
Empowering Real-Time Response and Decision-Making in Public Transport with Edge Computing Technology

Public transport information systems are evolving towards greater intelligence. As a computing paradigm, edge computing provides new technical support for public transport information systems, enabling real-time response and decision-making, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and service levels.
1. Architecture and Advantages of Edge Computing

Edge computing refers to the decentralization of computing, storage, and networking resources from the cloud to the network edge, closer to data sources or users, providing real-time and efficient data processing and services. The architecture of edge computing consists of three layers: the terminal layer, the edge computing layer, and the cloud computing layer, as illustrated in the diagram below (image source: internet):
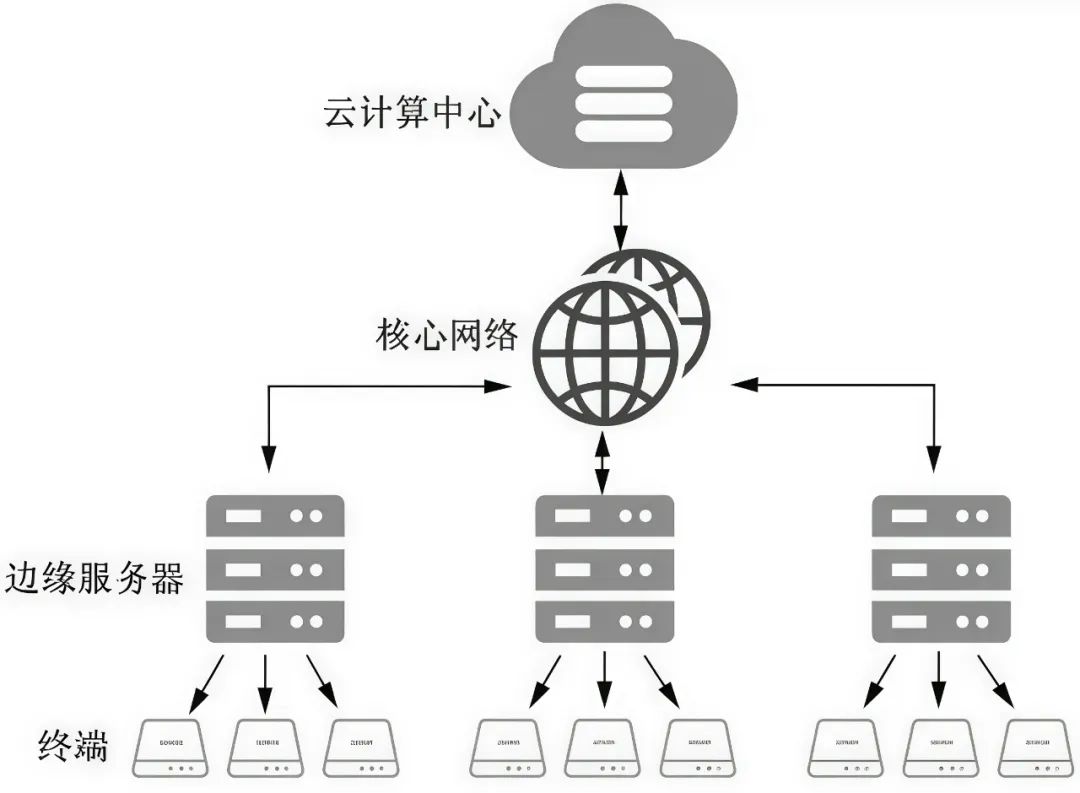
Compared to traditional cloud computing models, edge computing has the following advantages:
Low latency: Data processing occurs at edge nodes close to the data source, reducing data transmission delays and meeting the real-time requirements of public transport systems.
Low bandwidth: Edge nodes can process large amounts of data locally, alleviating network transmission pressure and improving data processing efficiency.
High reliability: Edge computing can mitigate the impact of network interruptions on systems, enhancing system reliability and stability.
These advantages make edge computing an ideal choice for empowering real-time response and decision-making in public transport, effectively addressing issues of timeliness, bandwidth, and reliability faced in public transport information systems.

2. Applications of Edge Computing in Public Transport

Edge computing technology has broad application prospects in the field of public transport information systems, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Vehicle Safety
Edge computing technology provides comprehensive safety guarantees for public transport through real-time data processing and low-latency responses. In Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), edge devices analyze camera data in real-time to complete lane departure warnings or automatic emergency braking, significantly reducing collision risks. It can also dynamically perceive driver behavior and work status, monitor and analyze facial features, and accurately identify fatigue or distracted driving, triggering localized warnings to support safe operation and ensure vehicle safety.
2. Intelligent Dispatching
Edge computing significantly enhances the accuracy and efficiency of public transport intelligent dispatching through localized real-time data processing capabilities. In terms of real-time vehicle positioning, onboard edge devices accurately locate vehicle positions and calculate arrival times. For managing the distance between vehicles, it dynamically calculates the spacing and relative speed of adjacent vehicles, automatically coordinating speed or triggering warnings when safe distances are insufficient. In response to sudden road conditions, it uses image recognition to monitor congestion, accidents, and other anomalies in real-time, pushing optimal detour paths and conducting real-time dispatching. Additionally, edge computing supports multi-vehicle collaborative dispatching; when a vehicle malfunctions, the system automatically calculates the optimal connection path for surrounding vehicles, ensuring overall network stability. Through collaborative computing of distributed edge nodes, the public transport dispatch system achieves an intelligent upgrade from “passive response” to “proactive prediction.”
3. Cabin Occupancy Rate
Edge computing technology provides an efficient solution for real-time monitoring of bus cabin occupancy rates. In-cabin monitoring devices can collect and analyze passenger data in real-time, using lightweight AI algorithms to quickly identify key information such as the number of standing passengers and seat occupancy. The localized processing of edge computing avoids the bandwidth pressure of uploading video data to the cloud while ensuring timely responses. The dispatch center can monitor the occupancy status of each cabin in real-time, and when the occupancy rate is too high, the system automatically sends alerts to the dispatch platform. Furthermore, by combining historical passenger flow data, edge nodes can predict passenger flow trends for the next period, providing data support for dynamically adjusting departure intervals, thus enhancing operational efficiency while ensuring passenger comfort and safety. This technology has transformed the approach from passive statistics to proactive control, making public transport operations more efficient and user-friendly.

3. Future Challenges of Edge Computing

Despite the broad application prospects of edge computing technology in public transport information systems, it also faces several challenges:
Deployment and management of edge nodes: The deployment and management of edge nodes require significant investment in funds and resources, making efficient and low-cost management a challenge.
Data security and privacy protection: The data processed by edge computing nodes involves passenger privacy and traffic safety, making data security and privacy protection a critical concern.
Standardization and normalization: Currently, there is a lack of unified standards and norms in the field of edge computing, which restricts the application and promotion of edge computing technology.

4. Conclusion

Edge computing technology, by empowering public information dissemination, vehicle-road collaboration, intelligent video analysis, and autonomous driving, can provide passengers with more convenient, efficient, and safe travel services, driving the public transport industry towards greater intelligence and real-time capabilities. As technology matures, application scenarios expand, and standardization efforts progress, edge computing technology will play an increasingly important role in public transport information systems, providing strong support for building a more intelligent, efficient, and safe public transport service system.
end
Source: Jinan Urban Transportation Research Center

Click and hold to scan the QR code
Follow “Urban Public Transport”
Public transport colleagues are watching
