Click the blue text above to follow us
In the current era of rapid technological advancement, the wave of smart home technology is sweeping in with unprecedented momentum. From smart lighting systems that can automatically adjust brightness based on ambient light and user habits, to smart security devices that can monitor home conditions in real-time and alert users, and smart appliances that can be controlled remotely via smartphones, smart homes are fundamentally changing people’s lifestyles. This transformation not only brings convenience and comfort to consumers but also presents new opportunities and challenges for the electrician industry. For many electricians, how to expand their business landscape and enhance their skills in this wave has become the key to achieving new breakthroughs in career development.

1. Insights into the Smart Home Market and Business Expansion Directions
(1) Grasping New Market Demands
New Residential Projects: Nowadays, more and more real estate developers are beginning to incorporate smart home systems as standard features in new residential buildings. Electricians should actively establish partnerships with developers and builders, participating in the early planning and design stages of projects. For example, during the wiring phase of a house, it is necessary to reasonably plan the layout of electrical and network cables according to the architecture of the smart home system, ensuring that it meets the future power and data transmission needs of smart devices. High-end residential projects may be equipped with a whole-house smart control system, which requires electricians to reserve sufficient wiring interfaces and power locations in advance, laying a solid foundation for subsequent equipment installation and debugging.
Existing Residential Renovations: The vast stock of existing homes also represents an unlimited market potential. As residents pursue higher living standards, many families are willing to upgrade their traditional homes to smart homes. Electricians can provide personalized smart home renovation solutions for these customers. For instance, replacing traditional door locks with smart locks can be done with simple installation at the original lock position, enabling various unlocking methods such as passwords, fingerprints, and cards, greatly enhancing home security and convenience; or installing smart curtain motors that can be controlled wirelessly, allowing users to easily manage curtains remotely even when they are not at home.
(2) Expanding Diverse Business Models
System Integration Services: Smart home systems involve multiple subsystems, such as security, lighting, and appliance control. Electricians can integrate these different brands and functionalities of smart devices to provide users with one-stop system integration services. For example, connecting smart cameras, door/window sensors, smoke detectors, and other security devices to a smart gateway, allowing unified management through a mobile app, so that users can receive notifications immediately when abnormal situations occur at home. Additionally, linking the smart lighting system with smart speakers allows users to control the lights’ on/off, color, and brightness through voice commands, creating a personalized home atmosphere. Providing such system integration services not only meets users’ overall needs for smart homes but also increases the added value of electricians’ businesses.
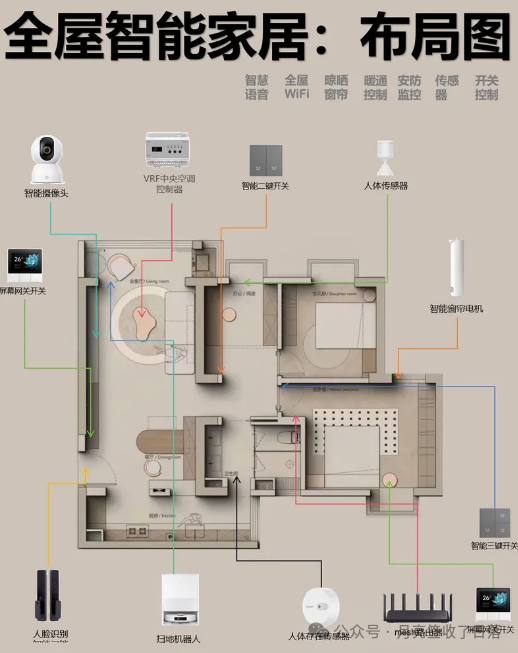
After-sales Service and Maintenance: Smart home devices inevitably encounter faults during use, which provides electricians with a broad after-sales service market. Establishing a professional after-sales service team that responds promptly to customers’ repair needs can effectively enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Service content can include troubleshooting device faults, software upgrades, and system optimizations. For example, when a smart appliance experiences a connectivity issue, electricians can quickly visit to check network settings, device hardware, and software versions, and perform necessary repairs and upgrades. Additionally, regularly providing maintenance services for smart home systems, such as cleaning smart camera lenses and checking sensor sensitivity, ensures the system operates stably over the long term and can provide electricians with a continuous source of income.
2. Key Points for Skill Enhancement to Adapt to Smart Home Demands
(1) Mastering Network Communication Knowledge
Wireless Network Technology: Most smart home devices transmit data via wireless networks, so electricians need to be proficient in Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, and other wireless network technologies. Understanding the characteristics of different network protocols, applicable scenarios, and parameters such as signal strength and frequency settings is essential. For example, when installing smart devices, electricians should be able to reasonably choose the placement of wireless routers based on the house structure and user needs, ensuring signal coverage without dead zones; for devices that require high network stability, such as smart cameras, they should know how to optimize network settings to avoid issues like lag or disconnection. Additionally, when encountering network failures, they should be able to quickly troubleshoot whether the issue is due to router failure, device connection problems, or network signal interference, and effectively resolve it.
IoT Communication Protocols: IoT communication protocols are the foundation for achieving interconnectivity among smart home devices. Electricians need to learn common IoT communication protocols such as MQTT and HTTP. The MQTT protocol is lightweight, low-power, and timely in message delivery, making it widely used for communication between smart home devices and servers. Electricians should understand the message publishing and subscription mechanisms of the MQTT protocol and be able to configure communication connections between smart devices and cloud platforms, enabling remote control and data upload. For example, through the MQTT protocol, users can remotely control their smart air conditioning via a mobile app and view the operating status and energy consumption data.
(2) In-depth Learning of Smart Control System Programming

Graphical Programming Platforms: Many smart home systems provide graphical programming interfaces, making it easy for electricians to configure systems and set scenes. For example, platforms like Tuya Smart and Xiaomi Home allow electricians to achieve interlinking between different smart devices through simple drag-and-drop and connection operations. For instance, setting a “Home Mode” where when the user unlocks the smart door lock, the system automatically triggers a series of actions such as turning on the lights, adjusting the air conditioning to a comfortable temperature, and gently opening the curtains. Electricians need to be proficient in operating these graphical programming platforms and flexibly customize various smart scenes based on users’ personalized needs, providing a convenient and comfortable smart home experience.
Basic Programming Language: For more complex smart home projects, electricians may need to have a certain foundation in programming languages, such as Python. Python is concise and efficient, commonly used in smart home development for device driver development, data processing, and automation script writing. For example, by writing scripts in Python, real-time collection and analysis of smart sensor data can be achieved, automatically controlling related devices based on changes in environmental parameters. For instance, based on data from indoor humidity sensors, automatically controlling the operation of humidifiers or dehumidifiers to maintain indoor humidity within an appropriate range. Learning programming languages like Python can expand electricians’ technical capabilities in the smart home field, enabling them to meet higher project demands.
(3) Enhancing Installation and Debugging Skills
Installation Techniques for New Smart Devices: There are various types of smart home devices, each with different installation methods. Electricians need to be familiar with the installation requirements and techniques for various smart devices. For example, the installation of smart switches not only requires correct electrical connections but also attention to their fit with the wall and aesthetics; the installation position of smart cameras should consider monitoring range and field of view while ensuring secure installation to avoid shaking that affects the shooting effect. During installation, care should be taken to protect the devices to avoid damage due to improper handling. For devices that require wiring to be embedded in ceilings or walls, electricians should possess precise measuring and wiring skills to ensure neat and safe wiring that does not affect the overall structure and aesthetics of the house.

System Debugging and Optimization: After completing the installation of smart devices, system debugging is a critical step. Electricians should be able to use professional tools and methods to comprehensively debug the smart home system. First, check whether the communication connections between devices are normal, ensuring that all devices can successfully connect to the system and exchange data with the control terminal. Then, perform functional tests on each subsystem, such as the alarm function of the security system and the dimming and color adjustment functions of the lighting system, to ensure that device functions meet design requirements. During debugging, various issues may arise, such as compatibility problems between devices or signal interference issues; electricians need to possess keen troubleshooting abilities to optimize the system by adjusting device parameters, changing device locations, or taking measures to shield against interference, ensuring that the smart home system operates at its best.
The wave of smart homes brings infinite possibilities to the electrician industry. Electricians who keenly observe market demands, actively expand business directions, and continuously enhance their skills can seize opportunities in this field full of challenges and achieve dual improvements in personal career development and industry status, contributing their professional strength to the advancement of the smart home industry while creating a smarter, more convenient, and comfortable living environment for users.