
Which is better, ASIC or FPGA? What are the differences in their processes? Is it necessary to switch from FPGA to ASIC design? Various questions about ASIC and FPGA are frequently seen online.
ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) refers to integrated circuits designed and manufactured to meet specific user requirements and the needs of specific electronic systems.
FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) is a product that has developed further from programmable devices like PAL (Programmable Array Logic) and GAL (Generic Array Logic). An FPGA is a chip that can reconfigure its circuits, a hardware reconfigurable architecture that allows its application scenarios to be changed at any time through programming.

Image source: Internet
Similarities and Differences Between FPGA and ASIC
Similarities: Essentially, both are chips. FPGA development strictly follows the ASIC development process, and both are in the direction of integrated circuits. Generally speaking, any electronic hardware product that can be made with FPGA can also be made with ASIC, meaning that the two different channels can achieve the same functionality.
Differences: The former involves downloading the completed netlist or circuit code into the FPGA to form a gate array. When problems are discovered during product delivery or usage, patches can be reapplied, and versions can be updated to continue functioning normally. In contrast, ASIC must go through the process of tape-out to become a chip, which has higher requirements! The design process is very lengthy, usually taking about a year, requiring multiple verification engineers. Once issues arise later, they can only be resolved by re-manufacturing, and bugs can be numerous or severe, potentially leading to a complete recall and even financial loss risks.
In the design process of ASIC, FPGAs are often used for prototype verification. Completing FPGA verification can be said to accomplish 50-70% of the entire ASIC process.
Differences in FPGA and ASIC Design Processes
FPGA design has the functionality of reconfigurable chips, while ASIC design generally has fewer reconfigurable chip functionalities.
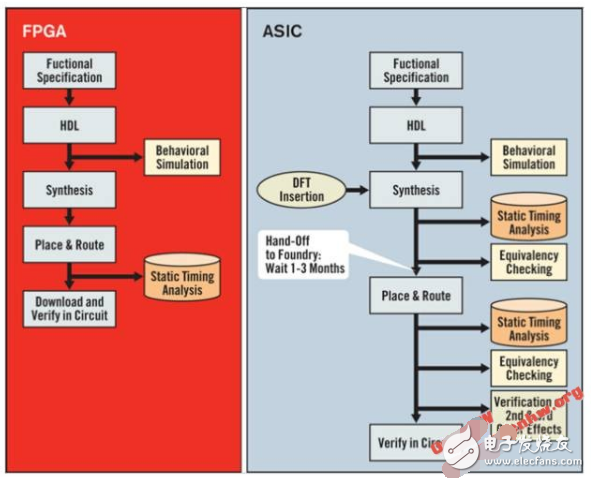
FPGA is also known as the “universal chip,” which contains a large number of configurable units (LUT-based slices), configurable IPs (DSP, CMT, PCIe, Serdes, etc.), and configurable memory. Users can download their designs onto FPGA chips to quickly realize their functionalities and rapidly build demo systems, resulting in a short design cycle.
ASIC chips must first go through complex design processes such as code design, synthesis, and backend, followed by several months of production processing and packaging testing, before the chips can be used to build systems. The complexity arises because, in addition to ensuring functionality, various power consumption and area requirements must be met, resulting in a long overall design cycle.
Which Design to Choose in Different Situations
Considering time constraints, the ASIC design process is lengthy, taking about a year, while FPGA design can generally be completed in a few weeks or a couple of months. If quick results are desired, choosing FPGA design is preferable.
In terms of performance, ASIC-designed chips are better, being fully customized and more stable. ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) itself is a type of dedicated integrated circuit chip. To illustrate, if a movie company wants to create a model of Yoda, option one would be to buy several boxes of LEGO blocks and build it quickly. Option two would be to contact a mold factory, draw blueprints, and mass-produce it. FPGA design produces a Yoda made from blocks, while ASIC design produces a finalized Yoda, which is more stable.

Regarding design costs, ASIC design typically costs millions to billions, but if the production volume is high, the cost per ASIC chip can be low, with particularly cheap chips costing around $2; whereas FPGA design can sometimes be completed for several hundred dollars, but again, if production volume is high, the per-unit cost remains significant. Therefore, for small batch production and usage, FPGA design is advantageous, while for large batch production and usage, ASIC is advantageous.
In fact, many domestic companies initially used FPGA designs when market development was still unstable; only after establishing a certain market and risk resistance did they start using ASIC designs.
Should FPGA Engineers Transition to ASIC Design Engineers?
Although the current job market for FPGA engineers is good, many are considering transitioning to ASIC design engineers.
On one hand, there are relatively many FPGA engineers in China, as many can develop their own projects by purchasing an FPGA board for a few thousand dollars during their studies, creating their own training environment. In contrast, ASIC design engineers are relatively scarce, as schools currently cannot establish a mature training environment for IC design, leaving many lacking knowledge in this area. Therefore, the choice between doing something that most people can do or something that only a few can do is clear.
On the other hand, considering the current situation, another straightforward point is that ASIC design generally offers higher salaries than FPGA design, with a significantly higher ceiling.
Those who originally worked with FPGA are usually familiar with Verilog, which provides a significant advantage when transitioning to ASIC, especially at a young age during their prime learning period, as they can learn quickly with just a little effort.
Scan to listen for free, and consult IC courses!




