Introduction by AliMei: What is network configuration? What are the different methods? Why is IoT network configuration technology so mixed and incompatible? This article will detail six methods of network configuration, including one-click configuration, device hotspot configuration, mobile hotspot configuration, Bluetooth configuration, router configuration, and zero configuration, summarizing and comparing the characteristics of each method and sharing insights on the future development of network configuration technology.
End of article benefit: Download the “AliOS Things Quick Development Guide” e-book for free!
1. Overview
-
Narrow Definition of Network Configuration: The process by which Wi-Fi devices obtain router information (SSID, password, etc.) and connect to the router.
-
Binding: The process of linking the user’s mobile app account with the device being configured.
-
Broad Definition of Network Configuration: Narrow definition + binding.
-
One-click Configuration
-
Broadcast Packet Length Method -
Multicast Address Method
-
Device Hotspot Configuration -
Bluetooth Configuration -
Mobile Hotspot Configuration -
Router Configuration -
Zero Configuration -
Others (such as voice configuration/camera QR code configuration, etc.)
2. Detailed Introduction
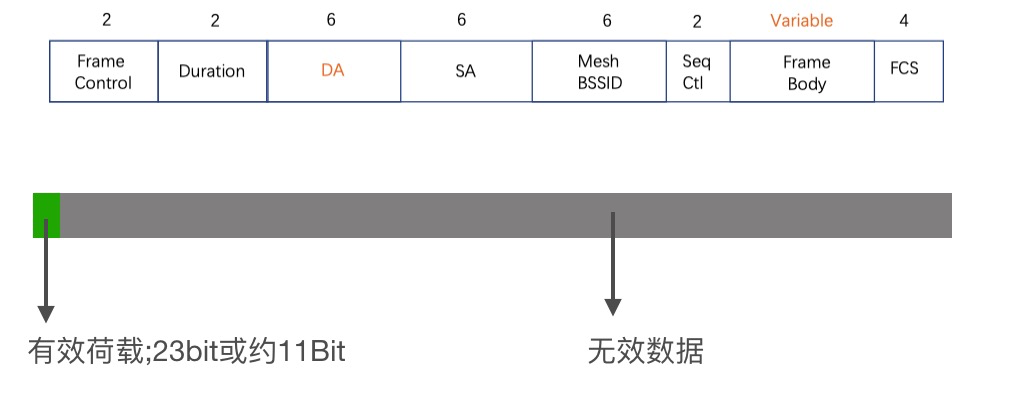
1. One-click Configuration
Process
Data Transmission Methods
-
Advantages:
-
Simple user operation, good experience (when successful).
-
Disadvantages:
-
Strict compatibility requirements for both mobile phones and routers. For example, some routers have broadcast/multicast forwarding disabled by default, preventing the device from receiving the forwarded packets; if the mobile phone connects to the router on the 5G frequency band, the 2.4G device cannot receive the packets, etc. These uncontrollable factors lead to overall poor compatibility and low configuration success rates.
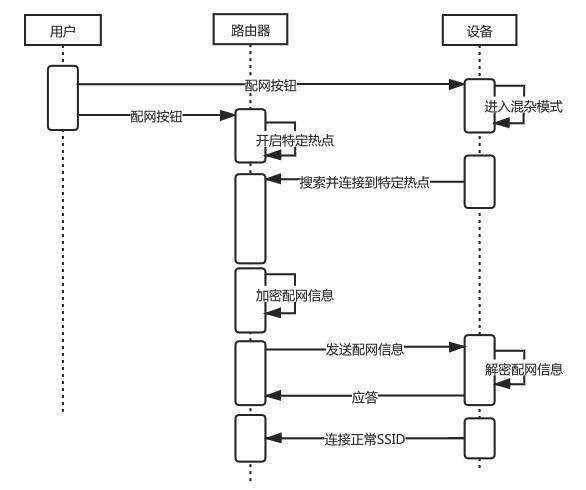
2. Device Hotspot Configuration
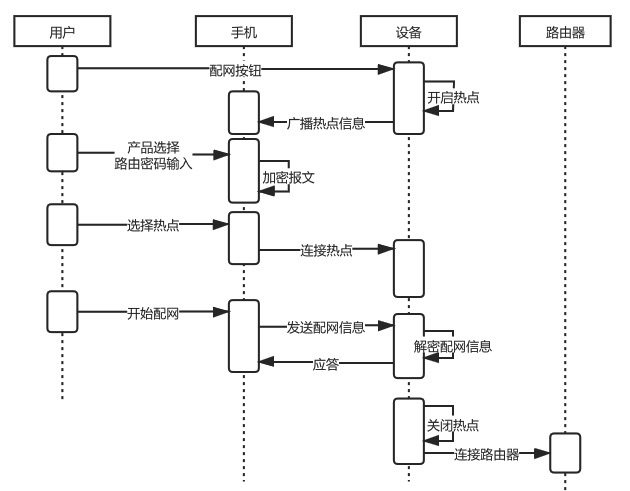
-
Advantages:
-
High success rate and reliability.
-
Disadvantages:
-
User operation is slightly more complex compared to one-click configuration (iPhone users need to manually switch to the wireless LAN settings to connect to the device hotspot indicated in the app).
3. Mobile Hotspot Configuration
-
Advantages:
-
The device does not need to support hotspot mode, resulting in lower development workload on the end; -
Can coexist with one-click configuration (enabled simultaneously). In Aliyun IoT’s mobile hotspot configuration, the mobile hotspot SSID is fixed as ‘aha’, so devices in one-click configuration mode will attempt to connect to ‘aha’ as soon as they scan for the surrounding hotspot. This is commonly used as a backup configuration scheme.
-
Disadvantages:
-
User experience is poor, especially on iOS devices where the app cannot automatically create a hotspot; users need to manually navigate to the settings to change the device name and enable the hotspot.
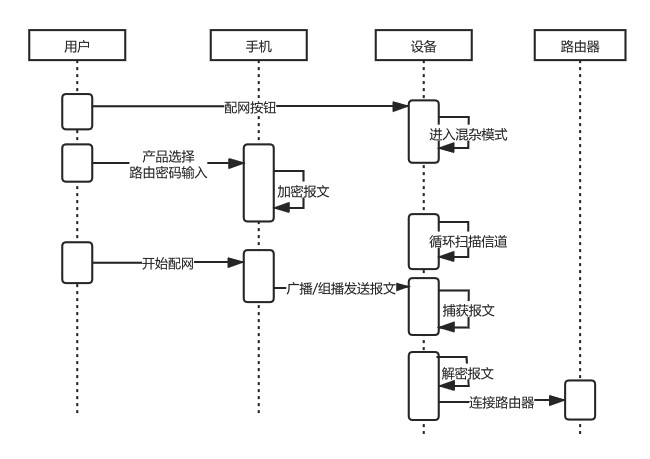
4. Bluetooth Configuration
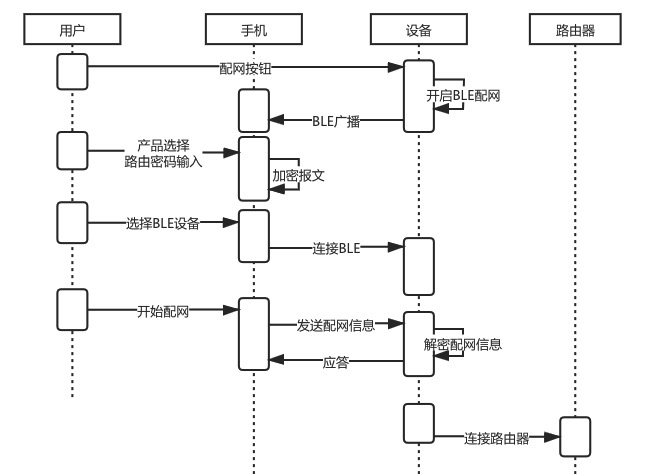
-
Advantages:
-
Good compatibility and high success rate. -
Good user experience.
-
Disadvantages:
-
Costs are slightly higher. Compared to other configuration modes, additional Bluetooth hardware costs need to be incurred.
5. Router Configuration
-
Advantages:
-
Better user experience.
-
Disadvantages:
-
Narrow application scope; both the device and router must meet the same scheme.
6. Zero Configuration
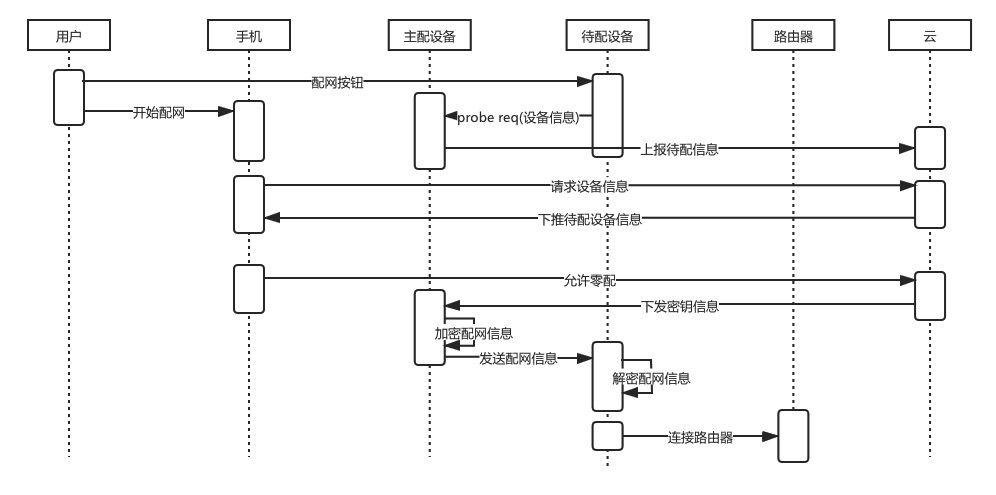
-
Advantages:
-
Good user experience and high success rate; for example, smart speakers can use this method to configure smart devices.
-
Disadvantages:
-
Narrow application scope; requires the existence of already configured devices in the same scheme under the router.
3. Summary Comparison
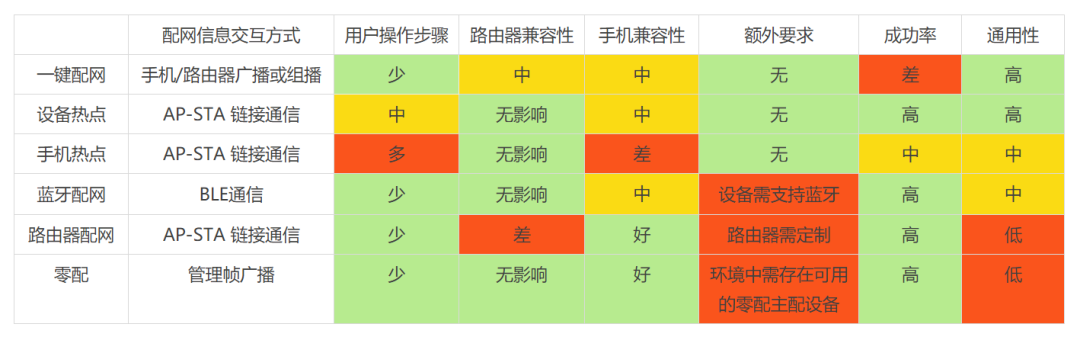
4. Development Direction
-
Voice configuration (using local voice recognition technology to configure devices with voice recognition modules, such as smart speakers). -
QR code configuration for smart cameras (the camera actively scans the QR code generated by the mobile app), etc.
-
Guidance: Scanning a QR code or entering a string to trigger, obtaining the public key of the other device as well as information such as channel and MAC; -
Verification: The device to be configured and the main configuration establish a secure connection based on the information obtained in the previous step; -
Configuration: Transmitting configuration information to the device to be configured; -
Access: The device to be configured authenticates and connects to the target AP using the configuration information.