Learning Linux Shell commands is a gradual process. Beginners can start with basic commands and gradually master scripting and system management. During the learning process, it is recommended to practice hands-on and refer to online documentation and community resources. At the same time, as technology continues to evolve, Linux is also constantly updating. Maintaining a passion for learning and sensitivity to new technologies will keep you competitive in this field.
Basic Concepts of Linux Shell and Its Importance
In the world of computers, Linux is known for its open-source, stability, and powerful features. The Shell, as the command-line interface of Linux, serves as a bridge to interact with the operating system. Shell commands not only allow us to efficiently manage files and systems but also automate complex tasks. For developers, system administrators, and IT professionals, mastering Shell commands is an indispensable skill in their careers. Whether you are a newcomer to Linux or an experienced veteran, Shell commands are a valuable assistant in your daily work.
Getting Started Section: Basic Commands and Environment Setup
Basic Commands
Let’s start with the most basic commands, which are the stepping stones in the Linux world.
<span>ls</span>: Lists directory contents. For example,<span>ls -l</span>will display files and directories in a detailed list format.<span>cd</span>: Changes the current working directory. For instance,<span>cd /home</span>will take you to the<span>/home</span>directory.<span>cp</span>: Copies files or directories. Using<span>cp source destination</span>can copy files from the source location to the destination.<span>mv</span>: Moves or renames files.<span>mv oldname newname</span>can change a file from an old name to a new name.<span>rm</span>: Deletes files or directories. Use<span>rm -rf</span>with caution, as it will forcefully delete directories and their contents, and cannot be recovered.- man
- : View the manual page for commands. For example,
<span>man ls</span>is used to view the purpose and usage instructions for each command.
Environment Setup
In Linux, environment variables and Shell configuration files (such as <span>.bashrc</span> or <span>.zshrc</span>) are crucial for customizing your working environment.
Review of Previous Content
Bash Environment Variable Loading Process
<span>export</span>: Sets or exports environment variables. For example,<span>export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/bin</span>will add a new path to your PATH variable.<span>.bashrc</span>or<span>.zshrc</span>: These files are read at the start of each new Shell session and are ideal places to configure the Shell environment.
Common Tools
<span>grep</span>: Searches text.<span>grep "pattern" file</span>will search for the specified pattern in the file.<span>sed</span>: A stream editor used for text processing.<span>sed 's/old/new/g' file</span>will replace “old” with “new” in the file.<span>awk</span>: A powerful text processing tool used for pattern scanning and processing language.
Review of Previous Content
Introduction to Linux Shell Programming (Part 2) – grep, sed, awk
Introduction to Linux Shell Programming (Part 3) – Regular Expressions
Introduction to Linux Shell Programming (Part 7) – Text Processing
In-Depth Study of sed: From Beginner to Mastery
In-Depth Study of awk: From Basics to Advanced
Advanced Section: Scripting and Debugging Techniques
Scripting
Shell scripts are a collection of commands that can automate tasks.
- The basic structure of a script includes a shebang (
<span>#!/bin/bash</span>), variable declarations, commands, and conditional statements. - Loops and conditional statements are common control structures in scripts, such as
<span>for</span>loops and<span>if</span>statements.
Common Issues and Solutions
- When a script does not work as expected, use
<span>set -x</span>to enable debugging mode in the script, which will show the status before executing each command. - Check for permission issues to ensure you have the rights to execute commands in the script.
- Check for path issues to ensure all file and command paths are correct.
Review of Previous ContentIntroduction to Linux Shell Programming (Part 1)
Debugging Techniques
- Use the
<span>echo</span>command in scripts to print variables and messages, helping to understand the execution flow of the script. - Break complex commands into smaller parts and test them one by one until the issue is found.
Review of Previous ContentIntroduction to Linux Shell Programming (Part 4) – Shell Script Debugging
Advanced Section: System Management and Automating Tasks
System Management
<span>top</span>and<span>htop</span>: Real-time monitoring of system resource usage.<span>df</span>and<span>du</span>: Check disk space usage.<span>ps</span>and<span>kill</span>: View process status and terminate processes.
Performance Monitoring
<span>iostat</span>: Monitors system input/output devices.<span>vmstat</span>: Reports virtual memory, processes, I/O, and other system status information.
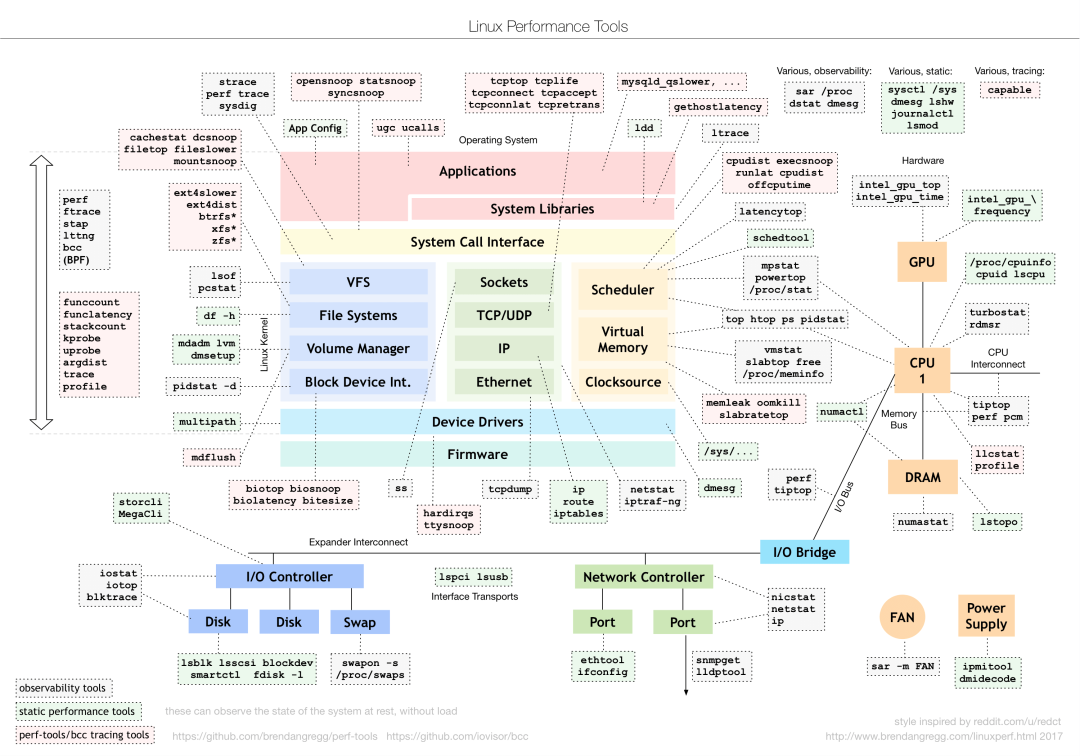 Review of Previous ContentLinux Performance Tools You Need to Know
Review of Previous ContentLinux Performance Tools You Need to Know
Automating Tasks
<span>cron</span>: Executes tasks at scheduled times. By editing the<span>crontab</span>file, you can set up scheduled tasks.<span>at</span>: Schedules one-time tasks to be executed at a future point in time.
Through Scheduled Tasks<span><span>cron</span></span>, you can automate the execution of Shell scripts. Use the <span><span>crontab -e</span></span> command to edit scheduled tasks, for example, to back up data every day at 2 AM:
0 2 * * * /path/to/backup.shConclusion: Suggestions for Learning Linux Shell and Future Development
Learning Linux Shell is an ongoing process, and with the development of technology, new commands and tools are constantly emerging. Here are some suggestions:
- Practice: Theoretical knowledge is the foundation, but practice is key to mastering Shell commands.
- Read Manuals: The
<span>man</span>command is a treasure trove for learning the detailed usage of each command. - Join Communities: The Linux community is a treasure trove of learning resources and help; do not hesitate to ask questions and share.
- Stay Curious: Technology is constantly advancing; maintain curiosity and explore new tools and commands.
With the development of cloud computing and containerization technologies, the importance of Linux Shell commands will only increase. Mastering these skills will keep you competitive in the tech world and open new doors for your career.
Of course, retirement may still be far away, but mastering Linux Shell commands will make your career more stable and secure.
— END–