Industrial 4.0 Bus – Profibus
What is Profibus?
[PROFIBUS]
PROFIBUS is a fieldbus standard used in automation technology, promoted in 1987 by Siemens and fourteen other companies along with five research institutes. PROFIBUS stands for PROcess FIeld BUS. PROFIBUS and PROFINET, which is used in industrial Ethernet, are two different communication protocols.

PROFIBUS is an international, open fieldbus standard that is independent of device manufacturers. The transmission speed of PROFIBUS can be selected within the range of 9.6kbaud to 12Mbaud, and when the bus system is started, all devices connected to the bus should be set to the same speed. It is widely used in manufacturing automation, process industry automation, and other fields such as building and traffic power automation. PROFIBUS is a fieldbus technology used for workshop-level monitoring and data communication and control at the field device layer. It enables decentralized digital control and field communication networks from the field device layer to workshop-level monitoring, providing a feasible solution for integrated factory automation and intelligent field devices.
★Features
As the most widely used fieldbus technology in the industry, Profibus not only has the advantages of general buses but also has its own characteristics, specifically as follows:
(1) The maximum transmission information length is 255B, the maximum data length is 244B, and the typical length is 120B.
(2) The network topology can be linear, tree, or bus type, with active bus termination resistors at both ends.
(3) The transmission rate depends on the network topology and bus length, ranging from 9.6Kb/s to 12Mb/s.
(4) The number of stations depends on the signal characteristics; for shielded twisted pairs, each segment can have 32 stations (without repeaters), and up to 127 stations with repeaters.
(5) The transmission medium can be shielded/unshielded twisted pairs or fiber optics.
(6) When using twisted pairs, the maximum transmission distance can reach 9.6km, and with fiber optics, the maximum transmission length is 90km.
(7) The transmission technologies include RS-485 transmission for DP and FMS, IEC1158-2 transmission for PA, and fiber optic transmission.
(8) A single bus orientation protocol is used, including token passing between master stations and master-slave mode between slave stations.
(9) Data transmission services include both cyclic and acyclic types.
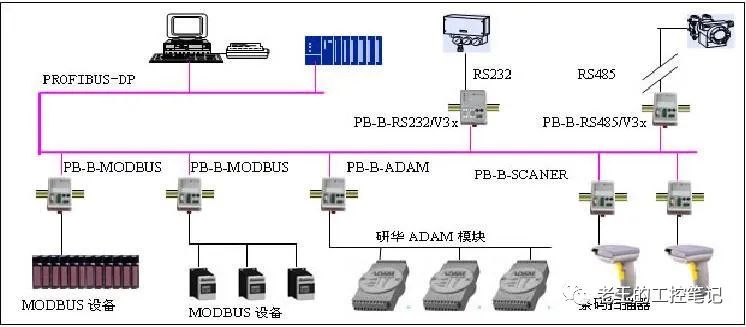
▲PROFIBUS Network
PROFIBUS PA and Profibus DP
Currently, PROFIBUS can be divided into two types: PROFIBUS DP, which is used by most people, and PROFIBUS PA, which is used in process control:
PROFBUS-DP is a communication protocol optimized for high-speed transmission of user data, particularly suitable for communication between programmable controllers and field-level distributed I/O devices. Profibus stands for “Process Field Bus” and DP stands for “Distributed Devices,” similar to the IO-Link mentioned in the previous article — https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzAwMDE3MzEwNg==&mid=2247486708&idx=1&sn=61c3b7e9eb6d648dee461dceca211286&chksm=9aedb9a9ad9a30bf3e512dabb490516fb668c06349ae6d68f47ba84b0f786355e8a27a67f353#rd
PROFIBUS DP is used for high-speed data transmission at the field level. The master station periodically reads input information from the slave stations and periodically sends output information to the slave stations. The bus cycle time must be shorter than the master station (PLC) program cycle time. In addition to periodic user data transmission, PROFIBUS DP also provides the non-periodic communication required for intelligent devices for configuration, diagnostics, and alarm processing.
Transmission technology: RS-485 twisted pair, dual wire cable, or optical cable. Baud rates range from 9.6K bit/s to 12M bit.

PROFIBUS-PA is suitable for process automation with PROFIBUS. PA connects automation systems and process control systems with field devices such as pressure, humidity, and level transmitters, and can replace the 4-20mA analog technology. PROFIBUS-PA has the following characteristics:
(1) It is suitable for process automation applications, allowing interoperability of field devices produced by different manufacturers.
(2) Adding and removing bus stations does not affect other stations, even in intrinsically safe areas.
(3) The PROFIBUS-PA segment for process automation is connected to the PROFIBUS-DP segment for manufacturing automation through a coupler, enabling transparent communication between the two segments.
(4) Remote power supply and data transmission are completed using twisted pairs with the same technology as IEC1158-2.
(5) Explosion-proof or non-intrinsically safe types can be used in potentially explosive areas.
IO-Link and Profibus DP
Although IO-Link and Profibus DP are both protocols suitable for distributed devices, they are two different digital communication protocols with some differences and similarities, as follows: Differences:
-
Different application scopes: IO-Link is mainly used for communication between intelligent sensors and actuators, while Profibus DP is more commonly used for communication between industrial field buses.
-
Different transmission methods: IO-Link uses a fully digital communication method, transmitting data, power, and ground through three wires, while Profibus DP uses serial communication based on RS485 differential signals.
-
Different data transmission rates: IO-Link typically has a data transmission rate between 230.4kbps and 4Mbps, while Profibus DP has a data transmission rate between 9.6kbps and 12Mbps.
Similarities:Both belong to digital communication protocols, enabling high-speed and reliable data transmission.Both provide standardized interfaces and protocols, allowing different types of devices to communicate with each other.Both can achieve automatic configuration and automatic diagnostic functions, simplifying device installation and maintenance.

▲Distributed Ecosystem
 END
END Official Account
Official Account
— Lao Wang’s Industrial Control Notes
Scan to follow for more information