In the current era of rapid digitalization and intelligence, embedded motherboards have become the brain of electronic devices. Procurement personnel must consider comprehensively and make precise choices to find the best products for their projects.

Understand Project Requirements
Before procurement, it is essential to be familiar with the project characteristics. For example, in industrial control scenarios, high temperatures, dust, and electromagnetic interference make the stability and durability of the motherboard very important. The motherboard procured should focus on wide temperature operation capabilities and reliable dust and electromagnetic interference protection. If used for intelligent security monitoring, the motherboard’s image and video processing capabilities are indispensable, requiring the ability to handle multiple video streams smoothly and perfectly compatible with various video decoding formats, ensuring that monitoring images can be transmitted clearly and in real-time. Additionally, ample storage interfaces are necessary to store massive amounts of data.
Pay Attention to Configuration Parameters
CPU
The CPU directly determines the computational power of the motherboard. The main frequency mainly affects the computation speed, and tasks with high real-time requirements will have certain demands on the CPU’s main frequency; the number of cores and threads plays an important role in multitasking scenarios. In situations where multiple instructions are executed simultaneously, multi-core and multi-threaded processors show their advantages. For example, the JH Technology commercial all-in-one motherboard CB4-X12-V0 has a processor with 12 cores and 16 threads, which can respond quickly in multitasking scenarios; the cache size is also not to be overlooked, as large capacity cache can reduce CPU data reading time and accelerate the overall system operation.
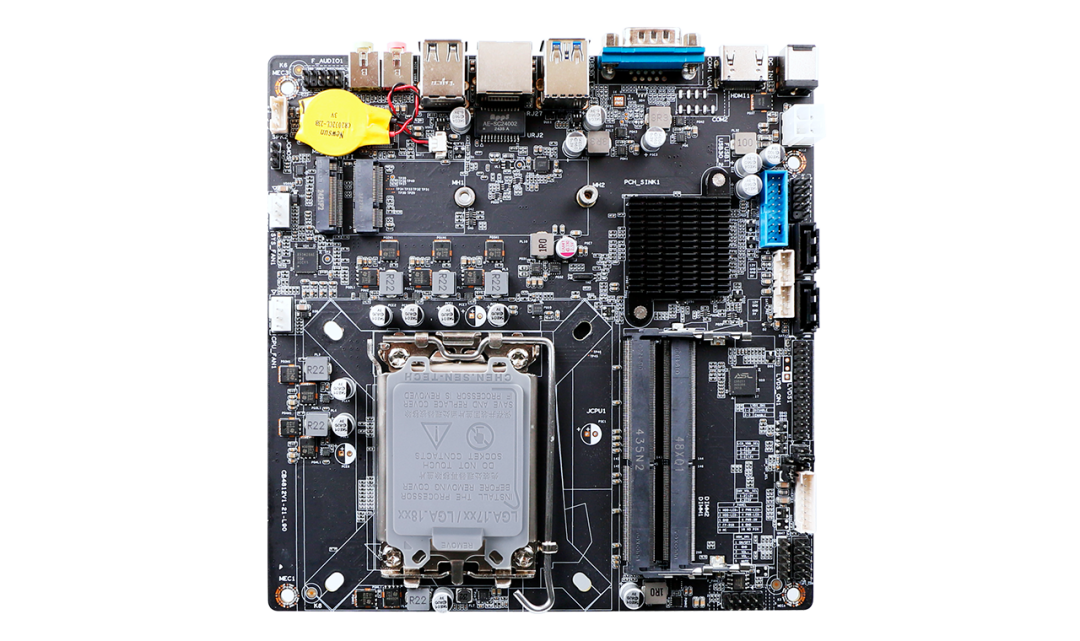

JH Technology commercial all-in-one motherboard CB4-X12-V0
Memory
The size of the memory determines how many programs the motherboard can run simultaneously and how much data it can process. For example, IoT gateway devices need to process data from multiple sensors, perform data aggregation and protocol conversion operations, usually requiring 1GB, 2GB, or larger memory to ensure system accuracy and smoothness. For embedded applications, such as smart home appliances, running a simple user interface, receiving, and processing user commands may only require 256MB or 512MB of memory. It is essential to pay attention to the types of memory supported by the motherboard, as DDR5, DDR4, and DDR3 have decreasing read and write performance; also, consider the number and specifications of memory slots, which determine future upgrade potential.

Storage
First, pay attention to storage capacity. If the application requires storing large amounts of data, such as in monitoring systems, then a large-capacity storage device is needed, which can be an embedded motherboard with large-capacity eMMC (embedded multimedia card) or one that supports SATA interface connection to hard drives. Secondly, consider the types and number of storage interfaces; SATA interfaces adapt to large-capacity mechanical hard drives for long-term archiving of massive data; M.2 interfaces are designed for high-speed solid-state drives, meeting the demands for rapid system boot and lightning-fast program loading. Finally, it is also essential to understand the maximum hard drive capacity supported by each interface for precise storage architecture planning.
Focus on Interface Types
Internal Interfaces
Memory Slots. Common types of memory slots include DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5. Compared to DDR3, DDR4 has a higher data transfer rate, while DDR5 is even faster and has lower power consumption. Memory slots are usually designed in dual-channel or quad-channel configurations, and installing memory in dual-channel or quad-channel mode offers better read and write performance than single-channel installation of the same capacity.

M.2 Interface. Mainly used to connect solid-state drives (SSD), M.2 interfaces come in various specifications, such as M.2 2242, M.2 2260, M.2 2280, etc., where the numbers represent the length of the solid-state drive. M.2 interfaces support multiple protocols, such as SATA and NVMe; NVMe protocol M.2 SSDs have extremely high read and write speeds, significantly improving system boot speed and application loading speed. M.2 interfaces also provide different rate supports, such as PCIe3.0x4 and PCIe4.0 x4, with higher PCIe versions meaning faster data transfer rates.
SATA Interface. Used to connect hard drives (including mechanical hard drives and SATA interface solid-state drives) and optical drives. A motherboard usually has multiple SATA interfaces for user storage device expansion. SATA interfaces use an L-shaped design, making the data and power connections more secure and reducing transmission issues caused by looseness.
External Interfaces
USB Interface. One of the most common external interfaces used to connect various USB devices, USB interfaces come in various versions, including USB1.0, USB2.0, USB3.0, USB3.1, and USB3.2. The higher the USB version, the higher the transfer rate. USB interfaces on motherboards typically have different colors to distinguish different versions, such as blue for USB3.0 or above.
HDMI Interface. Mainly used to connect monitors, TVs, and other display devices, achieving high-definition video and audio transmission. HDMI interfaces come in various specifications, such as HDMI1.4, HDMI2.0, and HDMI2.1. HDMI2.0 supports 4K/60Hz video transmission; HDMI2.1 supports higher resolutions, such as 8K/120Hz.
DP Interface. Used to connect display devices, this interface has advantages in certain aspects. For example, the DP interface performs better in high resolution and high refresh rate video transmission, enabling multi-display connections and is widely used in some professional graphics fields, such as connecting professional monitors for graphic design, video editing, and other tasks.
VGA Interface. Mainly used to connect older monitors. It transmits video through analog signals and is now primarily used in situations where display quality is not a high requirement or for connecting older devices. With technological advancements, its application on new motherboards is gradually decreasing, but it still has certain value.
Audio Interface. Includes headphone jacks, microphone jacks, etc. These interfaces allow users to connect headphones, microphones, speakers, and other audio devices. The audio interfaces on the motherboard typically use the 3.5mm interface standard, meeting user needs for music appreciation, voice calls, and other audio requirements.
RJ-45 Interface. Used to connect Ethernet cables, enabling the connection between computers and networks. It supports different network speeds, such as 100Mbps, 1000Mbps, etc. On the motherboard, the RJ-45 interface usually has indicator lights next to it to show network connection status and data transmission status, helping users determine whether the network is connected and functioning properly.

Focus on Brand After-Sales Service
Well-known brands often have strong R&D capabilities, strict quality control, and mature technology, like JH Technology’s embedded motherboards, which have passed market tests, offering excellent compatibility and stability. With a complete after-sales system, technical support and repair services can be quickly obtained for product faults and technical issues, ensuring worry-free after-sales.
Procurement of embedded motherboards involves a wide range of considerations and must be approached cautiously, starting from project requirements, covering performance and interfaces, and finally focusing on brand after-sales service to select the appropriate product.
Recommended Reading




More Products, Explore Further