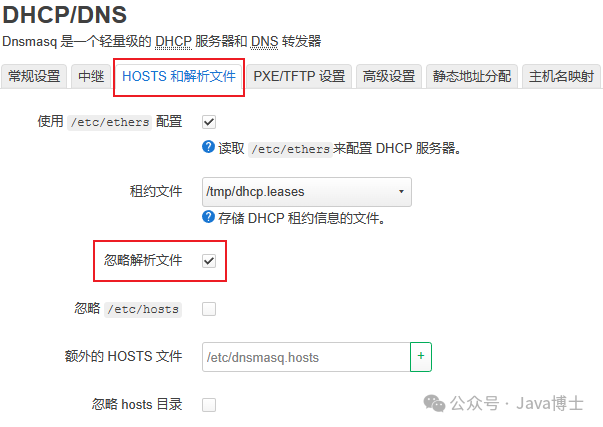
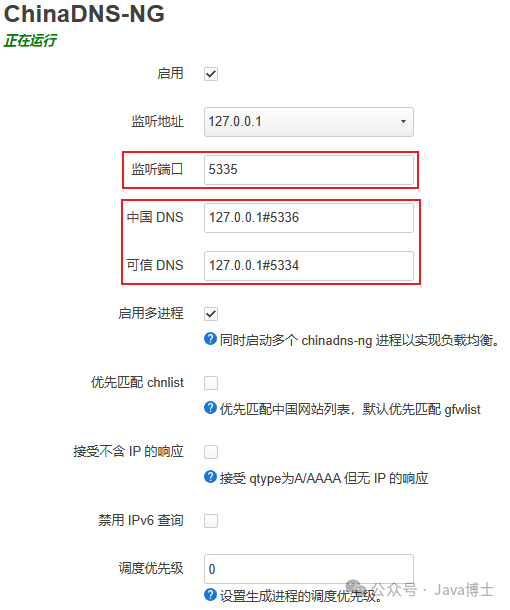
Key points for ChinaDNS-NG settings: Ensure that the “Listening Port” corresponds with the settings in Dnsmasq.“Chinese DNS” and “Trusted DNS” should correspond with the listening addresses of other DNS software.
Note: ChinaDNS-NG does not download domain name files by default upon installation. Please click the “Update Domain File” button to download the required files.
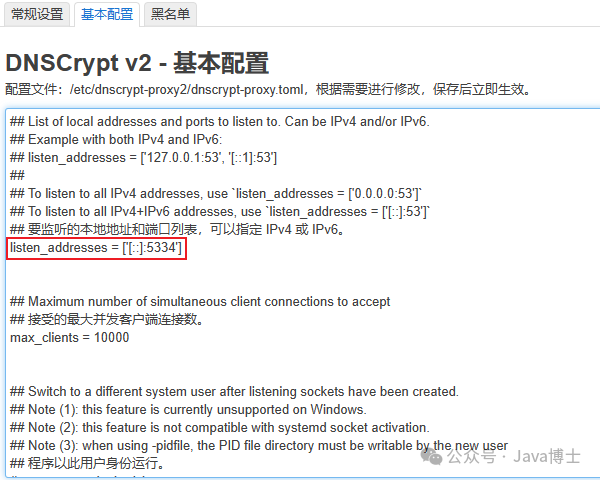
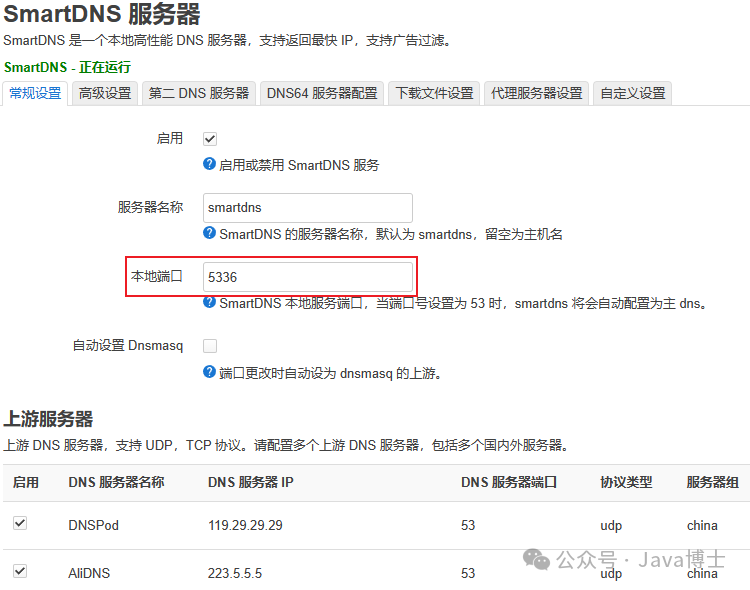
Key points for SmartDNS settings: Ensure that the listening port number does not conflict with other software.
Key points for DNSCrypt v2 settings: Ensure that the listening port number does not conflict with other software.