
In the last issue, we mainly introduced the definition of Profibus DP, the core content of its three different versions, and the differences in their applications.
This time, we will share the differences between Profibus DP and Profibus PA.

Three Types
There are three compatible versions of Profibus:
-
Profibus-DP
-
Profibus-PA
-
Profibus-FMS
Of course, in an automated factory, they can be mixed and matched based on actual application needs.
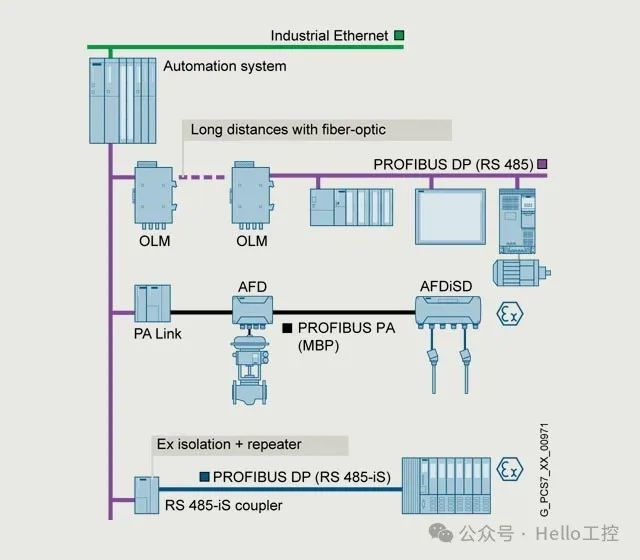

Detailed Explanation
The general scenario in an automated factory:
-
Control room, where several industrial computers (PCs, PLCs, etc.) are placed;
-
Workshop, where you can find many sensors.
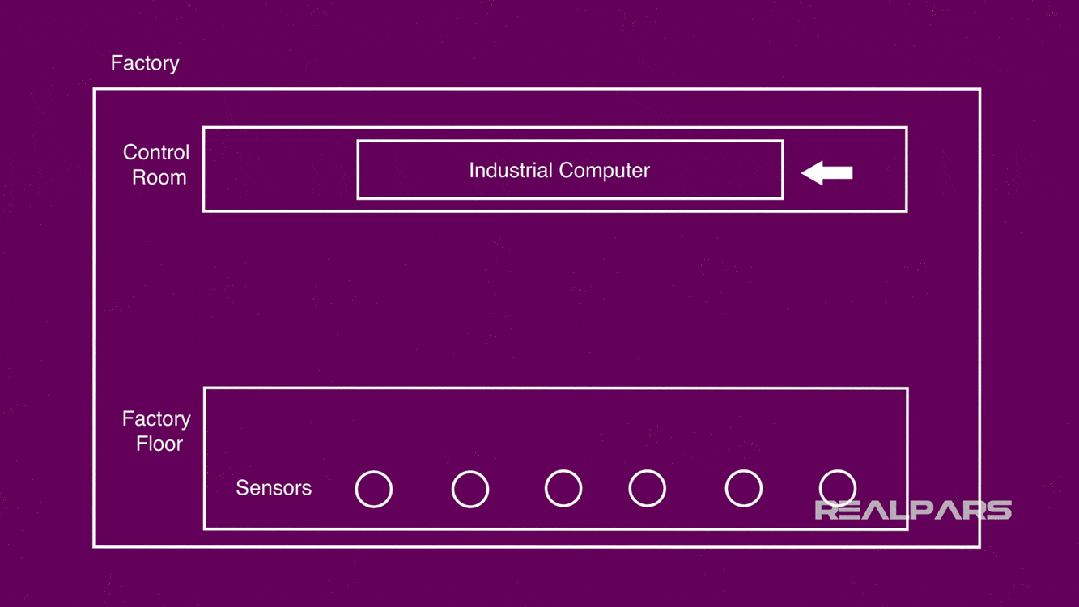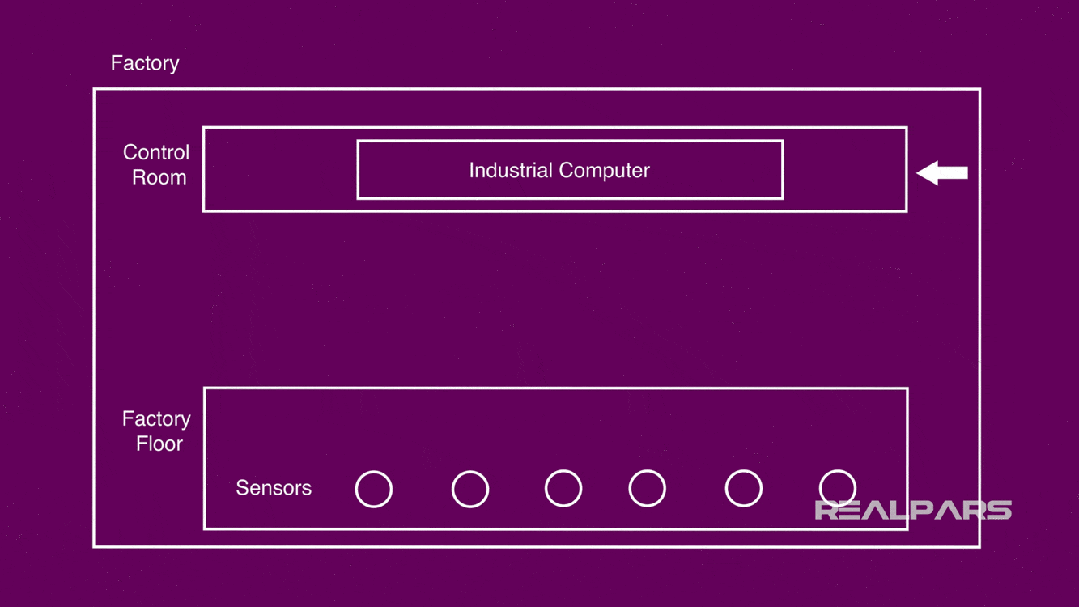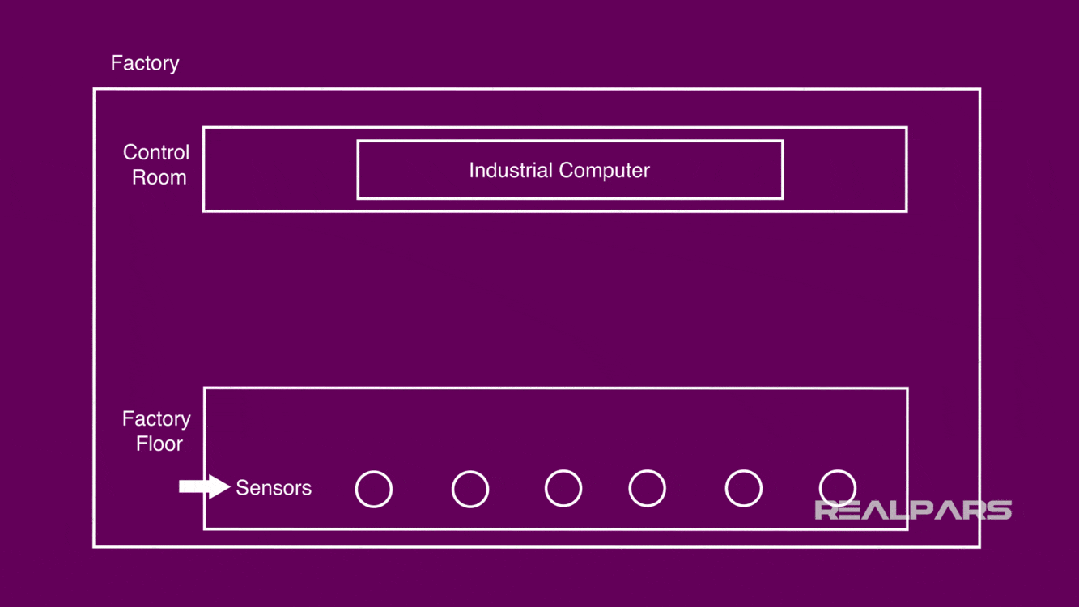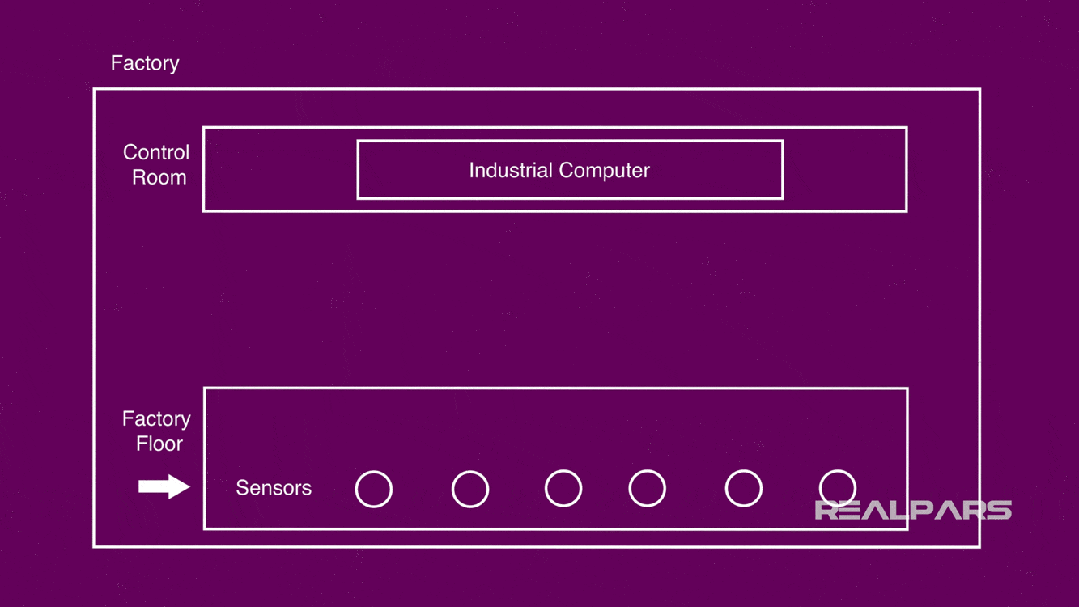
The core is how to connect them together and ultimately collect and control according to the actual processing needs of the factory.
The earliest method might have been to connect them one by one to the control system:
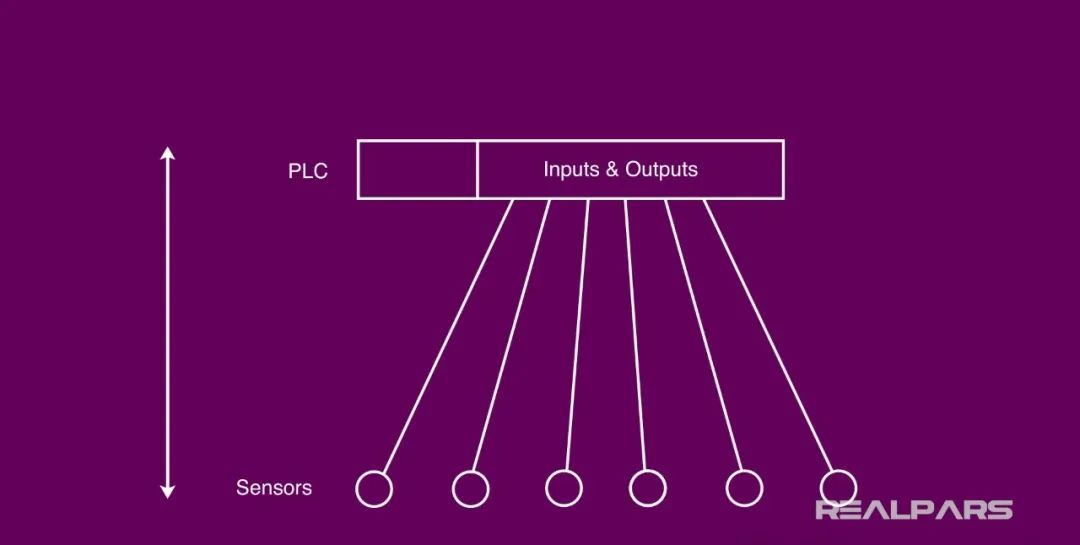
The drawbacks of this method are obvious: too many cables, complicated wiring, low efficiency, and poor maintainability. Using a bus can solve these problems.
Profibus-DP
PROFIBUS DP is one of the most commonly used types of Profibus, also known as standard PROFIBUS. The main advantages of this type are: plug and play, very fast data transmission, and it is the most commonly used in global production environments.
This type is specifically designed for high-speed data communication between automation control systems and device-level distributed I/O.Central controllers such as PCs or PLCs interact with their distributed field devices via high-speed serial links.Therefore, most data communication through distributed devices can be performed periodically.
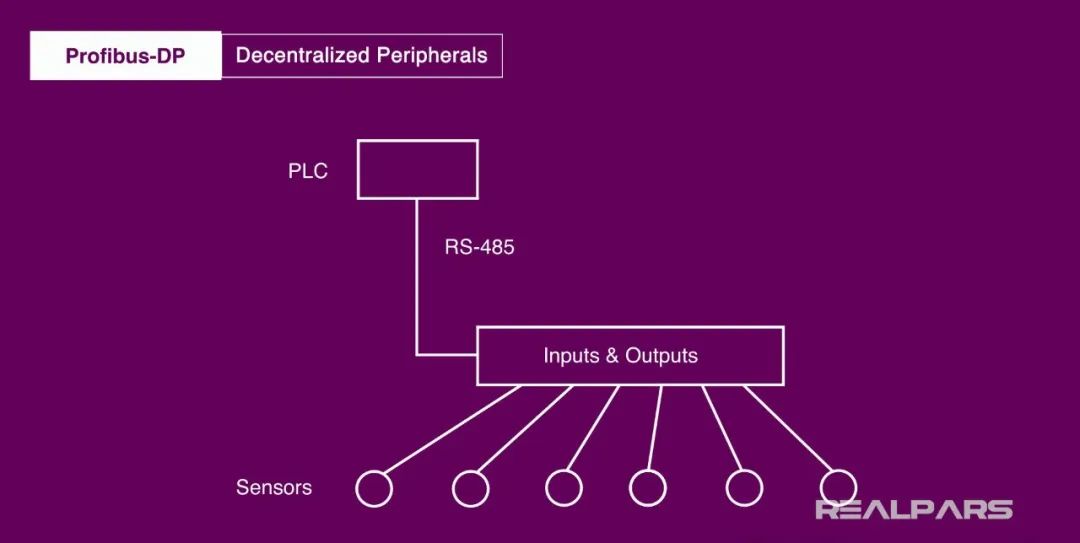
In addition to performing periodic functions, non-periodic communication functions can also be obtained by allowing configuration, diagnostics, and handling alarms, especially for intelligent field devices. Profibus DP supports up to 126 nodes on the bus, allowing multiple masters, but only available when all slaves are connected to a single master.
PROFIBUS DP includes three different versions: DP-V0, DP-V1, and DP-V2. We detailed this in the last issue:

Profibus-PA
Profibus PA is primarily designed for process automation. Therefore, it allows different sensors and actuators to connect on a single common bus, even in intrinsically safe areas.
PROFIBUS PA allows simultaneous digital data transmission and power supply over two wires (international standard IEC 1158-2), using intrinsically safe MBP transmission technology (Manchester coding; bus-powered), which fully meets these requirements. It is very suitable for directly integrating electromagnetic valves, sensors, and pneumatic actuators into process control systems, which are located in reachable hazardous areas zone 1/21 or 0/20.
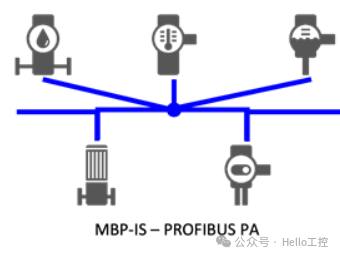
Profibus-PA improves and replaces traditional systems in process automation, such as 4-20 mA and HART. Compared to PROFIBUS DP, power and data are transmitted over the same two wires in Profibus PA. Additionally, PROFIBUS DP and PA are the same in usage and protocol.
The advantages of using the PROFIBUS PA profile for distributed field automation include low hardware overhead, high engineering cost-effectiveness, increased operational safety, and worry-free maintenance. These advantages are highlighted by the following features:
-
Modularity and uniformity from sensor to control level enable new plant designs.
-
Implementing intrinsically safe applications by using field buses in hazardous areas.
-
Redundant PROFIBUS PA architecture (with coupler redundancy in ring and linear topologies) supports flexible modular redundancy (FMR) from automation systems (controllers) to PA field devices.
-
Safety-related and fault-tolerant applications have low device and wiring requirements.
-
Reduce configuration costs through simple, centralized field device engineering (PROFIBUS PA and HART use SIMATIC PDM, also cross-vendor).
-
Simplified installation with dual-wire cables for common power and data transmission.
-
Reduce commissioning costs through simplified loop checks.
-
Lower maintenance costs due to simple wiring and comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
Profibus-FMS
Profibus FMS or PROFIBUS Fieldbus Message Specification is a generic solution, particularly for unit-level communication tasks. It is primarily designed for interaction by transmitting complex data between PLCs and PCs.
This is not suitable for low-complexity messages; otherwise, communication on more complex and broader networks would be necessary. The robust FMS service provides significant flexibility and can also be used for complex and extensive communication tasks.
Currently, PROFIBUS FMS is still used by more operators. Profibus-FMS (PROFIBUS Fieldbus Message Specification) is commonly used in industrial automation for the following scenarios:
-
Intercommunication between intelligent master stations at the workshop level: Profibus-FMS is best suited for general object-oriented communication between intelligent master stations at the workshop level. It provides a subset of MMS (Manufacturing Message Specification) functionality, supporting a large amount of data transmission, such as programs and data blocks, etc.
-
Complex data exchange: Profibus-FMS is suitable for transmitting complex data, especially in cases that require high flexibility and complex communication tasks. It supports multi-master and master-slave communication, point-to-point, broadcast, and local broadcast communication, periodic and non-periodic data transmission.
-
Factory automation and information management: Profibus-FMS can be used for factory automation and information management, connecting various devices on the production line, such as sensors, encoders, meters, etc. It can also connect upper-layer systems such as Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), achieving integration of factory automation and information management.
-
Medium transmission rate cyclic or non-cyclic data exchange tasks: Profibus-FMS primarily addresses workshop-level communication issues, completing medium transmission rate cyclic or non-cyclic data exchange tasks. It defines the first, second, and seventh layers, with the application layer including fieldbus information specifications and lower layer interfaces.
-
Communication between intelligent stations: Profibus-FMS provides robust application services that support communication between intelligent stations, suitable for connecting intelligent field devices such as PLCs, PCs, and MMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces).
-
Object-oriented protocol: Profibus-FMS is designed with object-oriented principles, where variables, parameters, and programs are all designed as objects, each with defined characteristics (such as read, write, etc.), and all objects are listed in the object dictionary (OD).
-
Multi-master network: Workshop-level monitoring networks can use Profibus-FMS, which is a multi-master network where the transmission rate of data is not the most important; rather, the ability to transmit large volumes of information is what matters.

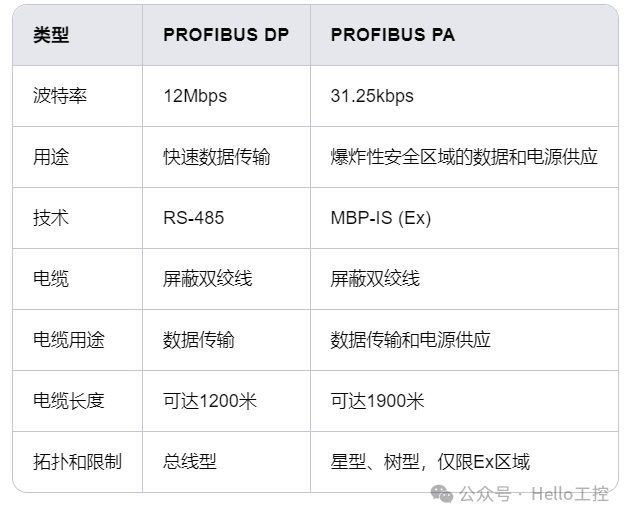
DP vs. PA
We illustrate the differences between DP and PA in the table below:
Reference Links:
-
https://procentec.com/content/profibus-dp-vs-pa-what-are-the-main-differences/
-
https://www.elprocus.com/profibus/
-
https://www.realpars.com/blog/profibus

-
[Video Course] Codesys V3.5 Series Introductory Course(128 people have learned) -
[Video Course] Codesys SoftMotion Basics Course(39 people have learned) -
[Video Course] Codesys SoftMotion Electronic Gears Course(12 people have learned) -
[Video Course] Codesys SoftMotion Electronic Cam Course(9 people have learned) -
[Video Course] Making Custom Libraries in Codesys(22 people have learned) -
Comprehensive collection of the most complete free materials for Codesys V3.5 series
-
Top 10 commonly used filtering algorithms (ST language)
-
What does a PLC integrated with Chat GPT look like?
-
Sharing the top 10 PLC programming books of 2023
-
Customize your exclusive CODESYS motion controller
-
MC_Power.status = FALSE, can the axis still move?
-
Summary of ST language learning materials

——–END——–

If you like this article, please share and “like” it below and “see” it.