 Column · Supply Chain Security
Column · Supply Chain Security
In the digital age, software is ubiquitous. Software acts as a “virtual person” in society and has become one of the fundamental elements supporting the normal operation of society. The security of software is becoming a fundamental and foundational issue in today’s society.
With the rapid development of the software industry, the software supply chain has become increasingly complex and diverse. A complex software supply chain introduces a series of security issues, making the overall security protection of information systems increasingly difficult. In recent years, security attacks targeting the software supply chain have been on the rise, causing increasingly severe damage.
To address this, we have launched the “Supply Chain Security” column. This column gathers information on supply chain security, analyzes supply chain security risks, and provides mitigation suggestions to safeguard supply chain security.
Note: For previously published content related to supply chain security, please see the “Recommended Reading” section at the end.
 Cybersecurity researchers have discovered three malicious Go modules that contain obfuscated code capable of extracting the next stage payload, which can irreversibly overwrite the main disk of a Linux system and render it unbootable.
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered three malicious Go modules that contain obfuscated code capable of extracting the next stage payload, which can irreversibly overwrite the main disk of a Linux system and render it unbootable.
The names of these malicious packages are as follows:
-
github[.]com/truthfulpharm/prototransform
-
github[.]com/blankloggia/go-mcp
-
github[.]com/steelpoor/tlsproxy
Kush Pandya, a researcher at Socket, stated, “Although they appear to be legitimate, these modules contain highly obfuscated code designed to extract and execute remote payloads.” These malicious packages aim to check if the operating system they are running on is Linux; if so, they receive the next stage payload via wget from a remote server. The payload is a destructive shell script that overwrites the entire main disk (“/dev/sda”) with zeros, effectively preventing the machine from booting. Pandya noted, “This destructive method ensures that no data recovery tools or forensic processes can recover data, as this method directly overwrites in an irreversible manner. This malicious script leads to a faster demise of the target Linux server or developer environment, highlighting the significant dangers posed by modern supply chain attacks, which can turn seemingly trusted code into catastrophic threats.”
Recently, several malicious npm packages were reported to exist in the registry, capable of stealing mnemonic seed phrases and cryptocurrency private keys to extract sensitive data. These packages were discovered by Socket, Sonatype, and Fortinet.
Malware-laden packages targeting cryptocurrency wallets have also appeared in the PyPI repository, capable of sniffing mnemonic seed phrases. These packages have been downloaded over 6,800 times since their release in 2024. Additionally, seven other PyPI packages have been reported to utilize Gmail’s SMTP server and WebSocket to extract data and achieve remote command execution, attempting to evade detection. These packages log into the service’s SMTP server using hardcoded Gmail account credentials and send messages to another Gmail address to indicate successful compromise. They then establish a WebSocket connection to create a bidirectional communication channel with the attacker. Attackers exploit the trust associated with the Gmail domain (“smtp.gmail[.]com”) and the fact that enterprise proxies and endpoint protection systems may not flag them as “suspicious,” making the attack stealthy and reliable.
To mitigate such supply chain threats, developers are advised to verify the authenticity of packages by checking the publisher’s history and GitHub repository links; regularly audit dependencies and enforce strict access controls on private keys.
Olivia Brown, a researcher at Socket, stated, “Be aware of unusual outbound connections, especially SMTP traffic, as attackers can use legitimate services like Gmail to steal sensitive data. Do not assume a package is trustworthy just because it has been around for many years without being taken down.”
 Open SourceGuardian trial address:https://sast.qianxin.com/#/loginCode Guardian trial address:https://codesafe.qianxin.comRecommended Reading
Open SourceGuardian trial address:https://sast.qianxin.com/#/loginCode Guardian trial address:https://codesafe.qianxin.comRecommended Reading
AI-generated code dependencies constitute new software supply chain risks
PoisonSeed: Supply chain attacks targeting cryptocurrency and email providers
GitHub Actions supply chain attack triggered by compromised SpotBugs token
GitHub Action compromised, triggering a chain supply chain attack
Popular GitHub Action suffers from supply chain attack
GitHub Actions vulnerability could allow attackers to poison development pipelines
Abuse of GitHub Actions for cryptocurrency mining on GitHub servers is spreading
Solana’s popular Web3.js npm library has a backdoor that can trigger software supply chain attacks
Software supply chain poisoning – Analysis of malicious NPM components
Software supply chain poisoning – Analysis of malicious NPM components (Part II)
Online reading version: Full text of the “2023 China Software Supply Chain Security Analysis Report”
NPM library XMLRPC inserts malicious code to steal data and deploy cryptocurrency miners
Entry points in Python, npm, and the open-source ecosystem can be used to launch supply chain attacks
NPM malicious package impersonates “noblox.js” to compromise Roblox development systems
Malicious npm packages hide backdoor code in image files
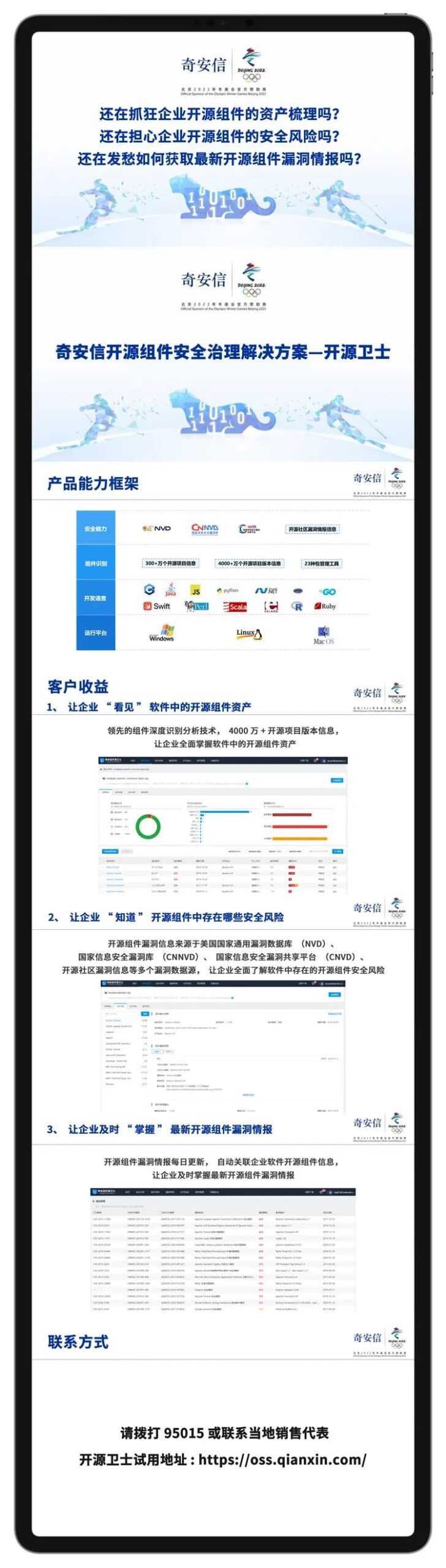
Qihoo 360 selected as a representative vendor in the global “Software Component Analysis Panorama”
Qihoo 360 selected as a representative vendor in the global “Static Application Security Testing Panorama”
Qihoo 360’s open-source guardian first passed the assessment of trusted open-source governance tools
Overview of global software supply chain security guidelines and regulations
UK-Korea: Lazarus hacker group exploits 0-day vulnerabilities in security certification software to launch supply chain attacks
Okta support system compromised, affecting three clients including Cloudflare and 1Password
Hackers compromise Okta to launch supply chain attacks, impacting over 130 organizations
Okta concludes investigation into Lapsus$ supply chain incident, stating it will strengthen third-party controls
Okta warns: Social engineering attacks are targeting super administrator privileges
“Software Vendor Handbook: Generation and Provision of SBOM” Interpretation
Original linkhttps://thehackernews.com/2025/05/malicious-go-modules-deliver-disk.html
This article is translated by Qihoo 360 and does not represent the views of Qihoo 360. Please indicate “Reprinted from Qihoo 360 Code Guardian https://codesafe.qianxin.com” when reprinting.


Qihoo 360 Code Guardian (codesafe)
The first product line in China focused on software development security.