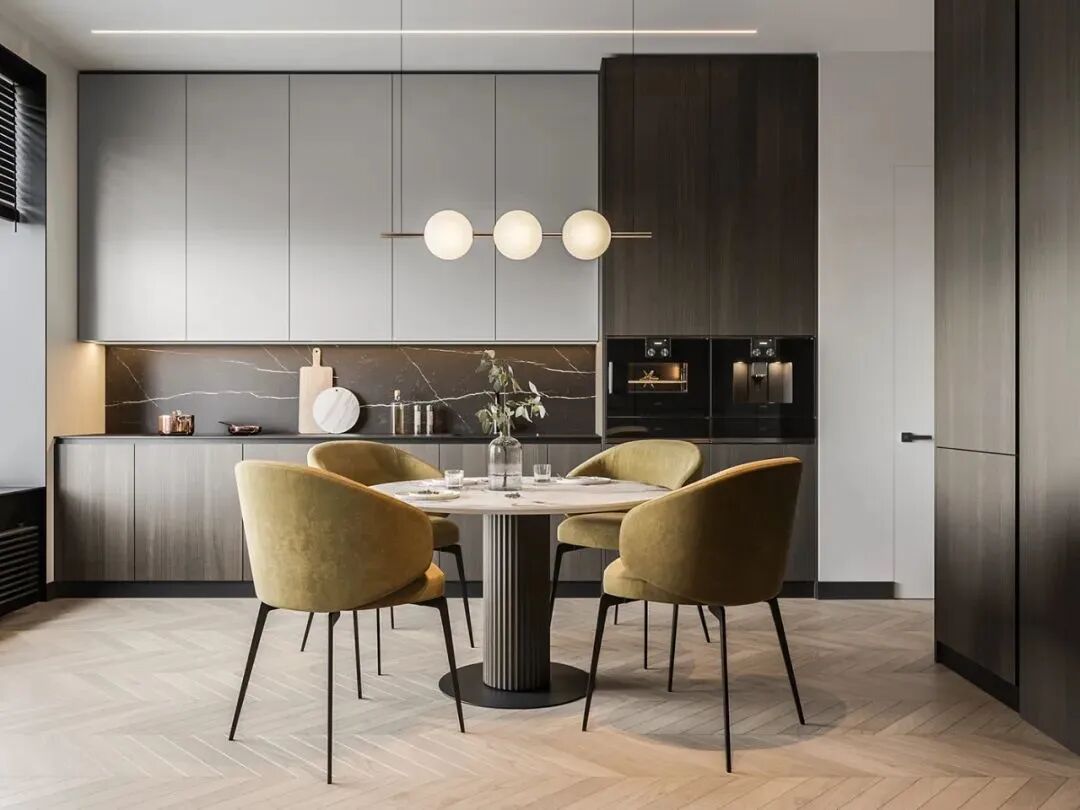
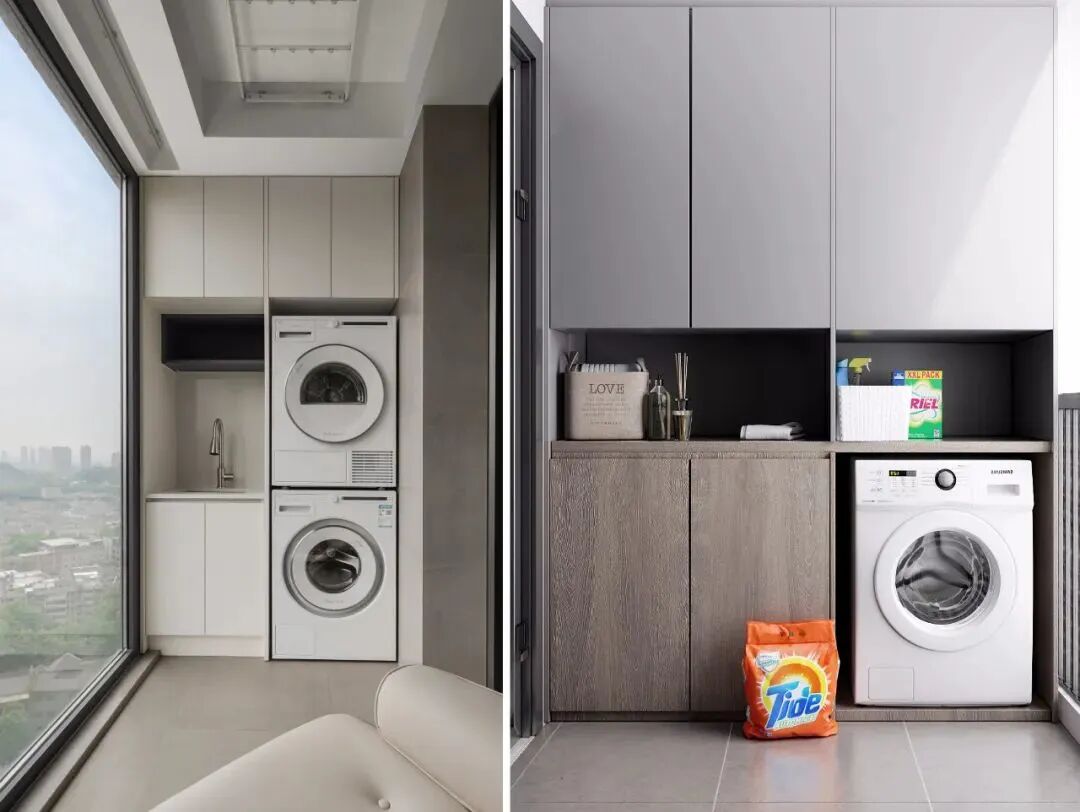
 In kitchen spaces and balconies, whether large or small appliances take up a lot of space. Cluttered appliances on the countertop or placed against the wall can make the space look very messy and uncomfortable. Therefore, embedded design addresses this pain point by concealing all appliances within cabinets or walls.
In kitchen spaces and balconies, whether large or small appliances take up a lot of space. Cluttered appliances on the countertop or placed against the wall can make the space look very messy and uncomfortable. Therefore, embedded design addresses this pain point by concealing all appliances within cabinets or walls.
So, how should the design of embedded appliances be approached? What factors need to be considered?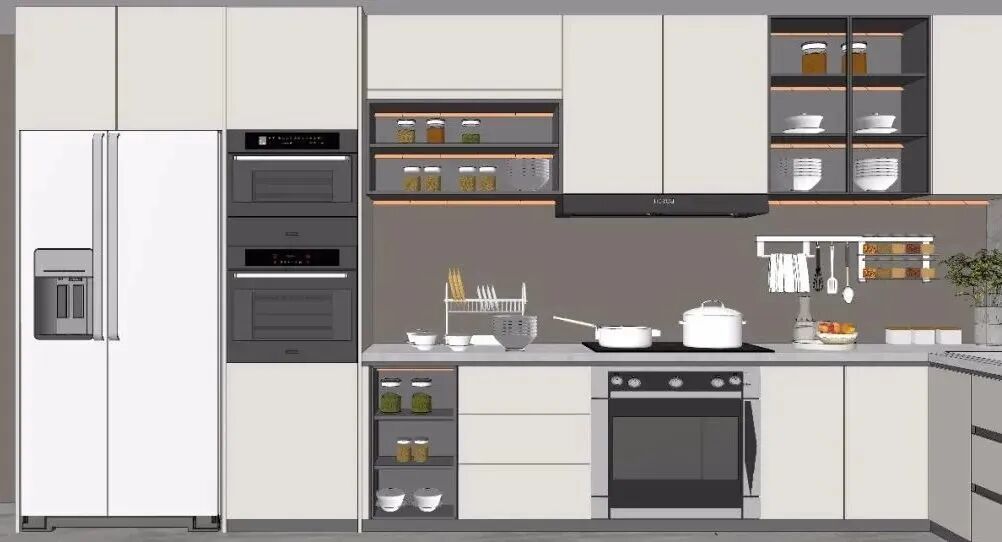 This article focuses on the following aspects:
This article focuses on the following aspects:
1. What is Embedded Design?
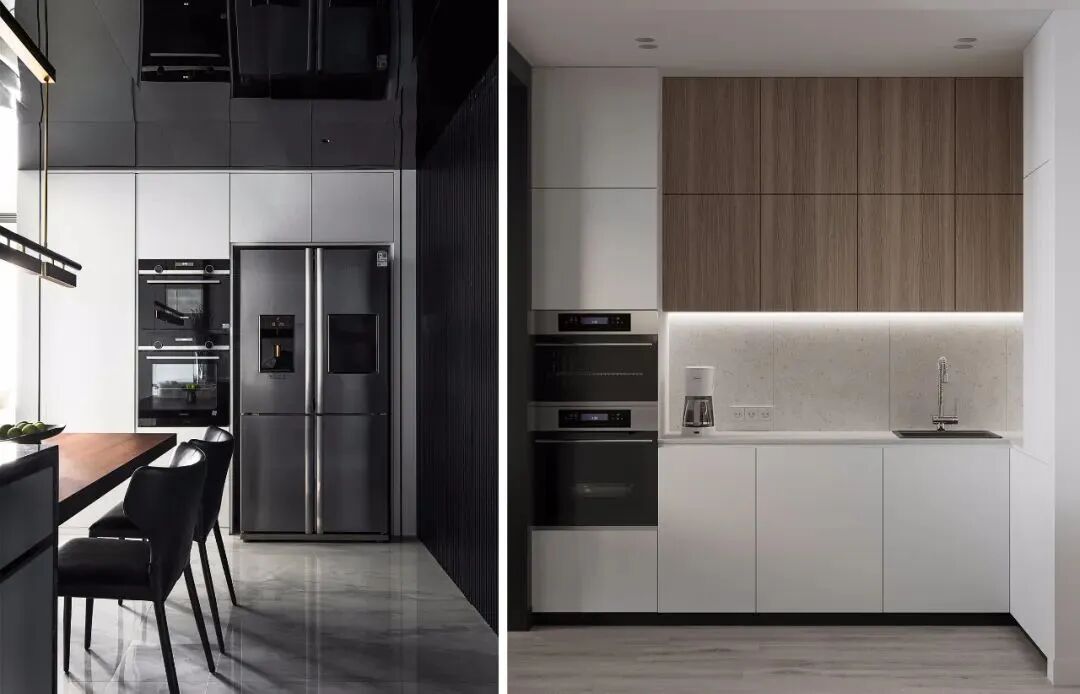
It refers to the installation of commonly used household appliances, such as refrigerators, ovens, steamers, microwaves, sterilizers, dishwashers, washing machines, dryers, televisions, etc., all embedded within custom cabinetry or walls.

This approach saves space, enhances the overall coherence of the space, makes it look cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing, significantly improves the usability of the space, and reduces waste.
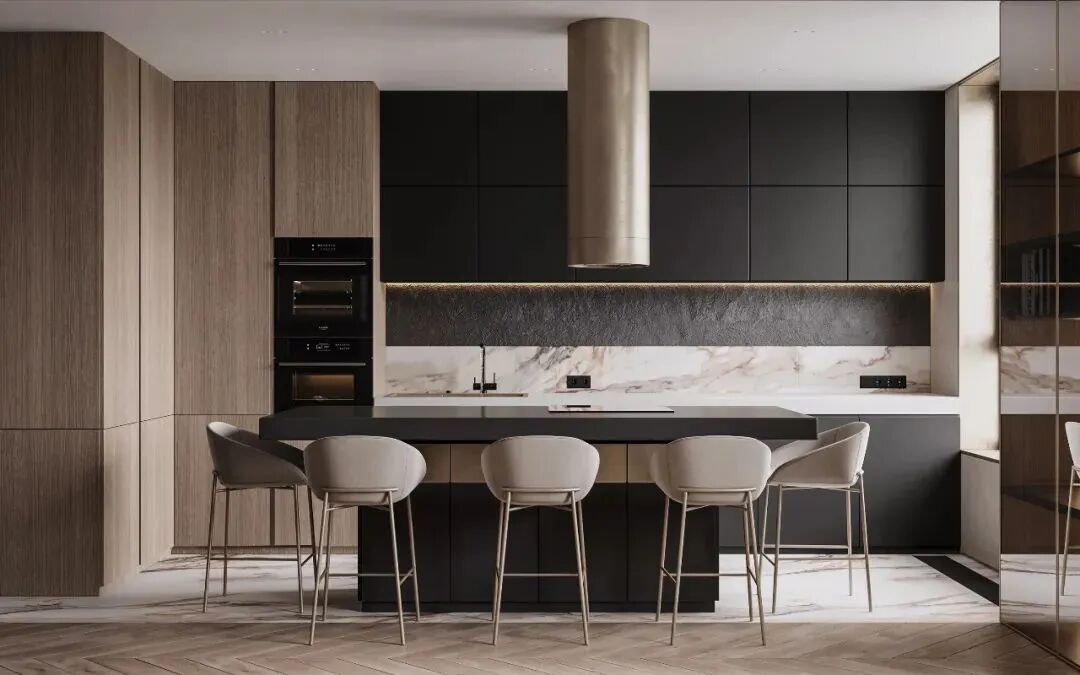

2. Prerequisites for “Embedded Appliance” Design
The design of embedded appliances is not suitable for all spaces; all designs should be practical. Therefore, the design of embedded appliances must meet the following conditions:
1. Sufficient Space Area
Generally, balcony spaces mostly adopt embedded designs, embedding washing machines, dryers, and sinks into custom cabinetry.
The biggest issue is the kitchen space. Embedded appliances do not mean tearing down part of the wall to shove appliances in; rather, it involves a flexible layout of appliance positions from an overall perspective.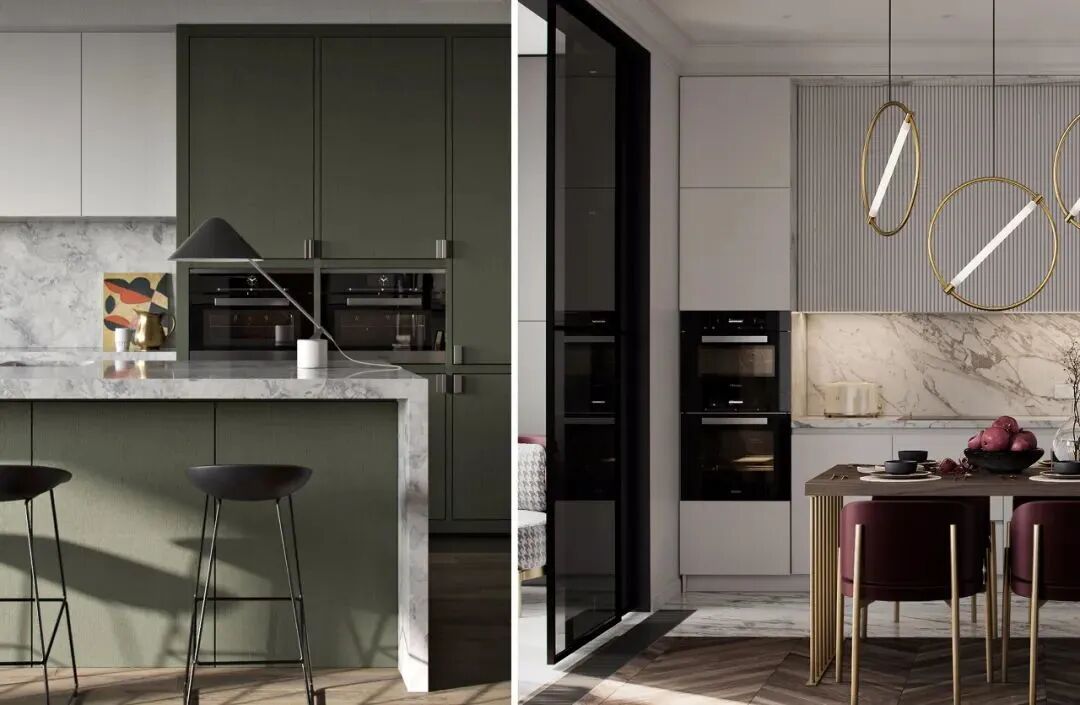
Essentially, it still occupies the kitchen’s space area. The opening of the appliance doors and the space for standing require sufficient dimensions. Therefore, if the kitchen is too small to provide adequate storage and passage space, then embedded appliance design cannot be implemented.
2. Sufficient Customer Budget
Embedding appliances, along with the appliances themselves and custom cabinetry, generally incurs a cost much higher than non-embedded designs. Thus, the feasibility of implementation still depends on whether the customer’s budget is sufficient.
3. Appliance Dimensions and After-Sales Service
Embedded appliances differ from regular appliances in that they require installation. It is crucial to pay attention to the dimensional relationship between the appliance and the cabinetry; otherwise, installation may not be possible. Additionally, after-sales service must be considered for future maintenance and care.
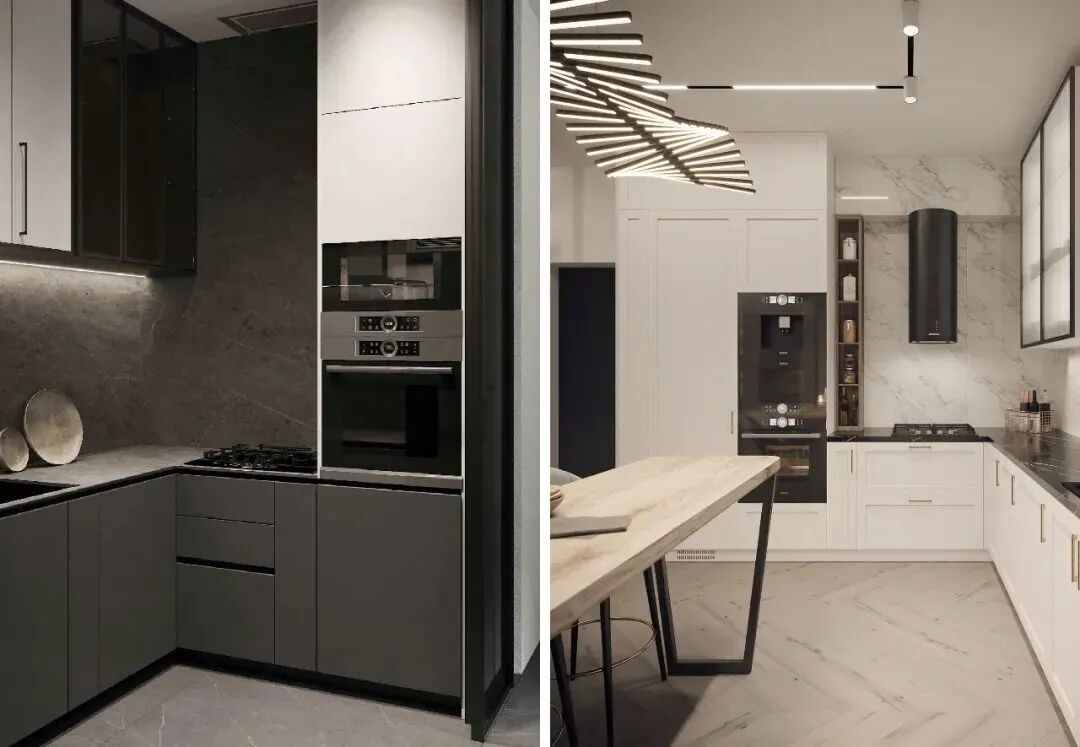

3. Dimensional Requirements for “Embedded Appliance” Design
Two main aspects of dimensions need to be considered for embedded appliances: cabinetry and appliances.
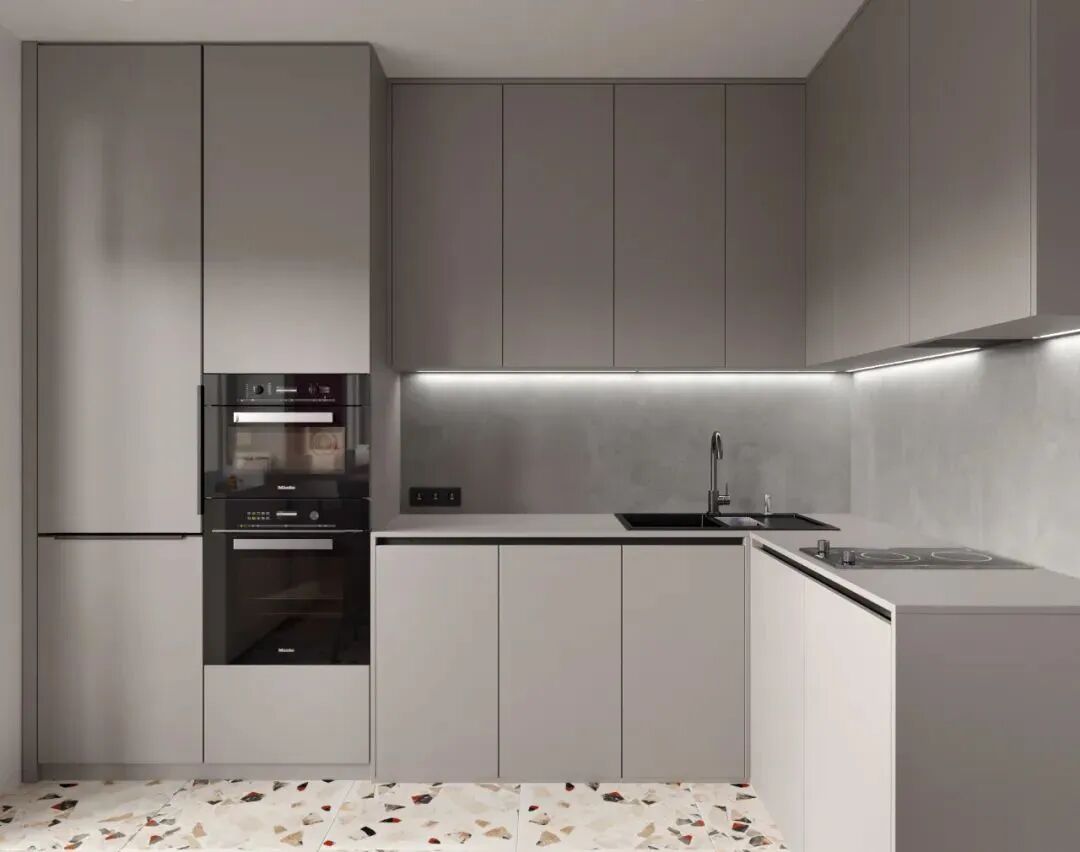
1) Cabinet Size Requirements
When considering cabinet size design, the opening dimensions of the appliances and the standing space for people must be taken into account. Appliances are generally embedded in base cabinets or full-height cabinets, with standard cabinet depths around 600mm. After arranging the cabinets, a passage width of ≥1200mm must be ensured.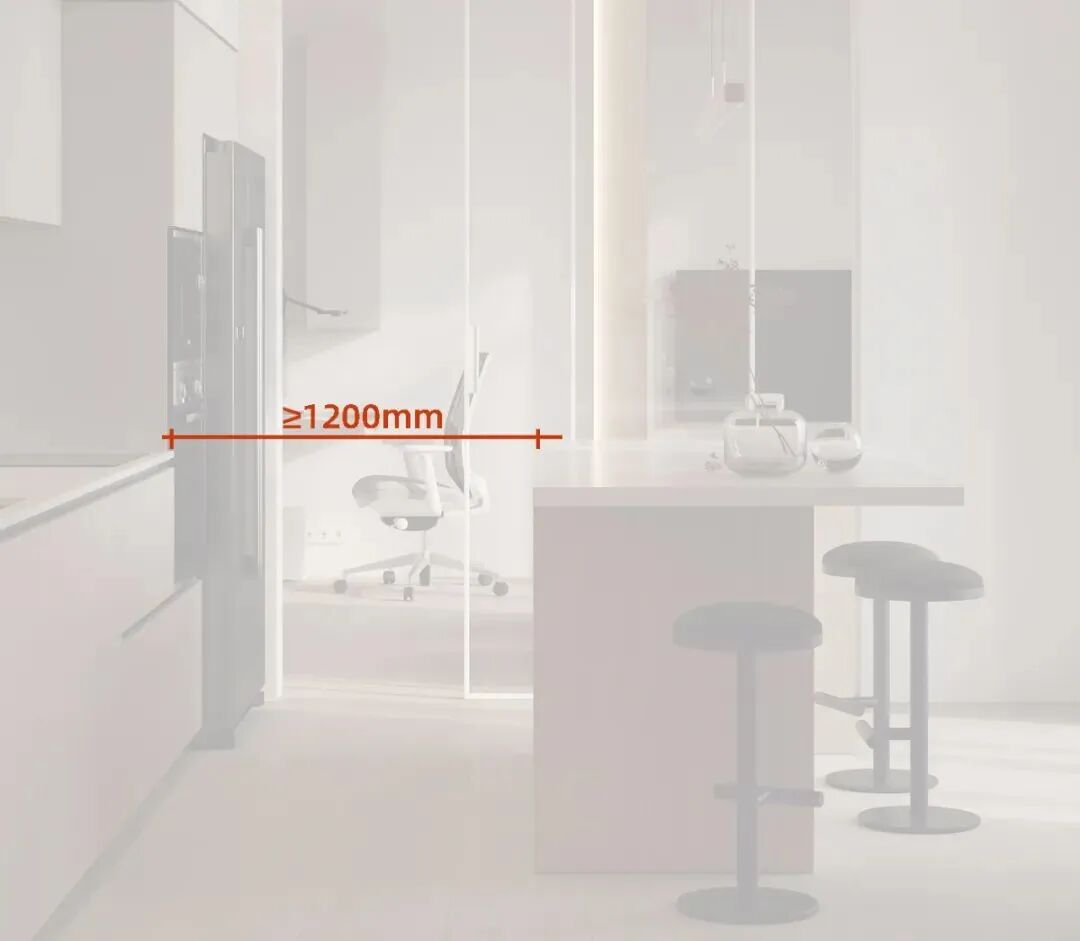
Embedded appliances typically have outward-opening doors, which occupy passage space when opened. The door opening size is approximately 500mm, so after opening, there must be sufficient standing space of at least 600mm in width. Therefore, for embedded appliance cabinets, the passage area must be at least 1200mm to meet requirements.
Passage area width ≥ appliance door opening size + standing space
2) Appliance Size Requirements
As for which appliances need to be embedded, including the dimensions of embedded appliances, all must be determined before making the cabinets to facilitate proper sizing and pre-reserving electrical outlets.

4. Design Requirements for Heat Dissipation and Electrical/Water Connections
1) Heat Dissipation Design Requirements
One crucial factor for these embedded appliances is heat dissipation, especially since they are in a closed cabinet. The enclosed state can slow down the heat dissipation speed, thus affecting efficiency.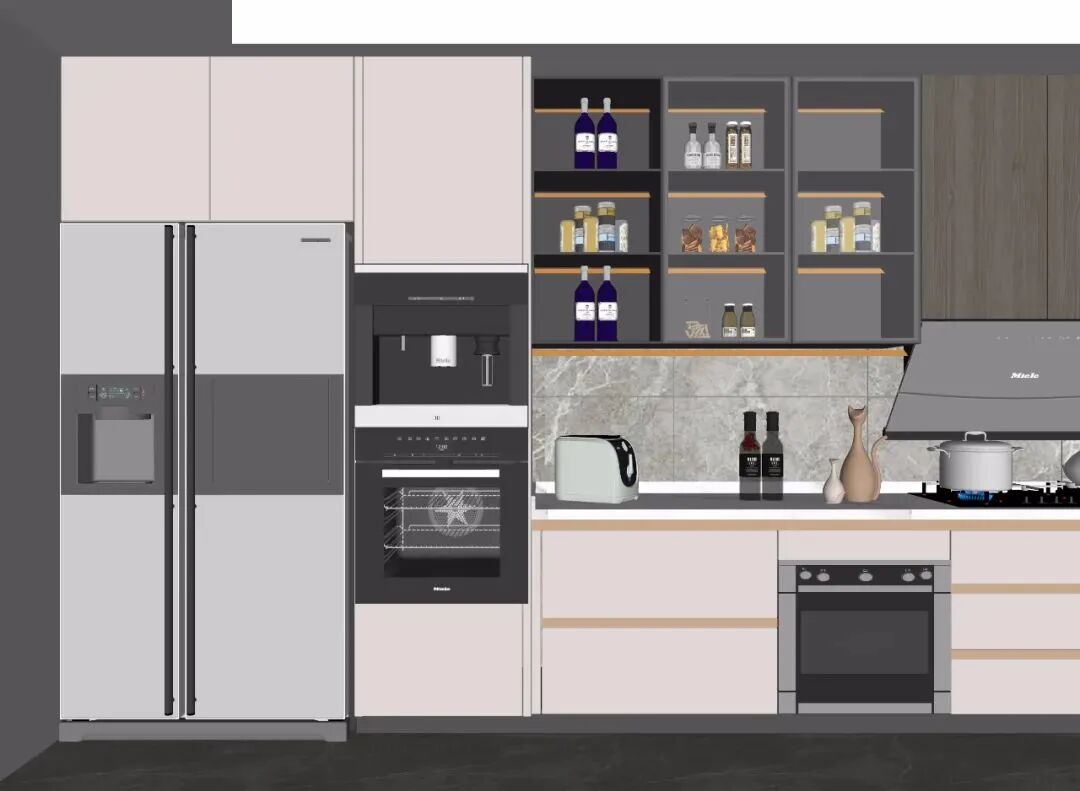 On the other hand, high temperatures can negatively impact the cabinet itself. Different appliances have different heat dissipation methods and locations. Some dissipate heat from the back or bottom, while others do so from all sides. Therefore, this must be considered during the design process.
On the other hand, high temperatures can negatively impact the cabinet itself. Different appliances have different heat dissipation methods and locations. Some dissipate heat from the back or bottom, while others do so from all sides. Therefore, this must be considered during the design process.
The core logic of heat dissipation is: maintain distance between the appliance and the cabinet while ensuring cabinet protection.

Therefore, when reserving cabinet dimensions, ensure that there is a certain distance between the appliance and the cabinet. Additionally, the choice of cabinet materials cannot be the same as those used for regular wardrobes or TV cabinets; materials that are heat-resistant and shape-retaining must be selected. Alternatively, heat-insulating boards can be arranged inside the cabinet to extend the appliance’s lifespan and protect the cabinet.

Different appliances have different heat dissipation measures and requirements
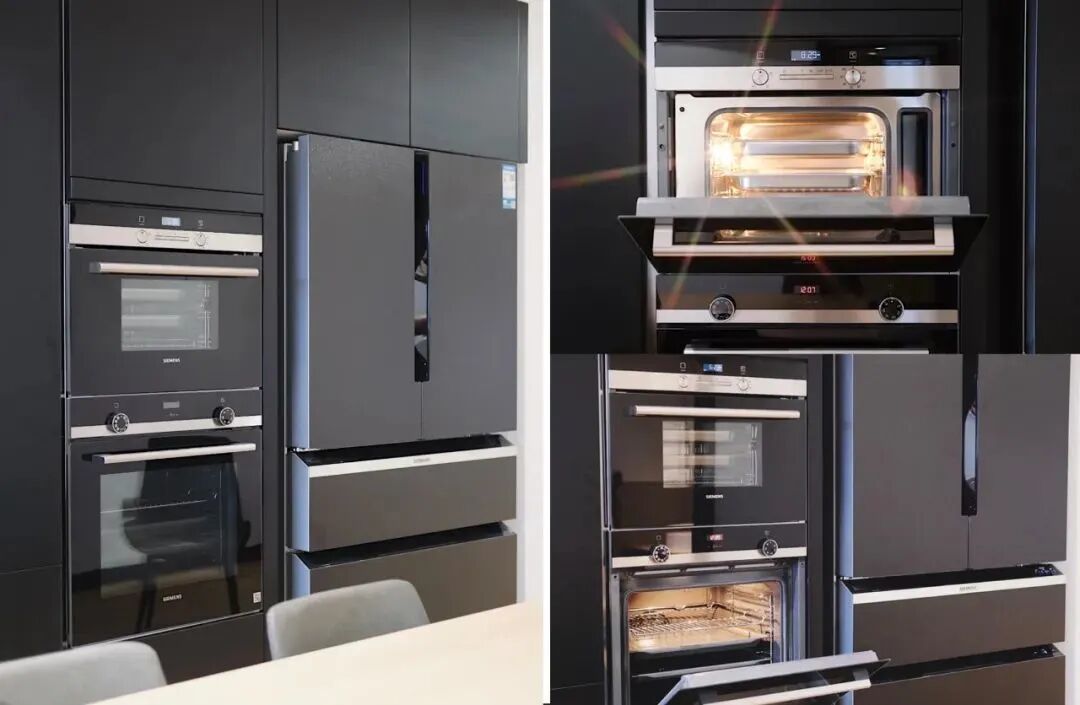
01. Oven
If the oven is to be embedded, it is best to choose a front-venting oven, and the cabinet where the oven is installed should not have a back panel. Maintain a certain gap between the oven and the cabinet to achieve ventilation and heat dissipation, and the cabinet material should be heat-resistant.

If the oven is installed in a base cabinet, it should not be placed directly under the stove, as both the gas stove and the oven have high heat dissipation requirements. Placing them together can damage the appliances and pose safety risks such as explosions.
02. Microwave Oven

The heat dissipation logic for microwaves is similar; they need to maintain distance from surrounding cabinetry. There should be at least 100mm of space between the microwave and the cabinet above, and 50mm on each side to achieve ventilation and heat dissipation. When selecting a microwave, choose a front-venting type.
03. Sterilizer
Sterilizers are generally installed directly below the stove, maintaining a distance of ≥150mm between them, and a square ventilation hole with a side length of 120mm should be pre-reserved in the cabinet behind to facilitate ventilation and heat dissipation.
04. Refrigerator
For embedded refrigerators, the sides and back are the main heat dissipation sources, so they need to maintain a certain distance from the cabinetry or walls, with a minimum gap of 100mm.

2) Water and Electrical Design Requirements
01. Socket Layout
It is necessary to consider the layout and placement of appliances in advance to design the socket layout. Generally, sockets should be placed on the side or in adjacent cabinetry (with pre-drilled holes), avoiding direct placement behind the appliances.
Why is this important? Imagine if the appliance has rear ventilation and the socket is also located behind it; this can damage the appliance and pose safety risks.
From a dimensional perspective, placing the socket behind the appliance occupies part of the embedded depth, causing the appliance to protrude from the cabinetry, severely affecting the aesthetic effect.

02. Water Supply and Drainage Layout
Before constructing the cabinetry, the positions of the water supply and drainage pipes, as well as the dimensions of the appliances, should be pre-reserved. Remember, in cases of limited depth, the water inlet and socket should not be placed directly behind the appliance,
as this can also cause the appliance to protrude, affecting aesthetics. The floor drain should not be placed directly below the appliance, as it can affect drainage. It should be positioned beside the appliance.
