Special Topic Directory
(Host/Reporter Jiang Hong Ren Fang)
-
Analysis of Trends in Warehousing and Logistics Technology Development
-
Development Path and Future Trends of Automated Warehousing Technology in China
-
Development of Warehousing Automation Technology and Innovative Practices of Kunming Ship Logistics
-
Da Fu: Technological Integration and Innovation Exploring Broader Application Scenarios —— Interview with Wang Lei, Deputy Director of the North China Sales Department of Da Fu (China) Logistics Equipment Co., Ltd.
-
Dematic: Insight into Changing Customer Needs and Keeping Pace with Technological Development—— Interview with Lü Gongdong, Director of Solution Development Department of Dematic China
-
Megvii: Empowering Logistics Systems with AI Algorithms —— Interview with Xu Qingcai, Senior Vice President of Megvii Technology Co., Ltd.
-
Fubos: Making Logistics Systems Easy to Manage—— Interview with Zhu Li, General Manager of Fubos (Shanghai) IoT Technology Co., Ltd.
-
Smart Logistics Technology Accelerates Transformation within Four Walls—— Interview with Yang Wei, CEO of Shanghai KuaiCang Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd.
Article by: Chairman of Beijing Wuqiang Technology Co., Ltd.
Yin Junqi
China’s automated warehousing technology has gone through a development process from “nothing to something”, “low-end to high-end”, “simple to complex”, “single to diversified”, and “local to global”. From the perspective of industry application, China’s warehousing logistics technology has transitioned from the stage of “moderate automation + high informationization” to “high automation + high informationization”, and has begun to evolve towards intelligence. From the perspective of technological development, larger scale, higher flexibility, higher automation level, higher efficiency, and lower cost are the development trends. The advancement of all technologies aims to improve service levels as a common goal.

Yin Junqi
Chairman of Beijing Wuqiang Technology Co., Ltd.
From the perspective of technological development, larger scale, higher flexibility, higher automation level, higher efficiency, and lower cost are undoubtedly the development trends. Automation, unmanned operation, and intelligence have become the overall trend of development.
1. Overview
Automated warehousing technology refers to the automation technology and information technology related to warehousing operations. Warehousing logistics technology spans multiple disciplines and forms its own system, but there is no clear definition of its classification both domestically and internationally. Due to the late development of logistics technology in China, it was initially classified as material handling technology according to the definition of the European Material Handling Federation (FEM). With the rapid development of warehousing logistics technology and the increasing market share, it is necessary to reclassify warehousing logistics technology.
If we classify technology and equipment solely based on warehousing logistics activities, although there are overlapping parts and the boundaries are not obvious, it is easier to understand.This article temporarily classifies it into several major categories: access technology (storage technology), conveying and handling technology, picking technology, checking and packaging technology, sorting technology, shipping technology, and information technology, as shown in Table 1.
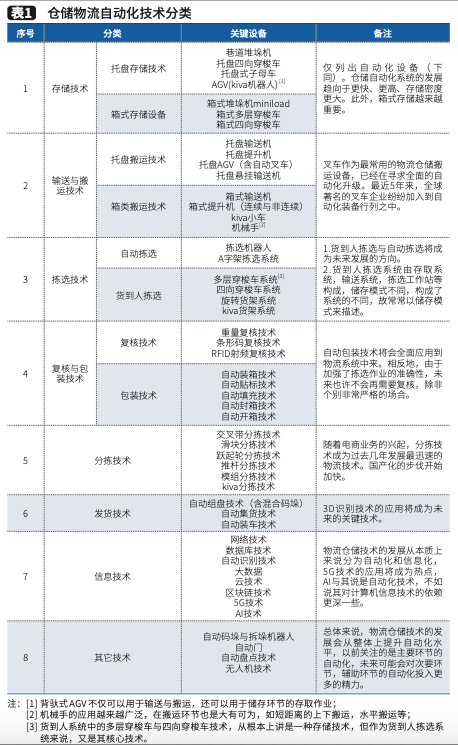
These technologies are not all of the automated warehousing technology; this article merely lists several that readers are familiar with as a basis for discussion.
2. The Development Process of Automated Warehousing Technology in China
General literature suggests that the development of logistics automation technology in China began in the mid-1970s, which is reasonable.A typical event was the construction of the first automated storage and retrieval system and the development of the first automatic sorting machine.Although research on automated warehousing technology has never stopped in China for over 20 years since then, and significant progress has been made in landmark products such as automated storage and retrieval technology and conveyor sorting technology, the variety of products, product quality, and innovation of new products have been unsatisfactory.This is partly due to the backwardness of China’s basic industry, which cannot provide automated products on its own; on the other hand, the lagging development of the national economy and low labor costs have led to insufficient market demand.Only limited industries, such as chemicals, automobiles, and aviation, have demanded automated warehousing systems.
Around 1998, with companies like Lenovo, Haier, and Kunming Cigarette Factory starting to build automated logistics systems, the development of logistics technology in China began to accelerate, achieving a qualitative leap in warehousing logistics technology marked by automated storage and retrieval systems.Entering the 21st century, with the deepening of reform and opening up and China’s successful entry into the WTO, the national economy has made rapid progress, and the development of automated warehouse technology has also welcomed its spring.
Overall, China’s automated warehousing technology has undergone a development process from “nothing to something”, “low-end to high-end”, “simple to complex”, “single to diversified”, and “local to global”.
From Nothing to Something:The earliest research and development focused on stackers and sorting machines, then expanded to AGVs, miniloads, Kivas, and many other products. From imitation to independent research and development, the “existence” problem has gradually been solved, developing into today’s flourishing situation.
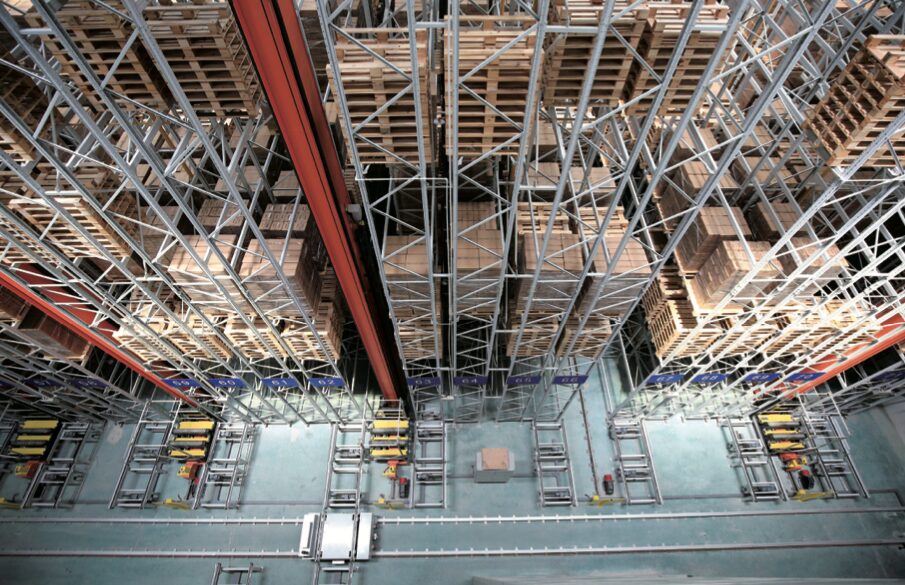
From Low-end to High-end:Taking stackers as an example, the earliest stackers used dual-speed motors and single-board control, gradually progressing to variable frequency motors and PLC control, up to today’s high-speed stackers using servo motors. The travel speed of stackers has also increased from the initial 20m/min to 60, 80, 120, 160, 200, 240m/min, and may go even higher in the future. The positioning technology of stackers has undergone multiple changes, from hole positioning, positioning piece positioning, to laser positioning, and now to barcode positioning. The performance parameters and reliability parameters of stackers have been significantly improved. Other products, such as conveyors, sorting machines, and AGVs, are no exception.
From Simple to Complex:What is called simple refers to the simplicity of product form, performance, and composition; on the other hand, it refers to the simplicity of the system and workflow. The design of logistics systems is also like this. Earlier designs might have been just a single storage system, but now, it is not uncommon for China to design large automated logistics centers exceeding 100,000 square meters, and our planning and integration capabilities for large logistics centers are increasing day by day, even comparable to world-class enterprises, demonstrating strong competitiveness, which was previously unimaginable.
From Single to Diversified:Products not only appeared simple but also reflected a single form and specification, with poor adaptability. The richness of products actually reflects the level of technological development in the industry. Up to now, the automated warehousing equipment produced in China can almost cover the entire product series, which is the best example of the level of development of China’s warehousing logistics technology. Especially in recent years, research on goods-to-person picking, robots, Kivas, drones, and 3D recognition has rapidly elevated China’s logistics technology level to a new height.
From Local to Global:The application of logistics automation technology did not initially involve all links. The earliest research applications were in storage and conveying links, as these are the most basic links, gradually developing to picking and distribution links, and later focusing on loading, unloading, and packaging links. Now, technologies such as automatic de-stacking, automatic palletizing, and automatic loading based on 3D technology have attracted industry attention.
The market demand is strong, and the industry is full of talent, which is the most accurate evaluation of China’s current automated warehousing industry.Since 2015, with large capital entering the market, China’s automated warehousing industry has shown unprecedented prosperity, with a large number of high-quality talents pouring in and many emerging enterprises rapidly rising, leading to a rapid improvement in logistics technology levels.
3. The Gap with World Advanced Levels
Despite significant progress in research and application of China’s warehousing logistics technology, and having surpassed the world in certain industry sectors such as e-commerce and tobacco, it can be said that through the efforts of logistics professionals, China’s warehousing logistics technology level is among the industries with the smallest gap from world advanced levels.This mainly depends on two key factors:Firstly, the rapid improvement of China’s manufacturing level and the continuous rise of market demand for warehousing logistics; Secondly, the entire industry is highly competitive, lacking monopolistic enterprises.
However, from an objective perspective, there is still a significant gap between China’s warehousing logistics technology and world advanced levels, and it is difficult to fundamentally change this situation in the short term.In summary, the gaps can be outlined as follows:
1. Basic Research and Core Components
Key components include motors, reducers, PLCs, control components, automatic identification devices, and robot bodies.
The motor reducer is one of the key components of logistics equipment. Although domestic motor reducers have been in use for over 20 years, the results have not been ideal, leading to the current situation where key equipment’s motor reducers mainly use German products.This situation will continue for a long time.Related products include bearings, sliding contact lines, flat cables, toothed belts, and other supporting products.
The application of PLCs and control components is dominated by brands such as SIEMENS, with domestic brands almost negligible, and the gap cannot be measured by time.
Automatic identification devices include laser ranging devices, laser navigation devices, barcode scanning devices, optical lenses, photoelectric switches, cameras, RFID systems, 3D cameras, and a series of products and technologies.These products and technologies are becoming increasingly important in logistics systems, with products from Europe, America, and Japan still in absolute control, and domestic brands show no hope in the short term.
Robots are increasingly used in logistics systems, but research on robot bodies is still in its infancy, with brands like ABB, KUKA, and Yaskawa holding absolute advantages.
In addition, it should be noted that beyond product performance, the inertia of the industry and competition dynamics will lead to these gaps not being bridged in the short term, entering a vicious cycle.
2. Performance Indicators of Key Equipment
Key equipment such as AS/RS (Automated Storage and Retrieval System), sorting machines, AGVs, etc., although the possibility of full domestic replacement has emerged, the gap remains obvious.The largest gaps are in equipment maturity and diversity.The root cause of this outcome is that many domestic companies have a relatively short production time, insufficient R&D funding, lack of specialized talent, and products have not undergone rigorous testing and practical application verification.Time, opportunity, and the methodology of research and development have all become important factors constraining technological progress.
Taking sorting machines as an example, although domestic cross-belt sorting machines have several decades of history, the key performance indicators—reliability, stability, noise, etc.—have never been comparable to imported equipment.As a result, large airport baggage systems and parcel sorting systems are almost monopolized by foreign products.Other products, such as stackers, miniloads, and shuttle vehicles, are in similar situations.
Some key equipment has only been researched in laboratories, has not been finalized, and has not undergone fatigue and reliability testing, meaning there is still a long way to go before mass production and large-scale application, with many difficulties and problems ahead.
Furthermore, many domestic companies are still young and lack experience, leading to significant gaps in design, production processes, materials, key components, control systems, testing methods, etc., especially in terms of talent and experience, which cannot be compensated for in the short term.
3. Innovation and Invention of Key Technical Equipment
Almost none of the key technologies and equipment in logistics systems are original innovations by Chinese individuals.From traditional equipment such as shelves, pallets, and forklifts to automated equipment like automated storage and retrieval systems, sorting machines, AGVs, shuttle vehicles, robots, drones, and technologies such as lasers, photoelectric switches, RFID, motor reducers, toothed belts, 3D recognition technology, and automatic navigation technology, these concepts and products are almost all not original innovations by Chinese individuals.Although these technologies have not been around for long, we have every opportunity to propose our own innovative ideas, but we have not.This is undoubtedly a huge gap.
In light of the above gaps, we must face reality and start from the basics.We must think creatively and continuously innovate; one day there will be significant innovations and inventions from China.
Innovation requires accumulation and inspiration, and more importantly, a profound understanding of demand.Logistics technology is highly practical; addressing this demand requires time, funding, patience, and open-mindedness.
4. World-renowned Enterprises and Global Competitiveness
An important indicator of the technological level of a company or product is its market share and competitiveness in the international market.Unlike the large influx of European, American, and Japanese equipment into China, our logistics equipment, while having some competitive advantages domestically, still lacks the capability to compete with world-class enterprises in the international market.On one hand, brand effect plays a role, but more importantly, it is the technological level and performance of the products.Only some low-end products, such as shelves, conveyors, and forklifts, have some opportunities; other products are still far from it.
Another measure is the scale of enterprises. Up to now, there has not been a single integrator or manufacturer in China whose revenue can enter the top ten in the world (excluding forklifts).This also indicates that the scale of our logistics technology and equipment enterprises is still too small, and the industry concentration is not high, leading to a fragmented market, all of which contribute to the existing gaps.
The above four aspects are the areas with significant gaps; in addition, the issue of standardization is also a fundamental indicator reflecting the industry’s huge gap. Although China has issued many logistics-related standards, the authority, technical level, and acceptance of these standards are obviously insufficient and need further efforts.
5. Development Trends of Warehousing Logistics Technology

From the perspective of industry application, the development of warehousing logistics technology in China has transitioned from the stage of “moderate automation + high informationization” to the stage of “high automation + high informationization” and has begun to evolve towards intelligence.This is the general direction.
From the perspective of technological development, larger scale, higher flexibility, higher automation level, higher efficiency, and lower cost are undoubtedly the development trends.Automation, unmanned operation, and intelligence have become the overall trend of development.
Overall, the development of logistics technology will experience significant breakthroughs in the following areas:
1. Comprehensive Application of Flexible Technology and Modular Technology
Flexible technologies in warehousing logistics, such as AGVs, Kivas, four-way shuttle vehicles, mother-child vehicles, and 3D palletizing technology, may also include walkable robots and drones in the future.Some are highly flexible, while others are semi-flexible (with differences in the indicators involved in complete flexibility, such as routes not being adjustable).The main characteristics are:(1) Their paths are non-fixed;(2) The number of devices can be increased or decreased;(3) The purposes of the devices are diverse.For example, the earliest AGV systems were only used for material handling, while today’s AGVs (including Kivas) can be used for handling, conveying, storing, and picking.In the future, AGVs are likely to widely replace forklifts and conveyors.
The “units” based on turnover boxes and pallets will maintain a consistent form throughout the entire supply chain system, enabling rapid connections and greatly improving warehousing logistics efficiency.The establishment of a shared system for carriers is only a matter of time.
2. Goods-to-Person Picking Technology will Become the Mainstream Technology for Picking
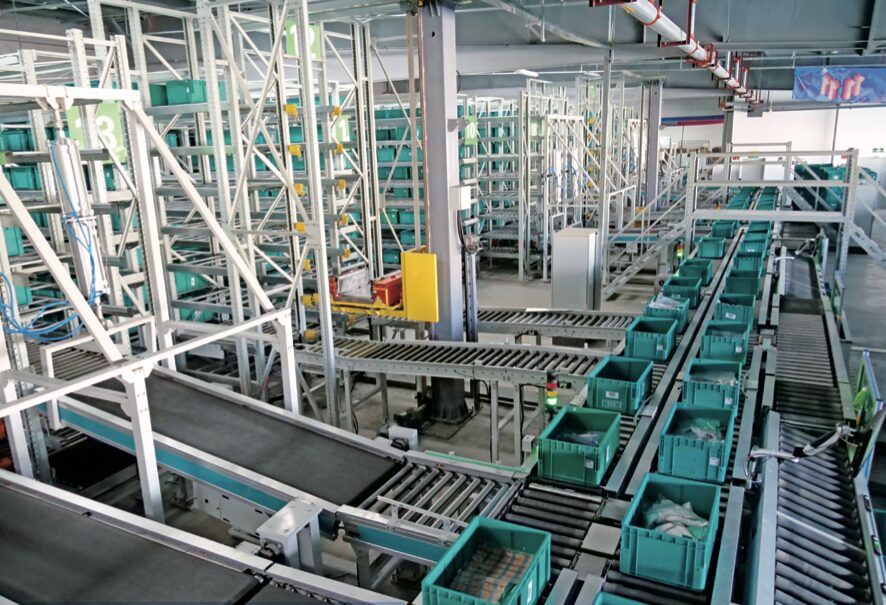
Goods-to-person picking (which may in the future become goods-to-robot picking) technology has gained widespread attention and rapid development in recent years, but it has not yet reached a universal level.This technology, with its immense advantages, will play a significant role in the picking process (not limited to just picking).Especially, various forms of shuttle vehicles and Kivas have made tremendous progress in access technology.Kiva robots have been recognized as one of the most widely used automation technologies in picking systems, leading the trend of global logistics technology development.Shuttle vehicle technology, including multi-layer shuttles and four-way shuttles, is also one of the fastest-developing technologies in recent years, playing a key role in large distribution centers, especially in e-commerce distribution centers.
3. Natural Navigation and 3D Recognition Technology will be Widely Applied in Logistics Systems
Natural navigation technology is widely used in autonomous driving technology and is a superior navigation technology compared to laser navigation.Kiva has applications in various types of warehousing logistics systems, including e-commerce.However, Kiva mainly uses QR code + magnetic strip navigation technology, which is a relatively low-cost navigation technology, but its drawback is poor flexibility.Natural navigation technology completely overcomes the previous need for predefined systems and environments, allowing it to simulate a car driving on an unfamiliar road.Of course, since warehouses are closed systems, the standardization is much higher than that of roads, thus reducing the difficulty of automatic navigation significantly.
The importance of 3D recognition technology lies in its ability to solve spatial positioning problems, making automatic picking, automatic palletizing and de-palletizing, and automatic loading and unloading possible. It is foreseeable that the comprehensive application of 3D technology will have a revolutionary impact on warehousing logistics technology.
4. Traditional Technologies are No Longer What They Used to Be
For instance, AS/RS systems will see significant breakthroughs in height, speed, etc., while the scale of storage systems will continue to grow.Additionally, the technological revolution in the front area of warehouses will also undergo significant changes, such as AGVs replacing forklifts and conveyors, which will be a major breakthrough in design philosophy.Future AS/RS systems will become more flexible, and the systems will become simpler.
Miniload technology will see a larger market.As the proportion of small-quantity business increases, box-based operational systems will gain more attention.The same applies to shuttle vehicles.
With the continuous maturity of AGV technology, the transformation of forklifts into automated forklifts has enormous market potential.
As the demand for cold chain markets increases, the need for automated systems suitable for environments of -18°C or even lower will grow, and the technology in this area is currently very scarce.
Moreover, high-speed sorting systems, automatic packaging systems, etc., will also see greater development.
5. AI Technology will be Fully Applied
A variety of robots participating in logistics operations across different segments will trigger a revolution in logistics operations.For example, the application of bipedal robots in various logistics segments will play an unexpected role in the loading and unloading operations of box-type trucks that are currently difficult to handle.The next few decades will mark the period when AI transitions from concept to practical application.A significant feature of intelligent logistics is the comprehensive application of AI.Regarding the huge driving force of AI technology on society and logistics technology, all current imaginations and predictions may be overly conservative; we can only glimpse the beginnings and cannot break through the vast imaginative space.
In summary, higher storage efficiency, faster operational efficiency, more accurate picking operations, and easier operations are the goals pursued by logistics systems.Fully utilizing space, improving logistics operational efficiency, and enhancing customer service experiences are the underlying motivations for technological development.All technological advancements aim to improve service levels as a common goal.