Abstract
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is defined as the application of Internet of Things (IoT) technology in the automation field using industrial communication technologies. The IIoT environment has penetrated various fields such as our cities, transportation, manufacturing, and infrastructure, while becoming a popular target for hackers. Honeypots and honeynets have proven crucial for understanding and defending against attacks on IIoT, as they can attract attackers and deceive them into believing they have gained access to real systems. Honeypots and honeynets can complement other mainstream security solutions (firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)) to effectively defend against malicious behavior. This article introduces research on honeypots and honeynets for IIoT.
1. Industrial Internet of Things and Similar Definitions
2. Industrial IoT Honeypots and Honeynets
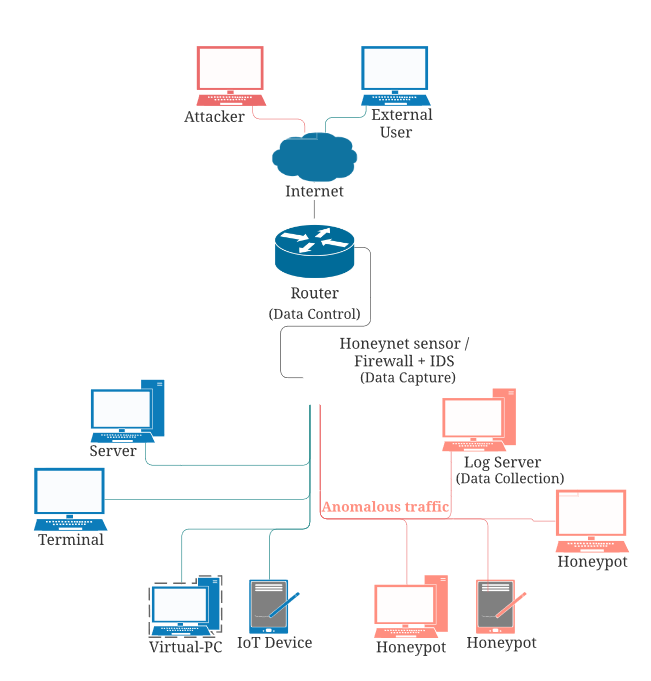
Figure 1 Base Honeynet Architecture
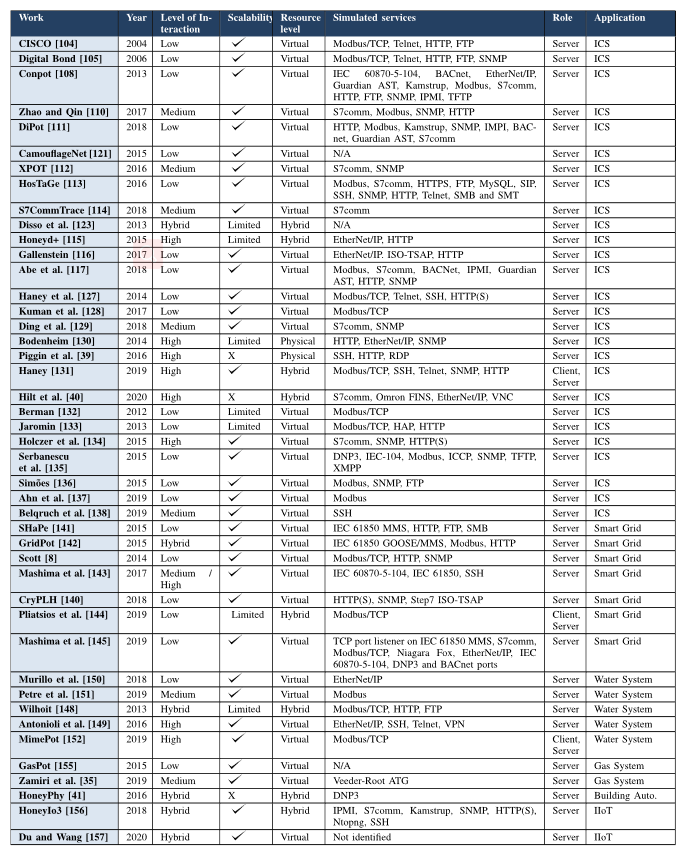
Figure 2 Classification of Honeypots and Honeynets Applicable to IIoT
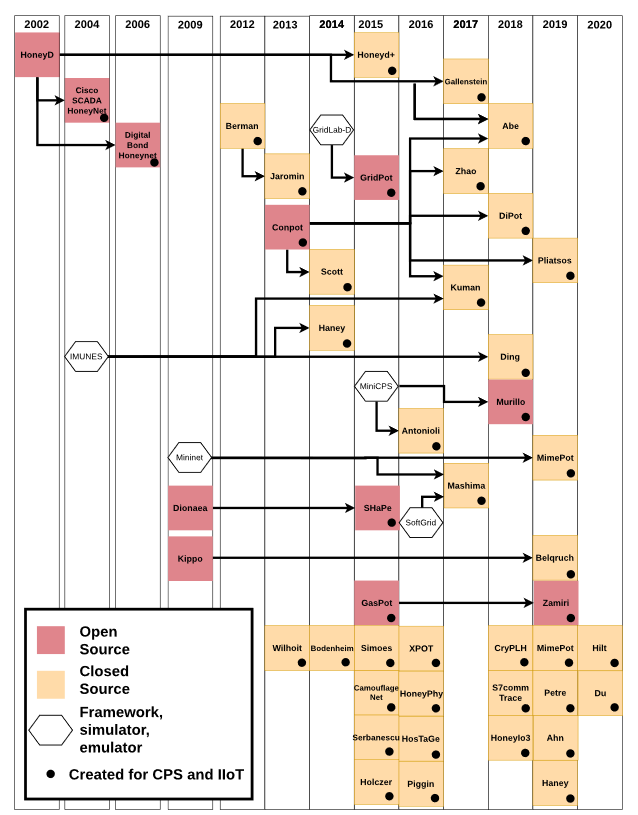
Figure 3 Development of IIoT Honeypots and Honeynets
(Some content in this article is translated and modified from A Survey of Honeypots and Honeynets for Internet of Things, Industrial Internet of Things, and Cyber-Physical Systems (J. Franco et al. 2021))
References
[1] E. Sisinni, A. Saifullah, S. Han, U. Jennehag, M. Gidlund[C]. Industrial Internet of Things: Challenges, opportunities, and directions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat.. 2018(4), vol. 14, no. 11, pp. 4724-4734.
[2] B. Bordel, R. Alcarria, T. Robles, D. Martín[C]. Cyber–physical systems: Extending pervasive sensing from control theory to the Internet of Things. Pervasive Mobile Comput. 2017, vol. 40, pp. 156-184.
[3] A. Humayed, J. Lin, F. Li, B. Luo[C]. Cyber-physical systems security—A survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 1802-1831.
[4] C. Greer, M. Burns, D. Wollman, E. Griffor[DB/OL]. Cyberphysical systems and Internet of Things. NIST, Gaithersburg, MD, USA. 2019, Rep. 1900-202.
[5] GB/T 26790, 工业无线网络WIA规范[S].
[6] L. Spitzner[DB/OL]. The Value of Honeypots, Part One: Definitions and Values of Honeypots. http://www.symantec.com/connect/articles/value-honeypotspart-onedefinitions-and-values-honeypots/, Apr. 14, 2020.
[7] P. Kumar, R. Verma[J]. A review on recent advances & future trends of security in honeypot. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci.. 2017, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 1108-1113.
[8] J. Franco, A. Aris, B. Canberk, A. S. Uluagac[C]. A Survey of Honeypots and Honeynets for Internet of Things, Industrial Internet of Things, and Cyber-Physical Systems. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials. 2021, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 2351-2383.
China Confidentiality Association
Science and Technology Branch
Scan to follow us

Author: Xiong Siqi, Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Editor: Xiang Lingzi
2022 Highlights Review
Cross-Network Attacks: An Introduction to Techniques for Breaking Physical Isolation
Thoughts on the Top-Level Design of Smart City Security
Revisiting Some New Issues Facing the Development of Digital Forensics Technology
The Development and Challenges of Low Earth Orbit Satellite Interconnected Networks
Introduction to LaserShark Non-Contact Attack Implant Technology
Recent Highlights Responses
The Zero Trust Architecture: Removing Implicit Trust and Breaking Traditional Security “Boundaries”
The Zero Trust Architecture: Removing Implicit Trust and Breaking Traditional Security “Boundaries”
Overview of Network Intrusion Detection Technology
Electromagnetic Radiation of USB 3.0 and Its Interference on 2.4GHz Wireless Devices