In May of this year,5 month, the FME 2025.1 version was released, which includes a significant update: FME Data Virtualization, that is, FME data virtualization.
1. What is Data Virtualization?
Data virtualization refers to the integration of multi-source heterogeneous data from different data sources by creating a logical layer, without the need for physical data replication or movement. This approach allows users to access and manage data resources scattered across different locations and formats through a unified interface, thereby simplifying the complexity of data access and usage.Data virtualization is widely used in enterprise data management, data integration, data analysis, and other fields, especially in cases where data sources are dispersed and data silos are severe, effectively enhancing the availability and flexibility of data.
2. FME’s Data Virtualization Capabilities
(1)Create custom data views through filtering functions, eliminating sensitive or irrelevant information, allowing only authenticated users and applications to access the API, enhancing control and security.
(2)Cache for high-speed endpoint requests, using caching for common or static requests can provide faster response times, better performance, and reduce system load.
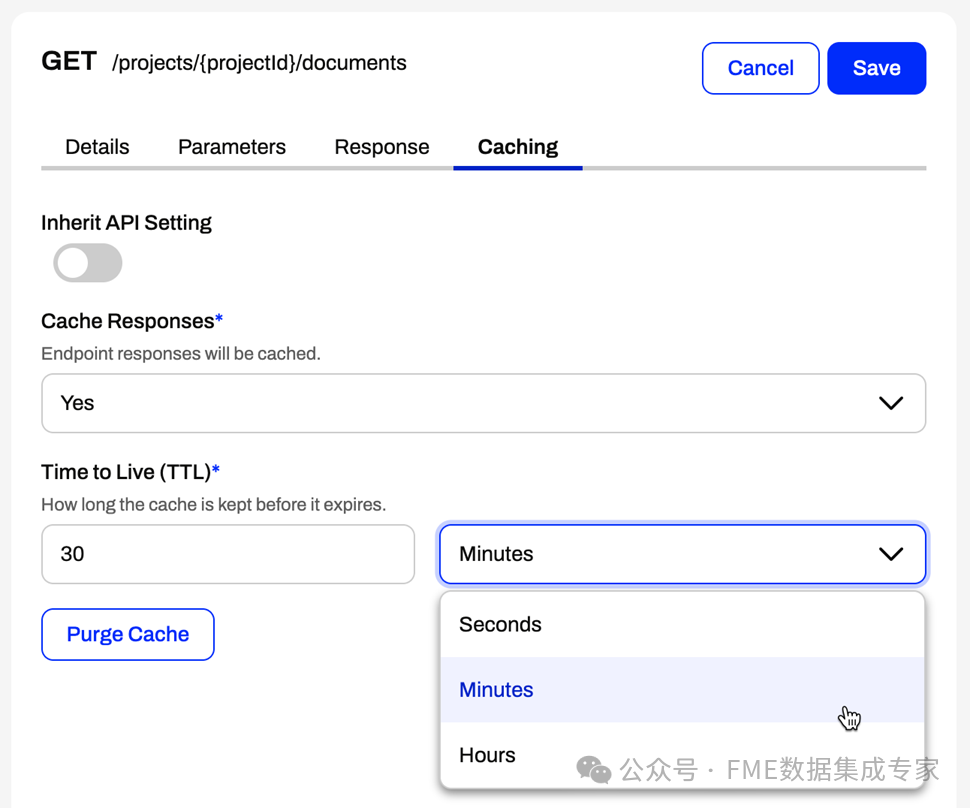
(3)Provide OpenAPI endpoints for AI access, allowing any AI tool to easily connect to the data virtualization endpoints, enabling users to interact with data using natural language.

(4)Provide synchronous and asynchronous endpoints, giving application developers maximum flexibility in deciding how they want to interact with the application layer.
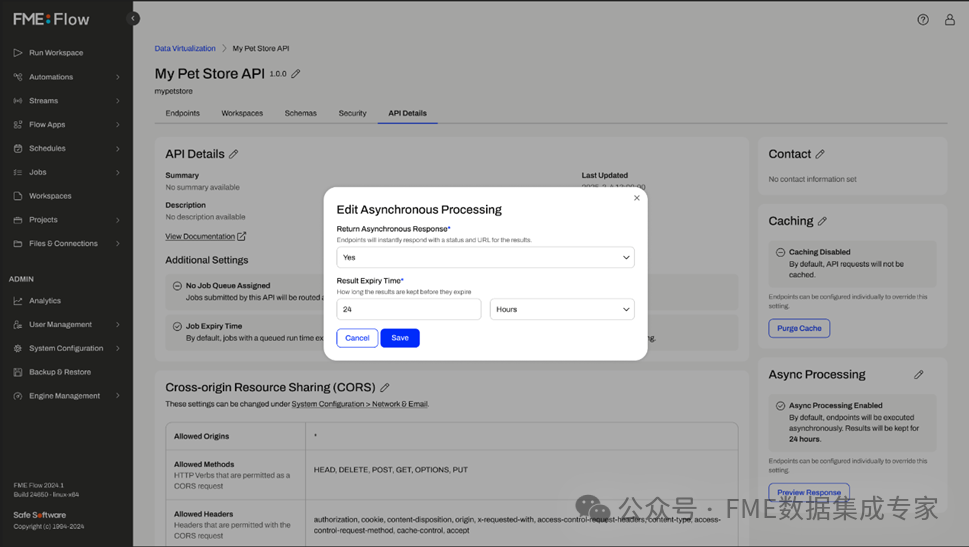
Asynchronous processing allows applications to receive immediate responses from the data virtualization API.
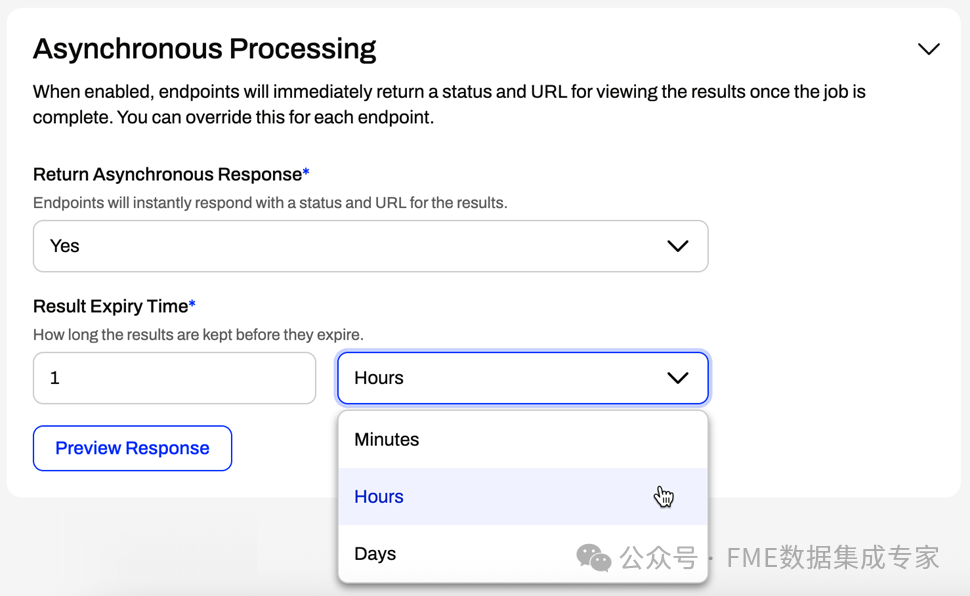
The results of the FME workflow are temporarily available for retrieval by client or end-user applications.
3. FME Data Virtualization Principles
In the data virtualization workflow, the FME platform acts as an intermediary layer between data users (such as applications, scripts, dashboards, or mobile devices) and data sources (such as databases, file systems, API interfaces, or cloud storage).
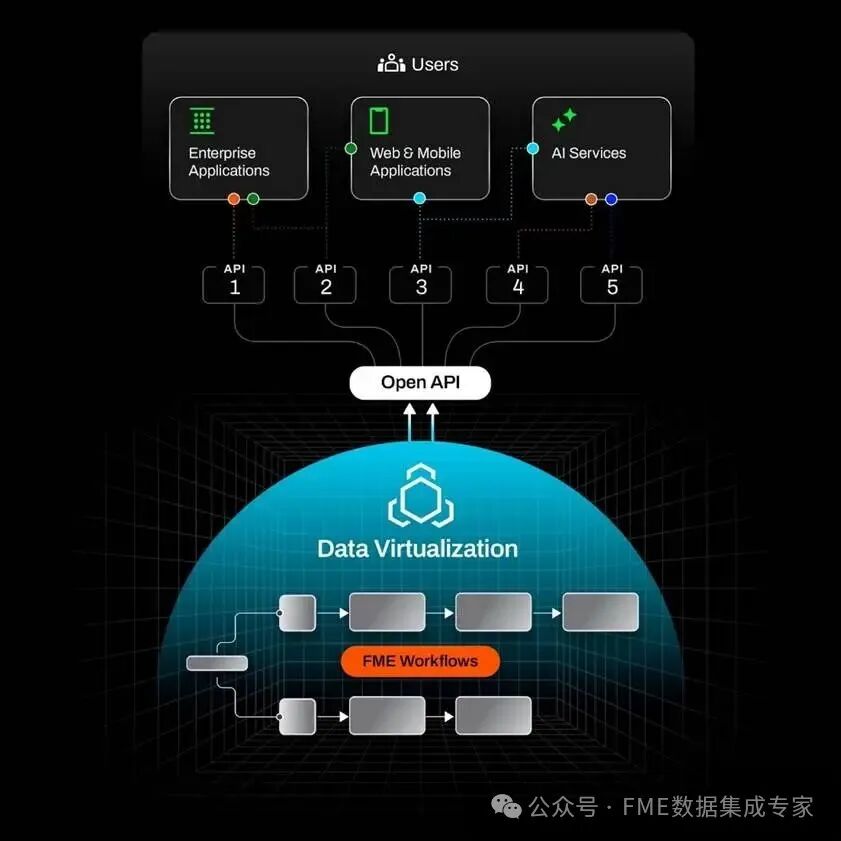
Clients interact with the data virtualization API by sending HTTP requests to predefined endpoints, each of which specifies how to process requests and how to produce responses. FME Flow receives these requests, processes the data according to the endpoint configuration, and returns the appropriate results to the client. The types of endpoints are divided into two categories:
Manual Endpoints: Fully configured within FME Flow, returning fixed responses for each request, very suitable for static information, such as service descriptions, metadata, or status messages.
Workspace Endpoints: Associated with FME workspaces created in FME Form. When a request is received, FME Flow runs the associated workspace in real-time. Data is retrieved through readers, processed by converters, and then formatted by writers before returning the response to the client.
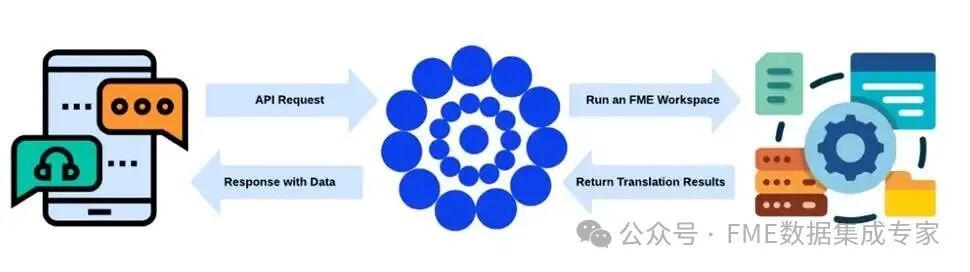
All communications follow standard REST protocols, supporting GET, POST and other request methods, with responses returned in JSON or XML data formats. Authentication and access control are centrally managed through FME Flow, supporting role-based permission configurations or API token verification mechanisms.
This architecture allows clients to connect to multi-source data through a unified API interface without directly accessing the underlying systems or understanding the data storage processing logic.
4. FME Data Virtualization Value
Compared to traditional ETL-driven data integration solutions, FME data virtualization avoids data replication and movement, significantly reducing the implementation workload of data integration as well as the investment and operational costs for enterprises in storing, managing, and applying data; more importantly, utilizing FME’s data virtualization capabilities allows AI, machine learning, and others to access and dynamically integrate multi-source heterogeneous spatial data without barriers.
Appendix: Explanation of Proprietary Names
|
Name |
Explanation |
|
Data Virtualization API |
Creates an OpenAPI that meets the REST API specifications in FME Flow, exposing data and logic through endpoints. |
|
Endpoint |
A predefined path in the API used to handle specific requests (e.g., https://api.example.com/users ). |