Introduction
In the field of computer security, encryption algorithms are one of the key technologies for protecting data integrity and privacy. Among them, MD5 is a widely used hash algorithm, and this article will introduce several use cases of MD5.
1. What is MD5?
MD5 is a one-way hash function used to convert input data of arbitrary length (such as strings or files) into a fixed length (128 bits, or 32 hexadecimal characters) hash value.
Characteristics of MD5:
- Irreversibility: It is theoretically impossible to derive the original data from the hash value.
- Determinism: The same input always generates the same hash value.
- Avalanche Effect: A small change in the input data will result in a completely different hash value.
- Fixed Length: Regardless of the input size, the output is always a 32-character hexadecimal string (e.g., c4ca4238a0b923820dcc509a6f75849b).
2. Applications of MD5
Here is an implementation class for MD5 encryption that can be copied and used directly.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyEncrypt
{
internal class MD5Example
{
public static string MD5Encrypt(string input)
{
using (MD5 md5 = MD5.Create())
{
byte[] inputBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(input);
byte[] hashBytes = md5.ComputeHash(inputBytes);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < hashBytes.Length; i++)
{
sb.Append(hashBytes[i].ToString("x2"));
}
return sb.ToString();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Get the MD5 hash of a file
/// </summary>
/// <param name="fileName"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static string AbstracFile(string fileName)
{
using (FileStream file=new FileStream(fileName,FileMode.Open))
{
return AbstracFile(file);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Get the hash from a stream
/// </summary>
/// <param name="stream"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static string AbstracFile(Stream stream)
{
MD5 MD5 = new MD5CryptoServiceProvider();
byte[] retVal=MD5.ComputeHash(stream);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < retVal.Length; i++)
{
sb.Append(retVal[i].ToString("x2"));
}
return sb.ToString();
}
}
}
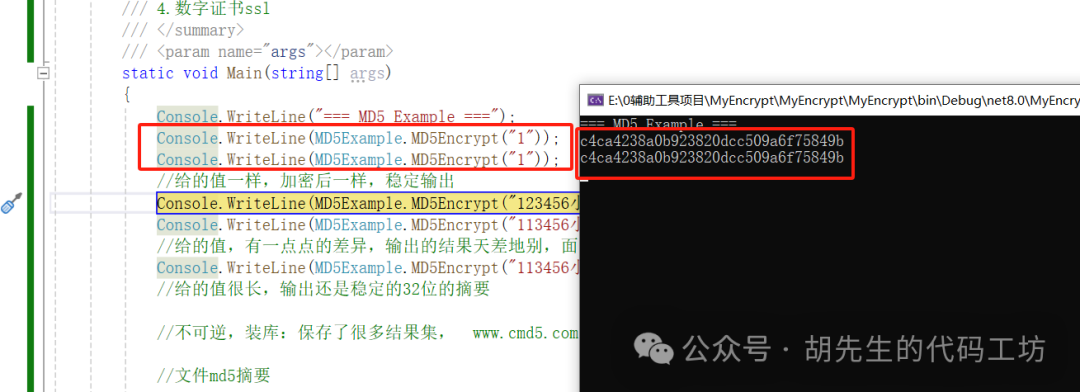
1. Determinism: The same input always generates the same hash value
Note: MD5 encryption is performed on the string “1” twice, and the output results are consistent.
Console.WriteLine("=== MD5 Example ===");
Console.WriteLine(MD5Example.MD5Encrypt("1"));
Console.WriteLine(MD5Example.MD5Encrypt("1"));
Execution Result
2. Avalanche Effect: A small change in input data will lead to completely different hash values
Note: MD5 encryption is performed on “123456小胡” and “113456小胡”. The two strings differ by only one character, but the output results are vastly different.
Console.WriteLine(MD5Example.MD5Encrypt("123456小胡"));
Console.WriteLine(MD5Example.MD5Encrypt("113456小胡"));
// The given values have a slight difference, but the output results are completely different.
Execution Result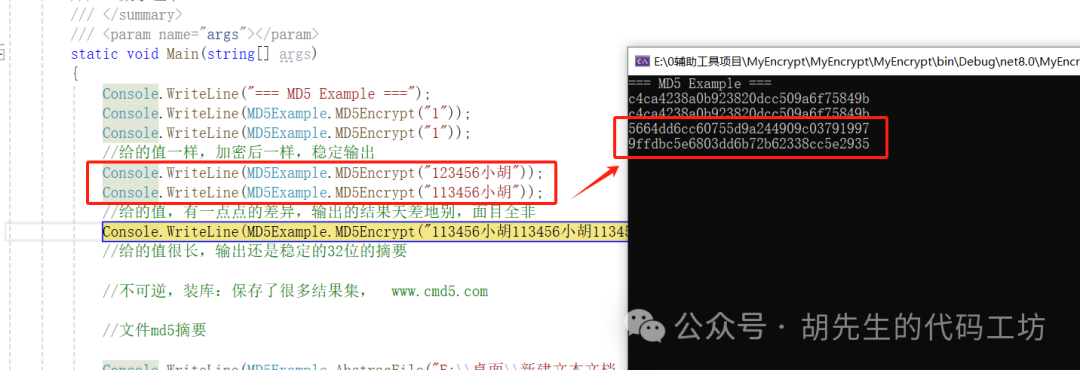
3. Fixed Length: Regardless of input size, the output is always a 32-character hexadecimal string
Note: Even if the input string is very long, the length of the MD5 encrypted output remains 32 characters.
Console.WriteLine(MD5Example.MD5Encrypt("113456小胡113456小胡113456小胡113456小胡113456小胡113456小胡113456小胡113456小胡"));
// The given value is long, but the output is still a stable 32-character hash.
Execution Result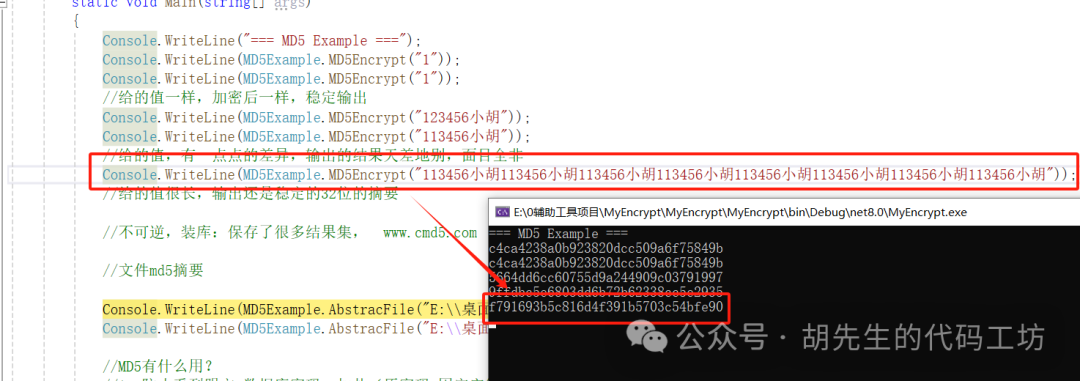
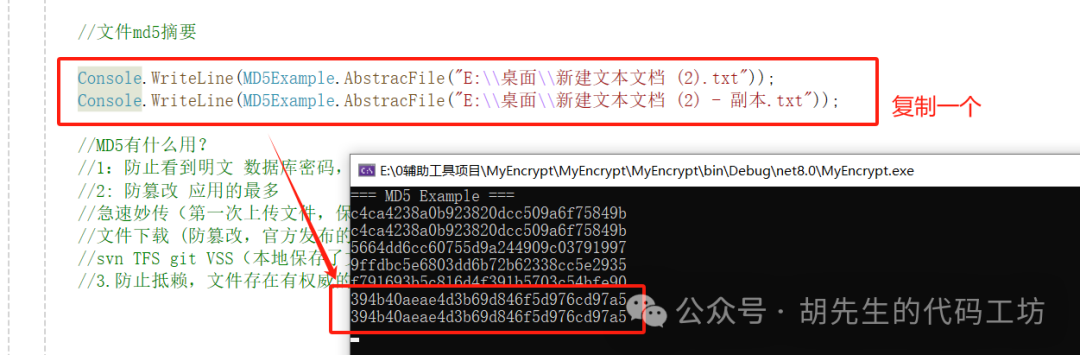
4. The MD5 hash of the same file stream is consistent
Note: Copy a file and then perform MD5 encryption on both files. Despite having the same file name, the MD5 hashes are still the same.
// File MD5 hash
Console.WriteLine(MD5Example.AbstracFile("E:\桌面\新建文本文档 (2).txt"));
Console.WriteLine(MD5Example.AbstracFile("E:\桌面\新建文本文档 (2) - 副本.txt"));
Execution Result
3. What is the use of MD5?
-
Prevent plaintext visibility – The simplest use case is for database passwords, where salting (original password + fixed string, then MD5/double MD5) is applied.
-
Prevent tampering – This is the most common application (1). Rapid file transfer (save the MD5 hash on the first upload, check the MD5 hash on the second upload)
(2). File downloads (to prevent tampering, an MD5 hash is provided during official releases, and the hash is checked first during installation).
-
Code management, for example: svn, TFS, git, VSS. The local MD5 hash of the file is saved, and any modification will affect the MD5.
-
Prevent non-repudiation The file exists with an authoritative institution, and the file generates a hash.
4. Online MD5 Decryption
Website: https://www.cmd5.com/
 MD5 is a one-way encryption, so why can it be decrypted online? The main reason is that a database of plaintext-ciphertext pairs has been created through exhaustive character combinations, with approximately 90 trillion records created.
MD5 is a one-way encryption, so why can it be decrypted online? The main reason is that a database of plaintext-ciphertext pairs has been created through exhaustive character combinations, with approximately 90 trillion records created.