Abstract: Conducting international assessments of disciplines is an inherent requirement for building world-class disciplines in line with international standards. It is also an important way to examine the effectiveness of discipline construction and a key approach to driving the connotation development of disciplines. This article focuses on the current research status of international assessments of disciplines, using the example of Tianjin University’s “SPI-IP” international assessment work, employing analytical tools such as UCINET for systematic analysis, and proposing a new approach to international assessment that adheres to the dual considerations of Chinese characteristics and world-class standards, self-evaluation and expert evaluation, as well as problem-oriented and goal-oriented frameworks.
Keywords: Discipline Construction; International Assessment; SPI-IP; “Double First-Class” Construction; Tianjin University
Authors: He Xi, Chen Tiankai, Zhang Liqian, Dong Wei, Hu Minglie
The main text is as follows
In the context of the “Double First-Class” construction strategy, Chinese universities must rely on Chinese characteristics, target international dimensions, gather first-class faculty, cultivate first-class talents, and produce first-class results to better serve national and regional development strategies. General Secretary Xi Jinping has repeatedly emphasized the need to “build China’s world-class universities,” “solidly run socialist universities with Chinese characteristics,” and “absorb advanced educational management experiences from around the world while rooting education in China.” This fully reflects the Party and the country’s high regard and earnest expectations for the development of higher education, serving as a guiding principle for high-quality development in higher education under new circumstances.
Since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, the development of higher education in China has entered a new stage. With the implementation of the strategy to strengthen education and modernize education, higher education in China has gradually formed its own characteristics. In the new global talent competition landscape, during the process of promoting “Double First-Class” construction in China, there is a pressing need to establish a number of disciplines that have leading positions in the world to further solidify the talent foundation for building an innovative country. Furthermore, the international competitiveness of disciplines needs to be examined within an international assessment framework.
Focusing on higher education discipline assessment, various institutions at home and abroad have constructed diverse assessment models. The history of discipline assessment in Western higher education is long, forming three main models: the assessment model that emphasizes teaching quality represented by the UK’s higher education quality assessment and the US’s professional accreditation system; the research-focused assessment model represented by the UK’s REF and the US’s ESI; and the comprehensive assessment model that emphasizes overall development represented by institutional accreditation. In comparison, the characteristics of China’s higher education assessment model are quite distinct, mainly including three types: assessments organized by government and education authorities; internal educational assessments conducted by universities; and educational assessments of universities by third-party social organizations.
In the process of building world-class universities and disciplines, it is essential to clarify the connotations and standards of world-class status, identify the factors that restrict discipline development in reality, and clarify construction and development ideas. This requires in-depth exploration within discipline organizations and conducting highly customized self-assessments. Zhang Jie believes that conducting medium- to long-term assessments based on international first-class standards is an inherent need for building world-class universities. For instance, high-level research universities in China, such as Tsinghua University, Peking University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and Fudan University, have all conducted international assessments. Huang Rongxia and others have analyzed the case of international assessments at Uppsala University in Sweden, asserting that international assessments are one of the important measures for universities to enhance quality. Yuan Guanglin argues that international assessments of disciplines, as a typical developmental assessment, have become an important measure for research universities in China to promote the construction of world-class disciplines. Introducing international assessments of disciplines and conducting related research and practice can meet the practical needs of discipline assessments in universities, benchmark against international first-class standards, examine the level of discipline construction, optimize discipline construction paths, stimulate internal motivation of disciplines, and accelerate the construction of world-class universities and first-class disciplines.
In March 2015, the “Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on Deepening the Reform of Social Systems and Mechanisms to Accelerate the Implementation of Innovation-Driven Development Strategies” pointed out: “Encourage higher education institutions to use international first-class disciplines as a reference to carry out international assessments of disciplines, expand exchanges and cooperation, and steadily advance the internationalization process of higher education institutions.” Tianjin University launched the international assessment work for its advantageous disciplines in 2016, and so far has organized international assessments for seven advantageous disciplines, including Optical Engineering, Computer Science and Technology, Software Engineering, Management Science and Engineering, Environmental Science and Engineering, Architecture, and Civil Engineering. Through practical exploration, a unique international assessment model with Tianjin University characteristics—”SPI-IP” has been developed, which includes self-evaluation, pre-evaluation, international on-site review, subsequent improvement, and post-evaluation. Through scientific analysis of self-evaluation reports and international expert evaluation reports, it further practices and improves to provide an important tool for achieving connotative development of disciplines and driving the construction of first-class disciplines.
1. Goals and Principles of the “SPI-IP” Model
The purpose of the international assessment of disciplines is to promote development through evaluation, driving connotative development of disciplines to reach world-class levels. On one hand, it places disciplines within an international framework to measure their construction levels against international standards, identifying deficiencies and gaps with world-class disciplines; on the other hand, it systematically understands the concepts, pathways, and measures of constructing world-class disciplines, improving the future development strategy and construction tasks of disciplines. Meanwhile, through the assessment work, it comprehensively showcases the achievements of discipline construction, engages in in-depth exchanges with world-class universities, first-class disciplines, and top scholars, enhancing the international influence and communication capacity of the disciplines.
Tianjin University’s international assessment work adheres to the principles of high standards, scientific rigor, and high quality. First, it insists on high standards, conducting international assessments based on world-class standards, closely aligning with the university’s strategic goal of building a world-class university, fully reflecting the unique characteristics and strengths of discipline construction, conducting extensive research, and deeply refining to aim for world-class and internationally advanced levels. Second, it emphasizes scientific rigor, following the basic laws of assessment work, combining discipline attributes and characteristics, and systematically collecting and organizing assessment materials around construction achievements. Third, it embodies the principle of high quality, focusing on benchmarking against world-class disciplines, identifying gaps and deficiencies, clarifying future strategic tasks and development plans for discipline construction, and revising discipline construction planning schemes to support the “Double First-Class” construction.
2. System Architecture and Implementation Process of the “SPI-IP” Model
The international assessment work of Tianjin University is based on thorough research of international assessment paradigms, grounded in China’s national conditions, and combined with the university’s actual situation, innovating assessment ideas and methods. It places greater emphasis on the organic unity of goal evaluation, process evaluation, and outcome evaluation of discipline construction, the integration of problem orientation and outcome sharing, and the design of a closed-loop system and long-term mechanism of “assessment-optimization-reassessment,” forming the “SPI-IP” model work plan for Tianjin University’s international assessment of disciplines. The main links are illustrated in Figure 1.
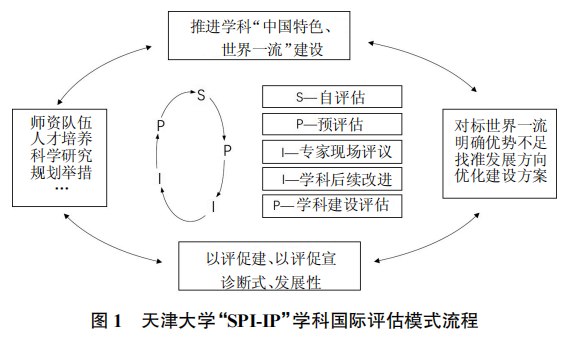
(1) Self-evaluation of the Discipline. The discipline conducts self-evaluation and forms a self-evaluation report, comprehensively summarizing the achievements and shortcomings in talent cultivation, faculty team, scientific research, and development strategy.
(2) Pre-evaluation. International experts review written materials such as discipline construction data and self-evaluation reports to understand the effectiveness of discipline construction, helping to identify issues in discipline development and providing preliminary suggestions.
(3) Expert On-site Review. Internationally renowned experts are invited to gain an in-depth understanding and overall evaluation of the discipline through various forms such as listening to reports and visiting discussions, proposing existing problems and improvement suggestions, and providing a written evaluation report within one month after the on-site review.
(4) Subsequent Improvement of the Discipline. The discipline refers to the international evaluation report, sets strategic goals based on international first-class standards, adjusts discipline planning, refines development directions, and further implements reform and enhancement measures to build a peak discipline.
(5) Post-evaluation of Discipline Construction. Following the discipline development planning after the assessment, a post-evaluation is conducted, with a cycle set at 3-4 years, to examine the effectiveness of discipline construction, assess the international standards of the discipline, and incorporate the performance evaluation of the policy resources’ “input-output”.
3. Analysis of Expert Reports from Tianjin University’s International Assessment
The analysis sample is derived from the evaluation opinions of 42 internationally renowned experts from seven disciplines at Tianjin University, including Optical Engineering, Architecture, and Management Science and Engineering. Using the UCINET social network analysis tool, high-frequency keyword extraction and analysis of expert evaluation reports were conducted, resulting in 24 discipline construction-related keywords with a frequency of five or more. As shown in Table 1, the keyword “faculty team” has the highest frequency at 87; followed by “talent cultivation” and “scientific research,” with frequencies of 82 and 75, respectively. Keywords such as “planning measures,” “discipline reputation and cultural construction,” and “international cooperation” also had frequencies exceeding 20 in the evaluation reports.
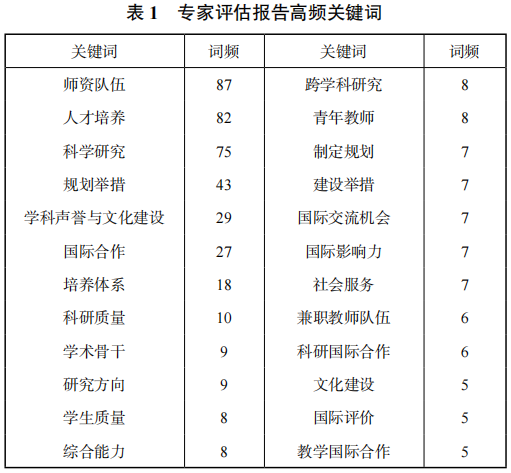
Based on the quantitative data analysis of the evaluation reports, Figure 2 constructs a highly cohesive relational network map. The network map of high-frequency keywords in the construction of world-class disciplines consists of numerous nodes and connections, indicating the interrelationships between high-frequency keywords. As seen in Figure 2, the faculty team, talent cultivation, scientific research, planning measures, discipline reputation, and cultural construction occupy important core positions. Additionally, international experts placed significant emphasis on comprehensive abilities of students, the development of young faculty, interdisciplinary research, international exchange opportunities, and attracting quality students in their evaluation reports.
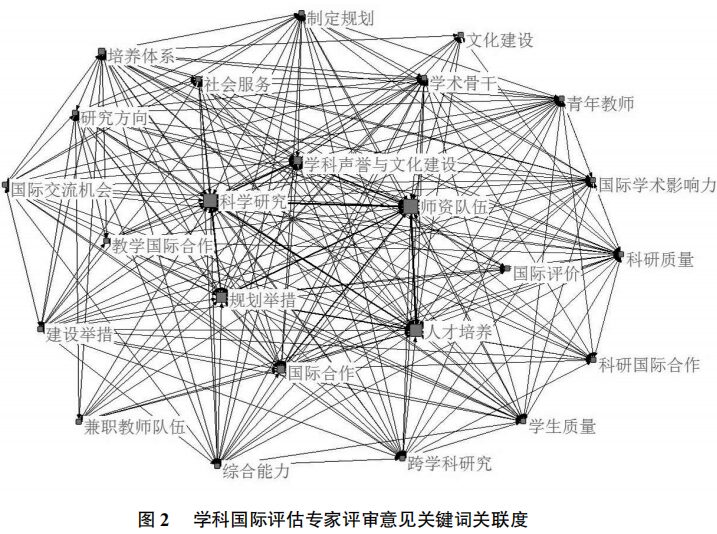
Table 2 lists the keywords and standardized degree centrality indicators extracted from the international assessment expert review reports, as well as a summary of expert evaluation opinions. Based on keyword frequency statistics and relevance analysis, this paper identifies six overarching indicators as primary keyword indicators: faculty team, talent cultivation, scientific research, planning measures, discipline reputation and cultural construction, and international cooperation. The larger the standardized degree centrality of an indicator, the more important it is in the construction process of world-class disciplines.
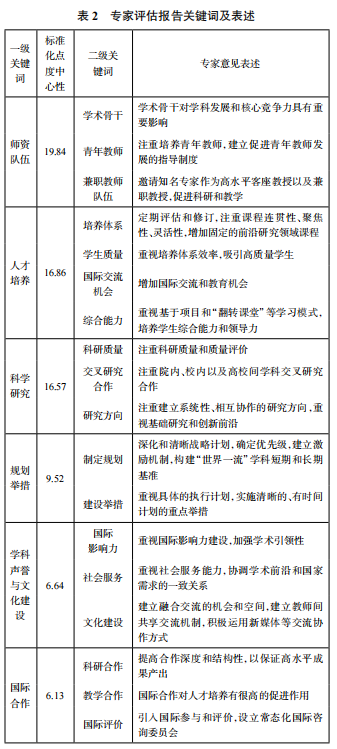
(1) Faculty Team. The faculty team is the core category with the highest overall proportion, and is a keyword of significant concern for international assessment experts. 86.5% of the reviewing experts believe that academic backbones are the leaders in the discipline construction process, serving as the backbone of teaching and research, which is crucial for building first-class disciplines. Additionally, there is a strong emphasis on recruiting, cultivating, and developing high-level young faculty, as this is seen as an important factor for the potential of discipline development. 54% of the assessment experts suggest inviting renowned experts as high-level guest professors and part-time professors to strongly support research and teaching, enriching the composition of the faculty team through a combination of full-time and part-time approaches.
(2) Talent Cultivation. 80.2% of the assessment experts believe that the cultivation system is the most important influencing factor for the quality of talent cultivation, and comprehensive measures should be taken to ensure the establishment of a high-level talent cultivation system, focusing on the focus, coherence, and flexibility of the cultivation system. 60.5% of the experts believe that enhancing leadership, bilingual expression, and other comprehensive abilities is very important for cultivating high-level talents with global competitiveness. Additionally, experts pay close attention to how to attract high-quality student sources and increase international exchange opportunities for students.
(3) Scientific Research. International experts believe that the single quantity indicators of SCI papers and highly cited papers do not truly reflect the academic level of the discipline; rather, attention should be paid to the scientific, systematic, and innovative nature of research quality and direction. Experts shift their focus from quantitative indicators of research performance to qualitative indicators, moving from incremental research to more innovative research. Furthermore, international assessment experts from disciplines such as architecture, civil engineering, computer science and technology, and management science and engineering all suggest promoting interdisciplinary research and conducting cross-disciplinary studies in innovative research methods and expanding research frontiers.
(4) Planning Measures. Assessment experts place great importance on the planning measures in the process of constructing world-class disciplines. The second-level keywords “developing plans” and “construction measures” have high degree centrality indicators, and the significance of deepening and clarifying strategic plans is repeatedly mentioned in the expert evaluation reports. They recommend constructing short-term and long-term benchmarks for “world-class” disciplines and emphasizing specific execution plans to ensure that strategic planning objectives are achieved through clear construction measures, matching resource support, and a complete reward and punishment mechanism.
(5) Discipline Reputation and Cultural Construction. 62.7% of the experts believe that the construction of world-class disciplines should emphasize social service and strive to serve academic frontiers and national needs. Simultaneously, assessment experts argue that although the construction strength of the assessed disciplines is good, there is still a need to strengthen international influence. 37.2% of the experts believe that cultural construction plays a positive role in building first-class disciplines and suggest establishing opportunities and spaces for integration and communication, as well as building mechanisms for sharing and communication among faculty.
(6) International Cooperation. Conducting multidimensional, deep-level, and long-term international cooperation is an effective tool for building world-class disciplines. International peer experts believe that deep international cooperation is very important for discipline construction. In terms of research collaboration, they suggest increasing the depth and breadth of cooperation to ensure high-level results. In terms of teaching collaboration, they fully acknowledge the role of international cooperation in talent cultivation and recommend introducing international participation and evaluation. By analyzing the overall and specific strengths and weaknesses of the discipline from an international perspective, it helps the discipline effectively address weaknesses and strengthen strengths, providing significant reference and guidance for building first-class disciplines.
Tianjin University’s international assessment work adheres to the philosophy of “looking towards the future, keeping an eye on the world, benchmarking internationally, and striving for excellence.” It enriches and improves the internal quality assurance system of the university, achieving the organic unity of process evaluation, value-added evaluation, and comprehensive evaluation of discipline construction. Additionally, by widely inviting international peer experts to diagnose and prescribe for the disciplines, it deeply promotes self-reform and connotative development of disciplines, further driving systematic reforms in resource allocation, organizational models, and dynamic management in discipline construction, providing important scientific guidance and strong support for the university’s push towards world-class universities and first-class disciplines, with far-reaching significance.
1. The “SPI-IP” International Assessment Model Becomes an Important Support for Tianjin University’s Discipline Quality Assurance System
The implementation of international assessments of disciplines is a new exploration in the reform of discipline construction mechanisms, establishing a self-assessment model for disciplines that aligns with international standards. Building on existing self-assessments of degree programs, teaching quality assessments, AMBA accreditation, ICHME accreditation, etc., Tianjin University has incorporated international assessments focused on disciplines, enriching and improving the discipline quality assurance system. Through the practice of the “SPI-IP” international assessment model, it has achieved a closed-loop evaluation from “self-evaluation” to “post-evaluation,” combining “diagnostic” and “developmental” evaluations, as well as integrating “Chinese characteristics” with “world-class” evaluations. The demonstration and shared radiation effects of international assessments have become more pronounced. The evaluation opinions of international experts provide important references for various disciplines to achieve connotative development and scientific planning under the goal of “Chinese characteristics, world-class.”
2. International Assessments of Disciplines Break the Fixed Mindset of Discipline Construction and Promote Connotative Development
In the international assessment work of Tianjin University, more than 40 top international experts, including foreign academicians, Turing Award winners, and editors of top academic journals, have been invited to diagnose the discipline construction. The important suggestions provided by experts have broadened perspectives and broken the fixed mindset of discipline construction, opening up a new pattern for discipline construction. Through scientific analysis of expert evaluation results, various assessed disciplines have developed targeted development strategies in areas such as faculty teams, talent cultivation, scientific research, and discipline reputation and cultural construction, deeply promoting connotative development and first-class construction. The Optical Engineering discipline, for instance, has combined expert opinions to refine key directions, focusing on strengthening the integration of original innovative basic research and high-level applied research, and establishing a platform for integrated optoelectronic devices, achieving breakthrough results in the frontier areas of the discipline. The Architecture discipline has worked to enhance its overall strength and international influence based on international assessment work, entering the top 50 in the QS World University Subject Rankings in 2021, contributing to the enhancement of China’s architecture discipline’s international influence and cultural communication capacity.
3. International Assessments Accelerate the Internationalization of “Double First-Class” Construction
Through international assessments of disciplines, international peer experts have gained an in-depth understanding of the advantages and characteristics of the assessed disciplines, expanding international cooperation channels and increasing the international influence of the disciplines. During the international assessment of Tianjin University’s Computer Science discipline, experts highly recognized the achievements of discipline construction, and after the assessment, deep research cooperation was initiated, resulting in breakthroughs in top research outcomes. By summarizing the international assessment work, Tianjin University has promoted the implementation of the “Global Vision Expansion Project for Students,” exploring new models for international talent cultivation, continuously enriching quality teaching resources, constructing an internationalized education environment, and building an education and teaching brand with Tianjin University characteristics. At the same time, through comprehensive diagnosis of the international assessment work and benchmarking against international first-class standards, it leads disciplines to strengthen connotative construction, providing scientific and powerful references for the university to promote discipline construction, resource integration and allocation, interdisciplinary innovation, and relevant institutional reforms, accumulating strength for the university’s accelerated advancement towards world-class universities and first-class disciplines.
1. Focus on Goals and Missions, Adhere to the Dual Considerations of Chinese Characteristics and World-Class Standards
International assessments of disciplines should focus on discipline construction goals and missions, firmly establishing evaluation concepts and guiding thoughts that promote connotative development as fundamental principles. In conducting assessments, two dimensions should be considered: first, the situation of discipline construction should be placed within an international framework, benchmarking against international standards to measure the international influence and contribution of the discipline; second, the situation of discipline construction should be placed within the framework of serving China’s economic and social development, rooted in Chinese soil, measuring the social service achievements and effects of the discipline, thereby achieving an organic unity of the internal logic and external performance of discipline construction and development in Chinese universities. These two dimensions should be reflected in international assessments through scientific, systematic, and comprehensive planning and design of assessment schemes, setting assessment indicators, and the system of discipline construction in China.
2. Focus on Quality and Effectiveness, Adhere to the Dual Evaluations of Self and Expert Assessments
International assessments of disciplines should focus on quality and effectiveness. The quality and effectiveness of assessments will directly affect the discipline’s self-positioning and future development direction, requiring the integration of self-assessments and expert evaluations. Self-assessment involves examining the discipline’s construction level from its own perspective, which can be achieved through pre-evaluation work. International expert evaluation, on the other hand, measures discipline strength from an international perspective, necessitating effective selection of assessment experts, summarizing and refining the effectiveness of discipline construction, and deeply integrating and organically unifying the selection of discipline strategies and goal setting, effectively grasping the influencing factors of discipline construction, clearly identifying potential advantages, pinpointing shortcomings and deficiencies, and defining paths and strategic measures for discipline enhancement, thereby effectively advancing discipline construction work that serves the creation of world-class universities.
3. Focus on Diagnosis and Development, Adhere to the Dual Orientation of Process and Results
International assessments of disciplines should focus on diagnosis and development, avoiding level assessments and elite evaluations, but instead conducting diagnostic and developmental assessments to build a discipline evaluation system that meets the actual needs of comprehensive universities. Simultaneously, assessments should adhere to the principle of “openness and commonality”: on one hand, during assessments, fully understanding and grasping the internal logic of constructing world-class disciplines, including concepts, models, and pathways, enhances the understanding of international standards in discipline construction; on the other hand, assessments should maintain problem orientation and goal orientation, with problem orientation focusing on accurately identifying key issues hindering discipline development, and goal orientation aiming to find fitting points against world-class standards, optimizing and improving discipline construction planning, accurately targeting efforts, strengthening advantages, and addressing weaknesses, thereby accelerating the construction of “peak disciplines” and the process of building first-class disciplines.
References:
[1] Jiang Xiaoli, Wang Zheng. Exploration and Practice of International Assessment of Disciplines in Research Universities: A Case Study of Zhejiang University [J]. Degree and Graduate Education, 2013(10): 44-48.
[2] Martin B, Geuna A. University Research Evaluation and Funding: An International Comparison[J]. Minerva, 2003(41): 277-304.
[3] Chang Wenlei, Qiu Hongwei, Liu Shuai. Review and Prospects of Research on International Assessment of Disciplines in Universities [J]. Research Management, 2015, 36(1): 483-489.
[4] Zhang Jie. Conducting Medium- to Long-Term Assessments Based on International First-Class Standards [J]. Chinese Higher Education, 2007(20): 4-7.
[5] Huang Rongxia, Lennart W. A Framework for International Assessment of Disciplines: A Case Study of Promoting World-Class University Construction through Discipline Assessment [J]. Chinese Higher Education Research, 2014(2): 42-46.
[6] Yuan Guanglin. Analysis of Developmental Assessment of World-Class Disciplines in Chinese Universities [J]. Chinese Higher Education Research, 2019(6): 21-26.
[7] Li Yonggang, Huang Ziming. Exploration of the Current Situation and Characteristics of International Assessment Implementation in Research Universities: Based on a Survey and Analysis of Graduate Schools in China [J]. Degree and Graduate Education, 2016(11): 6-12.
[8] People’s Daily. Opinions on Deepening Reform of Systems and Mechanisms and Accelerating the Implementation of Innovation-Driven Development Strategies [EB/OL]. http://ip.people.com.cn/GB/136672/395155/396330/, 2020-03-05.
[9] Tianjin University Graduate School. Creating “Double First-Class”: Diagnosing and Prescribing Good Solutions to Benchmark International Standards [EB/OL]. http://news.tju.edu.cn/info/1003/54336.htm?from=timeline&isappinstalled=0, 2020-12-15.
[10] Chen Tiankai, Dong Wei, Zhang Liqian, et al. Analysis of Pathways for Building First-Class Disciplines Based on Demand Orientation [J]. Degree and Graduate Education, 2020(3): 13-18.
[11] Huang Baoyin, Lin Mengquan, Ren Chao, et al. Efforts to Build a Discipline Assessment System with Chinese Characteristics and International Influence [J]. Chinese Higher Education, 2018(1): 13-18.



For more exciting content, please follow Tianjin University Graduate Education