Hi everyone! This is IT Home, and I am Lang Ge.
Recently, devices supporting Wi-Fi 7 have been emerging one after another.
Xiaomi previously released a new product called Xiaomi Router 7000. Although it did not explicitly state support for Wi-Fi 7, customer service informed us that the feature will be supported through a future OTA software update.
Meanwhile, the established router manufacturer H3C has also launched a new Wi-Fi 7 AP device, with actual speeds exceeding 10 Gbps. TP-LINK also released its flagship Wi-Fi 7 router – the Lighthouse Router – at the end of March, featuring a tri-band 12-stream design, with dual 10G + four 2.5G ports, making it a luxurious configuration.
New Wi-Fi 7 routers are emerging one after another, and terminal devices are also gradually starting to support Wi-Fi 7.
For instance, Lenovo’s flagship gaming laptop, the Savior 9000X, is equipped with the MediaTek Filogic 380 Wi-Fi 7 wireless card, supporting dual concurrent 2×2, with a maximum transmission speed of 6.5 Gbps.
There are also several new smartphones supporting Wi-Fi 7, such as the Xiaomi 13 and Redmi K60 released by Xiaomi at the end of last year, which will later receive Wi-Fi 7 support through OTA updates.
This year’s flagship phones, such as the vivo X90s, also support the new Wi-Fi 7 standard.
Some of you might be wondering, what advantages does Wi-Fi 7 have?
To discuss the advancements of Wi-Fi 7, we need to first talk about its predecessors.
The previously commonly used protocol IEEE 802.11g had a data transfer speed of only 54 Mbps, which was inadequate to meet the connectivity needs of the many smartphones that had emerged at the time. Therefore, in 2009, the Wi-Fi Alliance introduced the IEEE 802.11n specification, also known as Wi-Fi 4.
Wi-Fi 4 employed MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology, using multiple transmit and receive antennas to enhance data transmission rates, and utilized space-time block coding to increase transmission range. This allowed routers to provide dual-band Wi-Fi signals at 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
Wi-Fi 4 achieved a maximum data transmission rate of 600 Mbps, which basically met the needs at that time, especially since 10 Mbps internet speeds were just beginning to become popular.
TP-LINK also released its flagship Wi-Fi 7 router – the Lighthouse Router – at the end of March, featuring a tri-band 12-stream design, with dual 10G + four 2.5G ports, making it a luxurious configuration.
New Wi-Fi 7 routers are emerging one after another, and terminal devices are also gradually starting to support Wi-Fi 7.
For instance, Lenovo’s flagship gaming laptop, the Savior 9000X, is equipped with the MediaTek Filogic 380 Wi-Fi 7 wireless card, supporting dual concurrent 2×2, with a maximum transmission speed of 6.5 Gbps.
There are also several new smartphones supporting Wi-Fi 7, such as the Xiaomi 13 and Redmi K60 released by Xiaomi at the end of last year, which will later receive Wi-Fi 7 support through OTA updates.
This year’s flagship phones, such as the vivo X90s, also support the new Wi-Fi 7 standard.
Some of you might be wondering, what advantages does Wi-Fi 7 have?
To discuss the advancements of Wi-Fi 7, we need to first talk about its predecessors.
The previously commonly used protocol IEEE 802.11g had a data transfer speed of only 54 Mbps, which was inadequate to meet the connectivity needs of the many smartphones that had emerged at the time. Therefore, in 2009, the Wi-Fi Alliance introduced the IEEE 802.11n specification, also known as Wi-Fi 4.
Wi-Fi 4 employed MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology, using multiple transmit and receive antennas to enhance data transmission rates, and utilized space-time block coding to increase transmission range. This allowed routers to provide dual-band Wi-Fi signals at 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
Wi-Fi 4 achieved a maximum data transmission rate of 600 Mbps, which basically met the needs at that time, especially since 10 Mbps internet speeds were just beginning to become popular. With the increasing demand from consumers for faster internet speeds, in 2013, the Wi-Fi Alliance launched Wi-Fi 5.
Due to the excessive number of devices using the 2.4GHz band and interference from devices like microwaves, the 5GHz band began to receive more attention.
The biggest technological innovation of Wi-Fi 5 was the expansion of the 5GHz band.
Wi-Fi 5 doubled the channel width from 40MHz to 160MHz, improved the modulation scheme from 64-QAM to 256-QAM, introduced MU-MIMO response mechanisms, and upgraded MIMO to 8 antennas, achieving a maximum data transmission rate of 3.5 Gbps.
However, a significant flaw of Wi-Fi 5 was that it only supported the 5GHz band. If routers wanted to support the 2.4GHz band, they needed to purchase Wi-Fi 4 chips separately, which was somewhat inconvenient.
With the increasing demand from consumers for faster internet speeds, in 2013, the Wi-Fi Alliance launched Wi-Fi 5.
Due to the excessive number of devices using the 2.4GHz band and interference from devices like microwaves, the 5GHz band began to receive more attention.
The biggest technological innovation of Wi-Fi 5 was the expansion of the 5GHz band.
Wi-Fi 5 doubled the channel width from 40MHz to 160MHz, improved the modulation scheme from 64-QAM to 256-QAM, introduced MU-MIMO response mechanisms, and upgraded MIMO to 8 antennas, achieving a maximum data transmission rate of 3.5 Gbps.
However, a significant flaw of Wi-Fi 5 was that it only supported the 5GHz band. If routers wanted to support the 2.4GHz band, they needed to purchase Wi-Fi 4 chips separately, which was somewhat inconvenient. This led to the emergence of Wi-Fi 6.
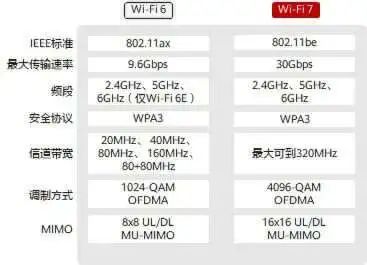
Compared to Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6 further expanded its applicability.
In terms of bandwidth, Wi-Fi 6 is identical to Wi-Fi 5, both offering 20/40/80/80+80/160MHz bandwidth.
However, Wi-Fi 6 covers both the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, adding a 2.4GHz band that accommodates both low-speed and high-speed devices.
In modulation, Wi-Fi 6 improved from 256-QAM in Wi-Fi 5 to 1024-QAM, increasing the maximum number of supported data streams from 4 to 8, and also utilized OFDMA technology along with uplink/downlink MU-MIMO, CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance), and TWT (Target Wake Time) mechanisms.
With this combination, Wi-Fi 6 achieved an astonishing data transmission rate of 9.6 Gbps, far exceeding the bandwidth provided by home wired networks.
This led to the emergence of Wi-Fi 6.
Compared to Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6 further expanded its applicability.
In terms of bandwidth, Wi-Fi 6 is identical to Wi-Fi 5, both offering 20/40/80/80+80/160MHz bandwidth.
However, Wi-Fi 6 covers both the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, adding a 2.4GHz band that accommodates both low-speed and high-speed devices.
In modulation, Wi-Fi 6 improved from 256-QAM in Wi-Fi 5 to 1024-QAM, increasing the maximum number of supported data streams from 4 to 8, and also utilized OFDMA technology along with uplink/downlink MU-MIMO, CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance), and TWT (Target Wake Time) mechanisms.
With this combination, Wi-Fi 6 achieved an astonishing data transmission rate of 9.6 Gbps, far exceeding the bandwidth provided by home wired networks. However, for users with high local area network traffic transfer needs, this speed still falls short, such as for transferring video materials or NAS backups, which place higher demands on routers.
At this point, the Wi-Fi Alliance introduced the Wi-Fi 6E technical specifications.
Wi-Fi 6E primarily adds a new frequency band, introducing the 6GHz band on top of Wi-Fi 6, expanding from 2.4GHz/5GHz to 2.4GHz/5GHz/6GHz.
The expansion of the frequency band effectively doubles the number of devices that can be accommodated, making it more user-friendly for commercial environments that require numerous connections.
However, the new 6GHz band of Wi-Fi 6E is not available for use in all countries; for example, in China, this band has been allocated for 5G base stations.
Additionally, Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E are not without flaws. A testing report from China Mobile indicates that while mainstream Wi-Fi 6 routers perform well in terms of throughput and interference resistance, their performance in OFDMA transmission delay and MU-MIMO transmission capabilities leaves much to be desired.
In other words, while mainstream Wi-Fi 6 routers have made significant progress in terms of interference resistance and signal attenuation, their capabilities in terms of latency and wall penetration are still insufficient.
However, for users with high local area network traffic transfer needs, this speed still falls short, such as for transferring video materials or NAS backups, which place higher demands on routers.
At this point, the Wi-Fi Alliance introduced the Wi-Fi 6E technical specifications.
Wi-Fi 6E primarily adds a new frequency band, introducing the 6GHz band on top of Wi-Fi 6, expanding from 2.4GHz/5GHz to 2.4GHz/5GHz/6GHz.
The expansion of the frequency band effectively doubles the number of devices that can be accommodated, making it more user-friendly for commercial environments that require numerous connections.
However, the new 6GHz band of Wi-Fi 6E is not available for use in all countries; for example, in China, this band has been allocated for 5G base stations.
Additionally, Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E are not without flaws. A testing report from China Mobile indicates that while mainstream Wi-Fi 6 routers perform well in terms of throughput and interference resistance, their performance in OFDMA transmission delay and MU-MIMO transmission capabilities leaves much to be desired.
In other words, while mainstream Wi-Fi 6 routers have made significant progress in terms of interference resistance and signal attenuation, their capabilities in terms of latency and wall penetration are still insufficient. This is why in the past two years, various router manufacturers have promoted various MESH networking functions, as Wi-Fi 6 routers’ wall penetration abilities have been somewhat lacking.
Of course, the Wi-Fi Alliance is actively addressing these pain points by rapidly rolling out the next generation of router protocols – Wi-Fi 7.
The biggest technical highlight of Wi-Fi 7 is its support for 320MHz channels, a channel that has never been used in home routers before.
Theoretically, a 320MHz channel allows devices to enjoy higher single-device throughput. Wi-Fi 6 can achieve a maximum of 160MHz, while Wi-Fi 7 doubles that, allowing connected digital devices to have greater wireless throughput capacity.
Even more impressive, Wi-Fi 7 allows the use of spectrum resources from 1GHz to 7.2GHz, with a focus on compatibility with the previous Wi-Fi standards’ 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, achieving a larger theoretical bandwidth through the expansive spectrum.
It is important to note that 1GHz is currently the most penetrating spectrum, and if it can truly be utilized, Wi-Fi 7 routers’ wall penetration capabilities may reach unprecedented levels.
This is why in the past two years, various router manufacturers have promoted various MESH networking functions, as Wi-Fi 6 routers’ wall penetration abilities have been somewhat lacking.
Of course, the Wi-Fi Alliance is actively addressing these pain points by rapidly rolling out the next generation of router protocols – Wi-Fi 7.
The biggest technical highlight of Wi-Fi 7 is its support for 320MHz channels, a channel that has never been used in home routers before.
Theoretically, a 320MHz channel allows devices to enjoy higher single-device throughput. Wi-Fi 6 can achieve a maximum of 160MHz, while Wi-Fi 7 doubles that, allowing connected digital devices to have greater wireless throughput capacity.
Even more impressive, Wi-Fi 7 allows the use of spectrum resources from 1GHz to 7.2GHz, with a focus on compatibility with the previous Wi-Fi standards’ 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, achieving a larger theoretical bandwidth through the expansive spectrum.
It is important to note that 1GHz is currently the most penetrating spectrum, and if it can truly be utilized, Wi-Fi 7 routers’ wall penetration capabilities may reach unprecedented levels. However, currently, relevant standards in our country are still being formulated, as some frequency bands of Wi-Fi 7 conflict with our 5G base stations. This is also why routers like Xiaomi need to later upgrade to Wi-Fi 7 via OTA, as the required chips have already been embedded, just waiting for our standards to be finalized.
How fast is Wi-Fi 7? Recently, Huawei deployed and tested Wi-Fi 7 APs at Southeast University, achieving astonishing speeds.
Under the testing of the Xiaomi 13 Pro, which supports the Wi-Fi 7 communication protocol standard, the single-terminal rate exceeded 4.3 Gbps. Compared to the Wi-Fi 6 environment, the Xiaomi 13 Pro’s rate increased by 100%, while the Apple 13 Pro’s rate increased by 300%.
In addition to the soaring speed, latency has also significantly decreased. Compared to the average latency of 10ms under Wi-Fi 6 protocol, the average latency of three phones under Wi-Fi 7 AP is below 4ms, which is great news for gamers!
However, currently, relevant standards in our country are still being formulated, as some frequency bands of Wi-Fi 7 conflict with our 5G base stations. This is also why routers like Xiaomi need to later upgrade to Wi-Fi 7 via OTA, as the required chips have already been embedded, just waiting for our standards to be finalized.
How fast is Wi-Fi 7? Recently, Huawei deployed and tested Wi-Fi 7 APs at Southeast University, achieving astonishing speeds.
Under the testing of the Xiaomi 13 Pro, which supports the Wi-Fi 7 communication protocol standard, the single-terminal rate exceeded 4.3 Gbps. Compared to the Wi-Fi 6 environment, the Xiaomi 13 Pro’s rate increased by 100%, while the Apple 13 Pro’s rate increased by 300%.
In addition to the soaring speed, latency has also significantly decreased. Compared to the average latency of 10ms under Wi-Fi 6 protocol, the average latency of three phones under Wi-Fi 7 AP is below 4ms, which is great news for gamers! Considering the explosive speed improvements of Wi-Fi 7, which have far exceeded current wired network speeds, it is estimated that the Wi-Fi 7 standard will be in use for a long time.
After all this, would you switch to a Wi-Fi 7 router?
Considering the explosive speed improvements of Wi-Fi 7, which have far exceeded current wired network speeds, it is estimated that the Wi-Fi 7 standard will be in use for a long time.
After all this, would you switch to a Wi-Fi 7 router?
-
IT Home – Huawei’s First Test of Wi-Fi 7 at Southeast University, Real Machine Single Terminal Rate Exceeds 4.3 Gbps
-
Internet of Everything – Differences Between WiFi4, WiFi5, and WiFi6
-
Super Energy Classroom – Brief Evolution of Wi-Fi
-
WiFine – Understanding the Differences Between Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 in One Image
Additionally, there are many popular contents recently, click the blue text below to view:
-
[Good Products] Fanxiang S790 4TB Solid State Drive 1098 yuan on sale, Deli Folding Desk Lamp 29 yuan on sale
-
Huawei HarmonyOS 4, quite capable!
-
Apple iPhone 15 launch event, finally reaching the “grand finale”
-
0-100 acceleration in 3.6s + 7 large screens, BYD’s million-dollar luxury car Yangwang U8 exposes Snapdragon 8+ configuration
Vote here:Like if you want to buy, click on “view” if you are indifferent ↓↓↓