In automotive electronic diagnostics,the UDS protocol is the core tool for engineers to “communicate” with the ECU. Today, we will delve into two key services:Diagnostic Session Control (SID 0x10) and ECU Reset (SID 0x11), analyzing the underlying mechanisms and application techniques!
1. Session Control Service (0x10): How to Avoid “Disconnection”??
-
The ECU defaults to Safe Mode (default session 0x01), but when flashing programs or performing deep diagnostics, it needs to switch to Non-default Session (e.g., Programming Session 0x02). At this point, the ECU will start theS3 Timer, and if there is no communication before timeout, it will automatically revert to the default session!
-
Core Knowledge Points:
-
Timeout Mechanism: If there are no diagnostic requests within the S3 timer (usually a few seconds to tens of seconds), the ECU automatically “downgrades” to the default session.
-
Keep Alive Magic 0x3E Service: Periodically sending
<span>0x3E 00</span>(Tester Present) can reset the S3 timer, maintaining a high privilege session! Message Example:<span>Request: 02 3E 00 55 55 55 55 55</span><span>Response: 02 7E 00 55 55 55 55 55</span>Tips: The sending frequency must be less than the S3 timeout! -
Session Switching Practice
-
P2=50ms: The maximum time for the ECU to respond to requests
-
P2=500ms*: If NRC 0x78 (Processing) is returned, the operation must be completed within this time
-
Request to enter Programming Session:
<span>02 10 02 55 55 55 55 55</span> -
Positive Response Example:
<span>06 50 02 00 32 01 F4 55</span>
2. ECU Reset Service (0x11): The Secret of One-Click Restart
Want to make the ECU “restart” to its initial state? SID 0x11 supports multiple reset modes, automatically returning to the default session after reset, ensuring system safety!
4 Types of Reset
| Sub-function | Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01 | Hard Reset | Simulates power-off restart, clears RAM and some NVM data |
| 0x02 | Key Power-Off Reset | Retains NVM data, clears RAM |
| 0x03 | Soft Reset | Only resets software state, does not affect stored data |
| 0x04 | Fast Power-Off Enable | Enters low power/sleep mode (not supported by all ECUs) |
CAN Message Example Analysis
1. Request Reset: 0x02 11 01 55 55 55 55 55: Request Hard Reset. 0x02 11 03 55 55 55 55 55: Request Soft Reset. Frame Structure:[Length] [SID] [Sub-function] [Padding].2. ECU Positive Response: 0x02 51 01 55 55 55 55 55: Confirm Hard Reset. 0x02 51 03 55 55 55 55 55: Confirm Soft Reset. Frame Structure:[Length] [SID + 0x40] [Sub-function] [Padding].
- Note: Unlike 0x10, 0x11 positive responses do not require additional parameters (like P2/P2*).
3. ECU Negative Response: 0x03 7F 11 12 55 55 55 55: Sub-function not supported.
0x12: NRC, indicating the current reset type is not supported.
3. UDS Diagnostic Session Security Jump Control ModelSession mode transitions follow these rules: The default session mode allows direct conversion to the extended session mode, but cannot jump directly to the programming session mode. To enter the programming session mode, one must first switch from the default session mode to the extended session mode as a transition. Conversely, when in programming session mode, one cannot directly return to the extended session mode, but must downgrade to the default session mode. Additionally, when an ECU hardware reset or S3 communication timer timeout occurs, the system will forcibly reset to the default session mode as the base state.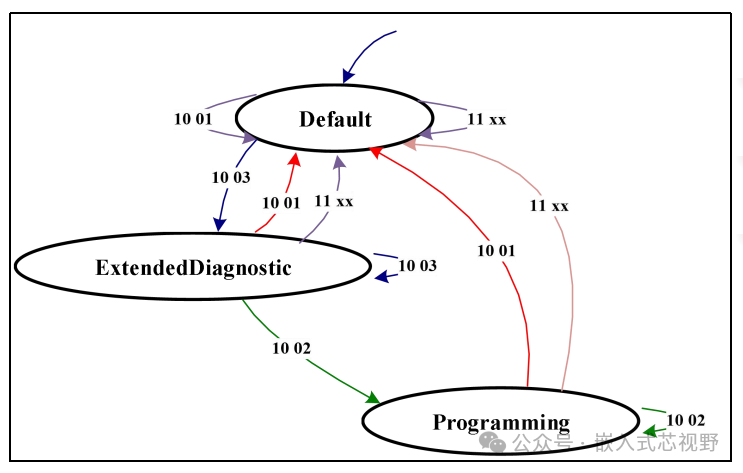
1. Session Mode Definitions
-
Default Session Mode (0x01): The initial state after ECU startup, only supports basic diagnostic services (e.g., reading DTCs, resetting ECU).
-
Extended Session Mode (0x03): Provides higher privilege diagnostic functions (e.g., writing memory, adjusting parameters), requires security validation to activate.
-
Programming Session Mode (0x02): Specifically for ECU software flashing (e.g., firmware updates, calibration data writing), requires strict security certification.
2. Normal Session Transition Process
-
Step 1: Default Session → Extended Session
-
Trigger Condition: Send diagnostic service
<span>0x10</span>(Session Control), sub-function<span>0x03</span>(Extended Session). -
Response Rules:
-
If the ECU accepts the request, it returns a positive response
<span>0x50 0x03</span>and starts the S3 Timer (to maintain the session’s active state). -
If the S3 timer times out without receiving subsequent requests, the ECU automatically reverts to the default session.
-
Step 2: Extended Session → Programming Session
-
Prerequisite: Complete Security Access (0x27) in the extended session, verified by key.
-
Trigger Condition: Send
<span>0x10</span>service, sub-function<span>0x02</span>(Programming Session). -
Response Rules:
-
Upon successful activation, the ECU enters the programming session and starts a new S3 Timer.
-
Only programming-related services are allowed (e.g.,
<span>0x34</span>request download,<span>0x36</span>transfer data). -
Step 3: Programming Session → Default Session
-
Direct Transition: Send
<span>0x10</span>service, sub-function<span>0x01</span>(Default Session). -
Forced Reversion: If the programming operation is completed or an error occurs, the ECU can actively reset to the default session.
-
Prohibited Transition Rules
-
The default session cannot directly connect to the programming session: Must transition through the extended session.
-
The programming session cannot return to the extended session: Must first downgrade to the default session, then re-enter the extended session.
3. Abnormal Scenarios and Session Reset
-
ECU Hardware Reset: In any session mode, ECU reset (e.g., power-off restart) will forcibly return to the default session.
-
S3 Timer Timeout:
-
If valid requests are not continuously sent in the extended/programming session, the ECU will automatically reset to the default session after S3 timeout.
-
-
Communication Interruption: Bus silence exceeding the specified time (dependent on S2 timer) will trigger session fallback.
4. Security Mechanisms
-
Security Access: Extended and programming sessions require the 0x27 service to complete seed and key exchange verification.
-
Permission Levels: Programming sessions typically require a higher-level key (e.g., Level 2), and may enable additional write protection mechanisms (e.g., 0x31 service control routines).