1. Background of the Intelligent Wireless Sentinel System Based on Wireless Sensor Networks
Wireless sensor networks can assist in achieving effective battlefield situational awareness, meeting the requirements of combat power situational awareness. A typical concept is to use drones to scatter a large number of micro sensor nodes across the vast battlefield. These nodes self-organize into a network to collect, transmit, and fuse battlefield information, providing intelligence services for various participating units. In recent years, research on the use of wireless sensor networks for intelligence detection has increased significantly worldwide. The United States has developed various battlefield sensor monitoring systems since the early 1990s, such as the “Wheelbus” system, which includes sound, vibration, infrared, and magnetic sensors that can identify people (recognition range 3-50 meters), wheeled vehicles (recognition range 15-250 meters), or tracked vehicles (recognition range 25-350 meters), and upload results in real-time to the command center via wireless transmission. The Pentagon commissioned Lockheed Martin to develop a series of various wireless sensors, some of which can be disguised as ordinary stones, equipped with solar panels, microcomputers, seismic sensors, cameras, and microphones. These wireless sensors can secretly monitor potential terrorists for up to 20 years.
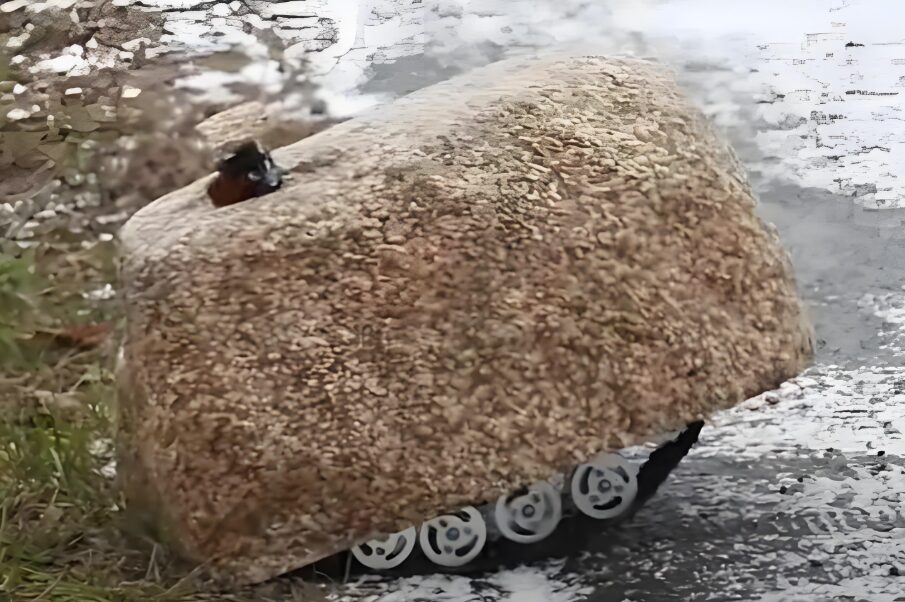
In Norfolk County, Virginia, Lockheed developed a data module connected by 50 palm-sized acoustic and seismic sensors. When the sensors detect a person or vehicle, they transmit signals from one network node to another using radio frequency, ultimately sending the information to satellites, tactical networks, and soldier terminals, or directly to the command center. These sensors consume very little energy and can be equipped with solar panels, allowing them to operate for more than 20 years. The Voronezh Air Force Academy in Russia invented a covert observation device called the “spy stone,” which is disguised as a stone and equipped with motion sensors, mini cameras, and a tracked walking device for information collection, processing, and transmission. Due to its appearance resembling a stone, it is difficult to detect in the field during combat. Especially in positional warfare, when neutral zones are under tight enemy surveillance and sniper fire control, ordinary scouts find it challenging to conduct reconnaissance activities, making the “spy stone” extremely useful.

2. Components of the Wireless Sentinel System
This proposal introduces an intelligent wireless sentinel based on wireless sensor network technology, primarily used for environmental detection and perception (vibration, sound, magnetic field, infrared) within a designated area, and uploads the aggregated data to a monitoring center. The intelligent wireless sentinel features small size, self-powering, long endurance, intelligent detection, and autonomous learning.
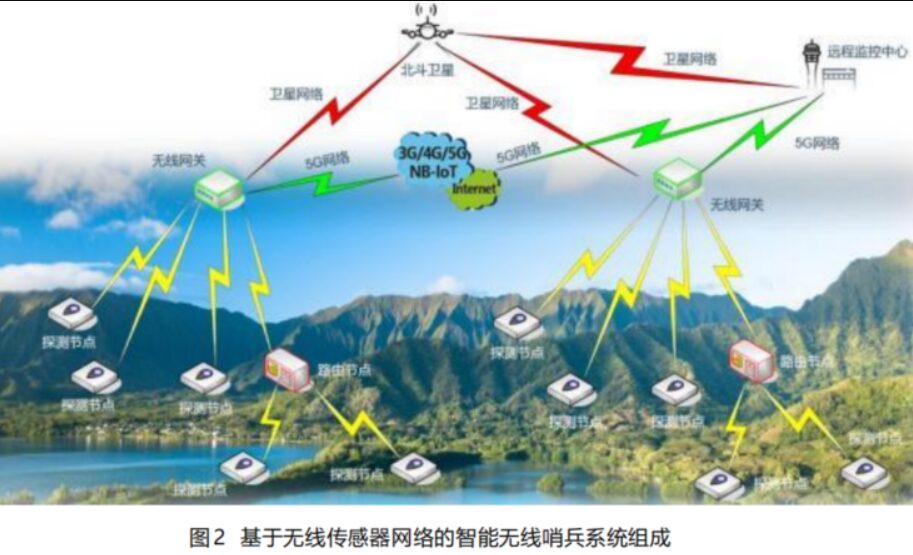
The intelligent wireless sentinel system based on wireless sensor networks consists of detection nodes, routing nodes, wireless gateways, and remote monitoring centers, as shown in Figure 2. The wireless detection nodes periodically or triggered detect the surrounding environmental data and send the analyzed detection results (node location, type of intrusion, and characteristic values) to the wireless gateway. The typical transmission distance of wireless detection nodes is 2000 meters. If the data cannot reach the wireless gateway directly, it can be relayed through routing nodes before being sent to the wireless gateway. One or more wireless gateways in an area will aggregate the data and upload it to the remote monitoring center via 4G/5G or Beidou satellites, where the remote monitoring center analyzes the battlefield situation and conducts comprehensive situational assessments.
3. Typical Application Areas of the Intelligent Wireless Sentinel System
The intelligent wireless sentinel system can be applied in the following scenarios:
(2) Border Line Monitoring: Deploying intelligent wireless sentinels based on wireless sensor networks near border lines can discreetly monitor the movement of personnel and vehicles, preventing smuggling and illegal crossings;
(3) Island Intelligence Reconnaissance: Deploying intelligent wireless sentinels in large numbers near the coastline of an island through drones to collect information on hydrology, environment, personnel, vehicles, and ships near the island coastline, and transmitting data via Beidou messaging to understand local defense conditions, providing data support and remote intelligence support for future military landing operations.
4. Main Features of the Intelligent Wireless Sentinel System
The main features of the intelligent wireless sentinel system include:
(1) Multi-node Networking: The intelligent wireless sentinel consists of multiple wireless detection sensor arrays, each capable of detecting one or more areas. The wireless detection sensor network contains a small number of wireless gateways that aggregate the data from detection nodes and upload it to the monitoring center;
(2) Detection of Multiple Data Types: Each detection node can achieve environmental detection, including vibration, noise, magnetic field, temperature and humidity, GPS location, as well as data analysis and identification;
(3) Combination of 4G/5G and Beidou Satellites: In areas covered by 4G/5G networks, the system utilizes 4G/5G networks for lower costs; in remote areas without 4G/5G networks, or in hostile non-friendly regions, data is transmitted using Beidou satellites;
(4) Good Concealment: Passive detection, small size, good concealment, can be disguised as stones, making it difficult to detect;
(5) High Density Detection: The small size and low cost of sensors allow for an increased number of sensors per unit area;
(6) Low Power Consumption: Using a solar + battery power supply method, typical operational endurance exceeds 2 years;
(7) Long Transmission Distance: The star communication method is used between detection nodes and wireless gateways, with communication distances of not less than 2km (line of sight). If a larger monitoring range is needed, routing nodes can extend the distance.
(8) Artificial Intelligence and Big Data: Combining data encryption technology, artificial intelligence technology, and big data applications to create an IoT perception, smart visual border data monitoring network, comprehensively building a year-round, all-around, three-dimensional intelligent sentinel security and prevention system, ultimately forming a smart border control system with all-time, multi-level, and wide-field capabilities.
(9) Low Cost: Using wireless sensor nodes significantly reduces monitoring costs, making large-scale future deployment feasible.
5. Main Technical Indicators of the Intelligent Wireless Sentinel System

The main performance indicators of the wireless detection nodes are as follows:
(1) Wireless detection nodes are equipped with built-in sensors for vibration, noise, magnetic field, temperature and humidity, GPS/Beidou;
(2) Camouflage: Disguised as stones, suitable for desert, jungle, beach, and other environments;
(3) Vibration Measurement: Range ±2g, sampling rate 5kHz, capable of analyzing vibration data and transmitting vibration characteristic values to detect the type of vibration source;
(4) Noise Measurement: Range 140dB, sampling rate 100kHz, capable of analyzing the type of noise source;
(5) Magnetic Field Measurement: Range 5 Gauss, capable of analyzing whether magnetic equipment has passed;
(6) Temperature and Humidity Measurement: Temperature measurement range -40℃~85℃, accuracy ±0.5℃, humidity measurement range 0%~100%RH, accuracy 5%;
(7) GPS and Beidou location measurement accuracy: 10m RMS;
(8) Sampling period: No less than 10 minutes to collect a set of data;
(9) Triggered Collection: If vibration or noise exceeds the threshold, the detection node can initiate collection and wake surrounding nodes into operational status;
(10) Battery: Built-in battery with standby time of not less than 2 years, capable of self-charging in sunny environments;
(11) Wireless Frequency: 433MHz;
(12) Transmission Distance: No less than 2km in open areas;
(13) Size: No larger than 50 mm×50 mm×40 mm;
(14) Weight: No more than 100g;
(15) Operating Environment: -40℃~85℃, humidity 0%~100%RH;
(16) Waterproof Rating: IP67;
(17) Shock Resistance: 1000g, able to adapt to airdrop environments from 100 meters.
6. Sensors Involved in the Intelligent Wireless Sentinel System by Sensory Technology


