This code implements the image dehazing algorithm based on the Dark Channel Prior (DCP), proposed by He Kaiming et al. The algorithm primarily utilizes the characteristics of the dark channel in the image to estimate the concentration of haze and perform dehazing processing. Estimated reading time: 5 minutes.
Code
I = imread('a3.png'); % Read hazy image[h, w, s] = size(I); % Get image dimensions
%% Calculate dark channel image
dark_I = zeros(h, w);for i = 1:hfor j = 1:w dark_I(i, j) = min(I(i, j, :));endend
%% Set parameters
w0 = 0.75; % Product factor to retain some haze, 1 means complete dehazing
t0 = 0.1;A = double(max(max(dark_I))); % Sky brightness
% Calculate transmittance
Iy = double(dark_I);t = 1 - w0 * (Iy / A);t = max(t, t0);
%% Perform dehazing calculation
I1 = double(I); % Convert original image to double type
J(:, :, 1) = uint8((I1(:, :, 1) - (1 - t) * A)./ t);J(:, :, 2) = uint8((I1(:, :, 2) - (1 - t) * A)./ t);J(:, :, 3) = uint8((I1(:, :, 3) - (1 - t) * A)./ t);
%% Get grayscale images of original and dehazed images
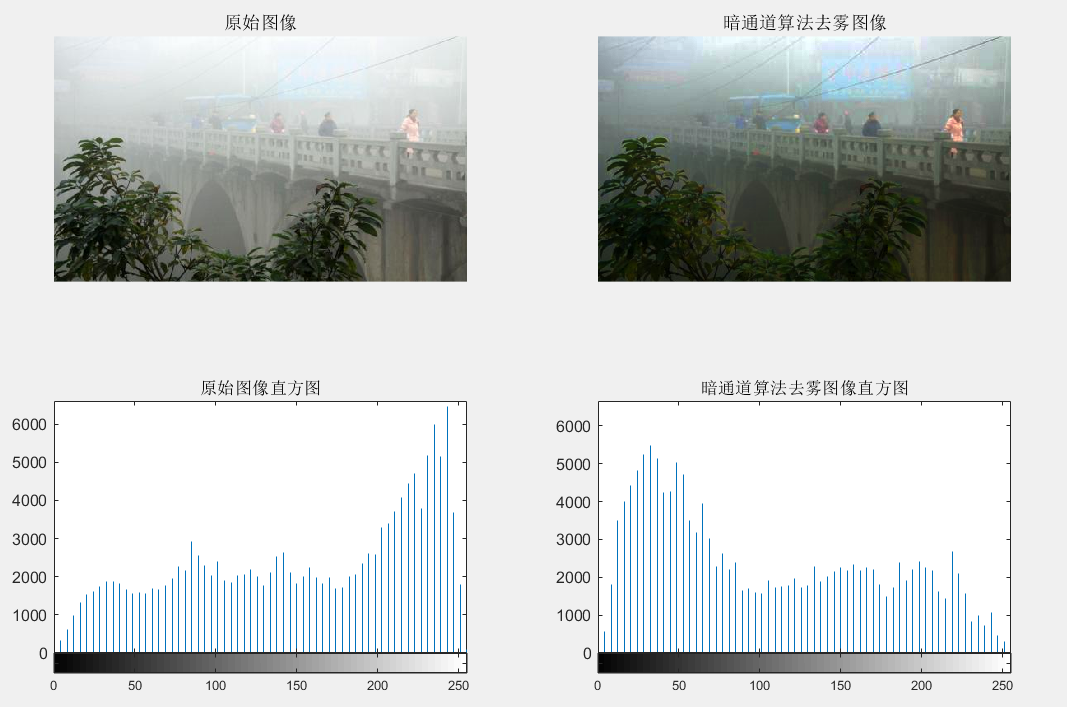
Q = rgb2gray(I);W = rgb2gray(J);% Display results
figure;subplot(2, 2, 1); imshow(I);title('Original Image');subplot(2, 2, 2);imshow(J);title('DCP Dehazed Image');subplot(2, 2, 3);imhist(Q, 64);title('Original Image Histogram');subplot(2, 2, 4);imhist(W, 64);title('DCP Dehazed Image Histogram');Principle
The basic principle of the Dark Channel Prior dehazing is implemented through the following steps and formulas:

Analysis
-
Calculate dark channel image:
This step involves selecting the darkest value from the three color channels of each pixel to obtain the dark channel image.
-
Set parameters:
w0 = 0.75;: Set the product factor w0 to 0.75, which controls the degree of dehazing, similar to adjusting a faucet. When w0 is 1, it indicates complete dehazing, while setting it to 0.75 means retaining some haze effect.
t0 = 0.1;: Set the threshold t0 to 0.1, which limits the minimum value of transmittance to prevent poor dehazing effects due to excessively low transmittance. It acts like a “threshold” to ensure that transmittance does not fall below this value.
A = double(max(max(dark_I)));: Estimate the sky brightness A by taking the maximum value from the dark channel image dark_I and converting it to double precision. This step is akin to finding the brightest part in the dark channel image and using it as an estimate for sky brightness.
-
Calculate transmittance:
t = 1 – w0 * (Iy / A);: Calculate the transmittance t using the formula, which combines the previously set parameters and information from the dark channel image to compute the haze transmittance for each pixel, similar to calculating a “haze concentration index” for each pixel.
t = max(t, t0);: Compare the calculated transmittance t with the threshold t0 and take the larger value to ensure that transmittance is not less than t0. This step is a “correction” of the transmittance to ensure it meets the requirements.
-
Perform dehazing calculation:
Calculate for each of the three color channels of the image:
J(:, :, 1) = uint8((I1(:, :, 1) – (1 – t) * A)./ t);
J(:, :, 2) = uint8((I1(:, :, 2) – (1 – t) * A)./ t);
J(:, :, 3) = uint8((I1(:, :, 3) – (1 – t) * A)./ t);
Obtain the dehazed image J and store it as uint8 type. This is like giving each channel of the image a “bath” to remove the effects of haze.
-
Get grayscale images of original and dehazed images:
Q = rgb2gray(I); and W = rgb2gray(J);: This step is akin to “removing the colorful exterior” of the image, retaining only the luminance information.
-
Display results:
imhist(Q, 64); displays the histogram of the grayscale image Q of the original image, where 64 indicates the number of bins in the histogram. The histogram provides insight into the grayscale distribution of the original image, similar to viewing a “distribution map” of the image’s grayscale.
Summary of Matlab Functions
-
double: Converts data type to double precision.
-
max: Returns the maximum value along a specified dimension of the matrix.
-
rgb2gray: Converts a color image to a grayscale image.
-
uint8: Converts data type to unsigned 8-bit integer type.
The Dark Channel Prior dehazing method effectively removes haze from images, enhancing contrast and clarity. However, it may result in color distortion or loss of details when processing certain complex scenes or images with special lighting conditions.
If you have any questions, feel free to leave a message.