Content reference from “2022 Best Practices for Edge Computing Implementation”, Source: SDN/NFV/AI Standards and Industry Promotion Committee.As MEC technology spans multiple fields including OT, IT, and CT, it involves network connectivity, data aggregation, as well as chips, sensors, and industry applications. To better meet the business needs of different industries, more open collaboration, joint innovation, and collective advancement of the MEC industry maturity are required across various fields. To this end, China Telecom will rely on the MEC Technology Innovation Alliance to comprehensively carry out MEC industry promotion work, aiming for real commercial implementation, focusing on demand mining for MEC-related scenarios, joint breakthroughs in key technologies, unified open network capabilities, collaborative innovation in business capabilities, solution integration verification, and innovation incubation pilots.(1) Operator MEC Development PlanningTo better meet the needs for real-time business response and integrated delivery implementation, China Unicom has established a national scheduling mechanism; set up one MEC business operation center, multiple innovation business incubation bases, and special expansion teams in various provinces, fully promoting the planning, construction, operation, and operation of national MEC edge cloud nodes and MEC business expansion; continuously focusing on three directions:1) In terms of ecosystem construction, build an edge application store ecosystem, establish the “China Unicom MEC Ecosystem Laboratory”, provide MEC testbed nodes, build end-to-end network environments, and offer services such as product testing, product listing, nationwide promotion, and operational support.2) In terms of deployment architecture, China Unicom’s MEC edge cloud is deployed in a three-layer architecture consisting of a nationwide central node, regional center/provincial capital nodes, and local core/edge nodes; the central node (MEAO) connects to the cloud-network integration portal, operation platform, and ecological open platform, completing the orchestration and management of edge business applications across the Unicom network; provincial nodes are responsible for managing, monitoring, scheduling, and operating all edge nodes’ ME_ICT-IaaS virtualization resources within the region, and the MEP access collaboration platform; edge nodes deploy ME_ICT-IaaS, MEP, ME-VAS, carrying specific business applications for customers.3) In terms of business deployment, four modes are mainly adopted for traffic diversion, including: shared + platform shared deployment mode, dedicated + platform dedicated deployment mode, shared + platform dedicated deployment mode, and platform sinking (DP) deployment mode;In the future, it will continue to enhance based on ETSI and 3GPP standards, open edge capabilities, deeply integrate IT, CT, and OT, promote cloud-network-edge business collaboration, continuously push for coordinated planning of layout-level nodes, and on-demand construction of site-level nodes, supporting various 2B businesses such as smart manufacturing, smart ports, smart education, smart healthcare, as well as various 2C businesses such as cloud gaming and VR/AR applications, promoting deep integration with the real economy, and accelerating the transition of 5G industry applications from demonstration to true commercialization.(2) Current Status of Industrial Ecosystem DevelopmentGartner predicts that by 2025, edge computing will have a market size exceeding one trillion, processing over 75% of various business data. In the face of such a vast market, telecom operators, public cloud service providers, equipment providers, and even industrial enterprises are continuously investing in the field of edge computing, actively promoting the development of the edge computing industrial ecosystem.Due to the influence of operational business and business network architecture, different types of enterprises adopt different strategies in the edge computing market, targeting different user needs, and providing different edge products.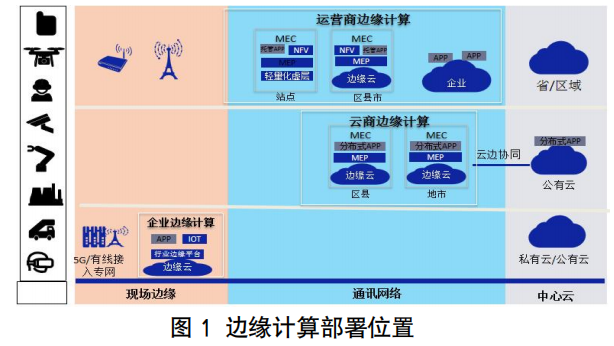 Telecom operators are currently in a leading position in the edge computing industry. The deployment and application of 5G networks can meet the mobility needs of business terminals and the low-latency requirements for business message transmission, making most edge application scenarios practical.(3) Overview of Technical RoutesWith the development of edge computing technology, three major technical systems of edge computing have emerged: one is the ETSI MEC technical system driven mainly by CT-based telecom enterprises (communication operators, equipment vendors); the second is the public cloud sinking technical system driven mainly by IT internet enterprises (cloud computing service providers, CDN vendors, etc.); the third is the edge hybrid cloud technical system. These three technical routes are accelerating competition and cooperation.1. MEC Technical RouteThe European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) established the Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) specification working group in 2014, officially announcing the promotion of MEC standardization. The project aims to build a service platform based on cloud technology and IT environment for application developers and content providers at the edge of mobile networks, and to open mobile communication network-side information through this platform, achieving high bandwidth, low latency business support and local management. The founding members of the alliance include HP, Vodafone, Huawei, Nokia, Intel, and Viavi.Currently, the ETSI MEC standardization organization has attracted hundreds of domestic and foreign operators, equipment vendors, software developers, and content providers to participate, and the influence of ETSI MEC is gradually expanding. In 2016, ETSI expanded the concept of MEC to Multi-Access Edge Computing, extending edge computing from mobile communication networks to other wireless access networks (such as WiFi). The main content of its standardization includes research on edge computing platforms, application management, resource orchestration, service APIs, edge collaboration, and edge computing security.
Telecom operators are currently in a leading position in the edge computing industry. The deployment and application of 5G networks can meet the mobility needs of business terminals and the low-latency requirements for business message transmission, making most edge application scenarios practical.(3) Overview of Technical RoutesWith the development of edge computing technology, three major technical systems of edge computing have emerged: one is the ETSI MEC technical system driven mainly by CT-based telecom enterprises (communication operators, equipment vendors); the second is the public cloud sinking technical system driven mainly by IT internet enterprises (cloud computing service providers, CDN vendors, etc.); the third is the edge hybrid cloud technical system. These three technical routes are accelerating competition and cooperation.1. MEC Technical RouteThe European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) established the Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) specification working group in 2014, officially announcing the promotion of MEC standardization. The project aims to build a service platform based on cloud technology and IT environment for application developers and content providers at the edge of mobile networks, and to open mobile communication network-side information through this platform, achieving high bandwidth, low latency business support and local management. The founding members of the alliance include HP, Vodafone, Huawei, Nokia, Intel, and Viavi.Currently, the ETSI MEC standardization organization has attracted hundreds of domestic and foreign operators, equipment vendors, software developers, and content providers to participate, and the influence of ETSI MEC is gradually expanding. In 2016, ETSI expanded the concept of MEC to Multi-Access Edge Computing, extending edge computing from mobile communication networks to other wireless access networks (such as WiFi). The main content of its standardization includes research on edge computing platforms, application management, resource orchestration, service APIs, edge collaboration, and edge computing security.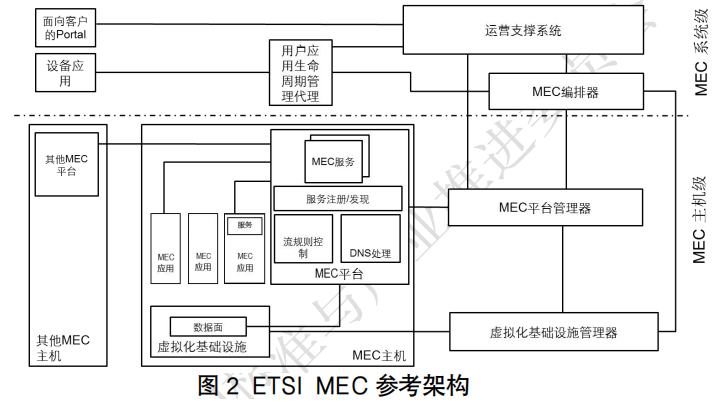 According to ETSI’s definition, MEC will provide a standardized, open system that can support various virtualization technologies, allowing applications to discover available applications and services on hosts and direct requests and data to one or more hosts. The diagram is the edge computing architecture defined by the ETSI MEC working group, which mainly consists of the MEC host side and the MEC system side. The MEC host side includes the MEC host, MEC platform manager, and virtualization infrastructure manager, where the MEC host consists of the MEC platform, MEC applications, and virtualization infrastructure. The MEC system side mainly includes the operation support system, user application lifecycle management agent, device applications, customer portal, and MEC orchestrator.
According to ETSI’s definition, MEC will provide a standardized, open system that can support various virtualization technologies, allowing applications to discover available applications and services on hosts and direct requests and data to one or more hosts. The diagram is the edge computing architecture defined by the ETSI MEC working group, which mainly consists of the MEC host side and the MEC system side. The MEC host side includes the MEC host, MEC platform manager, and virtualization infrastructure manager, where the MEC host consists of the MEC platform, MEC applications, and virtualization infrastructure. The MEC system side mainly includes the operation support system, user application lifecycle management agent, device applications, customer portal, and MEC orchestrator.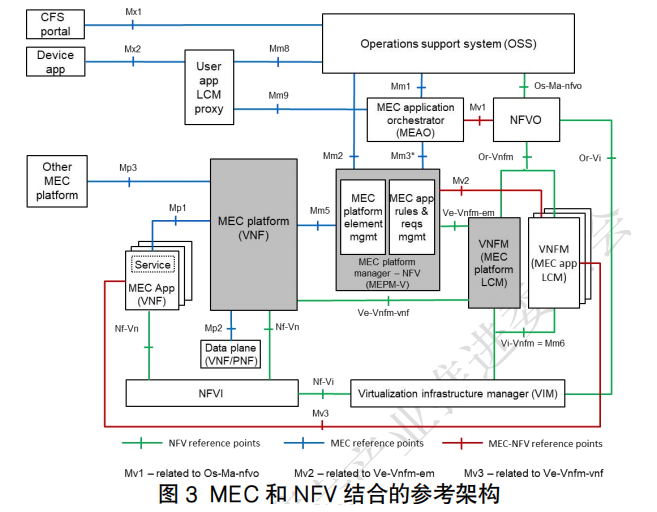 In addition, MEC also defines an MEC architecture based on NFV technology, as shown in the figure. This architecture allows MEC applications and virtualized network functions (VNFs) of mobile communication networks to be deployed on the same virtualization infrastructure and reuses components of ETSI NFV MANO for MEC management and orchestration.The ETSI GS MEC-IEG 004 specification released in 2015 lists seven typical application scenarios.
In addition, MEC also defines an MEC architecture based on NFV technology, as shown in the figure. This architecture allows MEC applications and virtualized network functions (VNFs) of mobile communication networks to be deployed on the same virtualization infrastructure and reuses components of ETSI NFV MANO for MEC management and orchestration.The ETSI GS MEC-IEG 004 specification released in 2015 lists seven typical application scenarios.
-
Enterprise diversion: Diverting user plane traffic to enterprise networks.
-
Internet of Vehicles: MEC analyzes data from vehicles and roadside sensors, sending sensitive information such as hazards to surrounding vehicles.
-
Assisted sensitive computing: MEC provides high-performance computing to process time-sensitive data, feeding results back to edge devices.
-
Video optimization: Deploying wireless analysis applications at the edge to assist TCP congestion control and bitrate adaptation.
-
Internet of Things: MEC applications aggregate and analyze messages generated by devices and make timely decisions.
-
Augmented reality: Edge applications quickly process user location and camera images, providing real-time assistance information to users.
- Video stream analysis: Performing video analysis processing at the edge, reducing the cost of video capture devices and decreasing traffic sent to the core network.
The above application scenarios reflect the localization of edge computing applications, regionalization of content, and marginalization of computing. In fact, the business scenarios of edge computing are far more than these seven; emerging 5G business scenarios such as XR, cloud gaming, and intelligent quality inspection have strong demands for edge computing.2. Public Cloud Sinking Technical RouteThe core of the public cloud sinking technical route is the extension of public cloud services to the edge. Domestic cloud service providers, taking Alibaba, Tencent, and Baidu as examples, rely on strong cloud ecosystems and technical advantages to extend cloud computing capabilities to the edge, creating an integrated product system of cloud, edge, and terminal, focusing on the technical development route of the “edge computing + X” model, relying on rich edge cloud and edge resource pool forms to develop edge computing as their main feature.From the IT architecture perspective, edge computing has a clear layered structure determined by business latency and computing scale, divided into “cloud”, “near-field edge”, and “site edge”, corresponding to public cloud/central cloud, lightweight edge cloud, and edge resource pool/edge hyper-convergence/edge gateway and other edge devices. Under the IT framework, as shown in Figure 4, cloud and edge are naturally an inseparable organic whole, and the collaboration of “cloud-edge-terminal integration” is currently a consensus technical solution for public cloud sinking.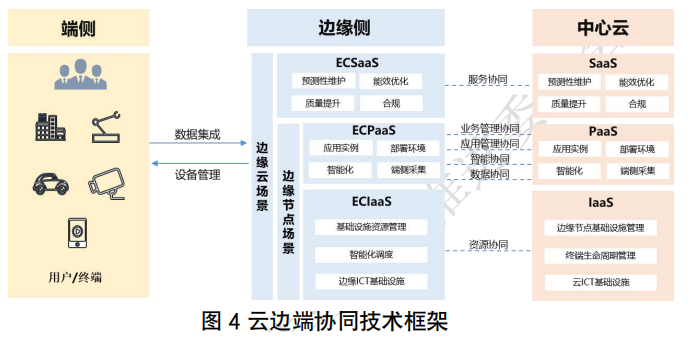 The infrastructure on the edge side, due to its lightweight resource characteristics, requires different management components for edge cloud/resource pool/node scenarios to achieve management collaboration and resource collaboration with public cloud/central cloud.In the edge cloud scenario, a complete lightweight cloud platform base is deployed on the edge side, achieving distributed computing power deployment and business bearing of edge cloud through multi-cloud collaboration with the central cloud. Representative products include Huawei IEC, Alibaba ENS, etc. In the edge resource pool and edge hyper-convergence scenarios, the edge side has certain management and operation capabilities, establishing networks and management with the central cloud to manage cloud applications on edge homogeneous/heterogeneous devices and resources. Representative products include Huawei IES, H3C Magic Pod, etc. Additionally, for edge heterogeneous, single-node devices, using cloud-native as the basis for virtualization platform implementation of productization on central cloud and edge side, through cloud-edge management channels, lightweight cloud service capabilities are sunk to the edge, making massive edge nodes and edge businesses the working carriers of the cloud system, thus completing the integration of business, operation, and ecology. Representative products include Huawei IEF, Alibaba ACK@edge, H3C HES, etc.Through the public cloud sinking technology, a consistent operational and maintenance experience with the cloud can be obtained, achieving better isolation and security while significantly improving efficiency.3. Hybrid Cloud Technical RouteChina’s three major operators have balanced development of network infrastructure and cloud infrastructure, allowing for the development of edge computing through both network cloud resource sinking and public cloud resource sinking. However, due to significant differences in the technical frameworks of the two clouds, different operation and maintenance management systems are required, making it impossible to achieve cross-technical architecture cloud-edge collaborative management. Therefore, it is necessary for network cloud and public cloud to merge architecturally, forming a unified operation and maintenance system to support hybrid edge cloud deployment methods.China Mobile has proposed a hybrid technical architecture for edge computing, leveraging its advantages in network cloud and public cloud resources, promoting the formation of a hybrid technical framework system from the aspects of operation, management, PaaS platform, and IaaS base, achieving multi-cloud collaborative management, heterogeneous cloud data transmission, and capability collaboration, as shown in the technical framework diagram.
The infrastructure on the edge side, due to its lightweight resource characteristics, requires different management components for edge cloud/resource pool/node scenarios to achieve management collaboration and resource collaboration with public cloud/central cloud.In the edge cloud scenario, a complete lightweight cloud platform base is deployed on the edge side, achieving distributed computing power deployment and business bearing of edge cloud through multi-cloud collaboration with the central cloud. Representative products include Huawei IEC, Alibaba ENS, etc. In the edge resource pool and edge hyper-convergence scenarios, the edge side has certain management and operation capabilities, establishing networks and management with the central cloud to manage cloud applications on edge homogeneous/heterogeneous devices and resources. Representative products include Huawei IES, H3C Magic Pod, etc. Additionally, for edge heterogeneous, single-node devices, using cloud-native as the basis for virtualization platform implementation of productization on central cloud and edge side, through cloud-edge management channels, lightweight cloud service capabilities are sunk to the edge, making massive edge nodes and edge businesses the working carriers of the cloud system, thus completing the integration of business, operation, and ecology. Representative products include Huawei IEF, Alibaba ACK@edge, H3C HES, etc.Through the public cloud sinking technology, a consistent operational and maintenance experience with the cloud can be obtained, achieving better isolation and security while significantly improving efficiency.3. Hybrid Cloud Technical RouteChina’s three major operators have balanced development of network infrastructure and cloud infrastructure, allowing for the development of edge computing through both network cloud resource sinking and public cloud resource sinking. However, due to significant differences in the technical frameworks of the two clouds, different operation and maintenance management systems are required, making it impossible to achieve cross-technical architecture cloud-edge collaborative management. Therefore, it is necessary for network cloud and public cloud to merge architecturally, forming a unified operation and maintenance system to support hybrid edge cloud deployment methods.China Mobile has proposed a hybrid technical architecture for edge computing, leveraging its advantages in network cloud and public cloud resources, promoting the formation of a hybrid technical framework system from the aspects of operation, management, PaaS platform, and IaaS base, achieving multi-cloud collaborative management, heterogeneous cloud data transmission, and capability collaboration, as shown in the technical framework diagram.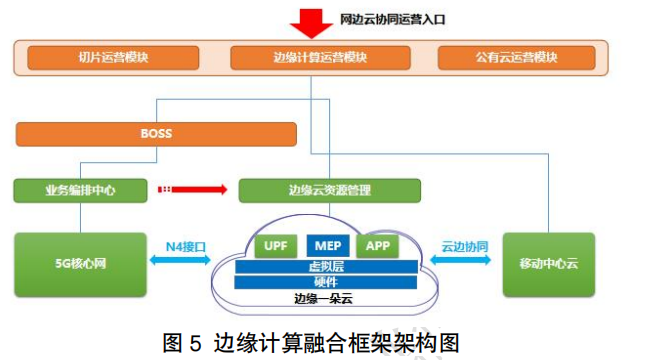 Based on this framework, unified configuration and management can be achieved, allowing edge computing services to be delivered and used in a consistent manner across multiple environments (public cloud, network cloud), fully exploring the value brought by hybrid deployment models.The edge cloud PaaS platform provides cloud services and IT environment services for edge applications and can be deployed lightweight through capability trimming components. The overall design of the edge cloud PaaS platform adopts a microservice framework, allowing for the introduction of new industry capabilities such as AI capabilities and big data capabilities to enrich and improve the capability layer as business needs change. The edge cloud PaaS platform mainly provides the following key capabilities:• Basic capabilities: The edge cloud PaaS platform must support middleware services such as MQTT, Redis, and common database capabilities for edge application deployment.• Network capabilities and capability opening: The edge cloud PaaS platform must support the opening of key network capabilities such as location service capabilities, wireless information capabilities, and QoS service capabilities to meet the business needs of third-party edge applications.• Industry capabilities and capability opening: The edge cloud PaaS platform can integrate third-party vertical industry capabilities based on specific business scenario needs and provide them externally, enabling the edge cloud PaaS platform to have the core capabilities to carry industry applications.• Application management capabilities: The edge cloud PaaS platform must support on-demand provision of application lifecycle management capabilities, configuration capabilities, and monitoring capabilities to third parties, allowing third parties to have flexible and autonomous operational permissions and capabilities.• Edge management layer: The edge management layer must support the capabilities required for edge computing business operation management, such as providing edge application service portals, business orchestration management, business policy management, FCAPS management, lifecycle management, and virtual resource management.
Based on this framework, unified configuration and management can be achieved, allowing edge computing services to be delivered and used in a consistent manner across multiple environments (public cloud, network cloud), fully exploring the value brought by hybrid deployment models.The edge cloud PaaS platform provides cloud services and IT environment services for edge applications and can be deployed lightweight through capability trimming components. The overall design of the edge cloud PaaS platform adopts a microservice framework, allowing for the introduction of new industry capabilities such as AI capabilities and big data capabilities to enrich and improve the capability layer as business needs change. The edge cloud PaaS platform mainly provides the following key capabilities:• Basic capabilities: The edge cloud PaaS platform must support middleware services such as MQTT, Redis, and common database capabilities for edge application deployment.• Network capabilities and capability opening: The edge cloud PaaS platform must support the opening of key network capabilities such as location service capabilities, wireless information capabilities, and QoS service capabilities to meet the business needs of third-party edge applications.• Industry capabilities and capability opening: The edge cloud PaaS platform can integrate third-party vertical industry capabilities based on specific business scenario needs and provide them externally, enabling the edge cloud PaaS platform to have the core capabilities to carry industry applications.• Application management capabilities: The edge cloud PaaS platform must support on-demand provision of application lifecycle management capabilities, configuration capabilities, and monitoring capabilities to third parties, allowing third parties to have flexible and autonomous operational permissions and capabilities.• Edge management layer: The edge management layer must support the capabilities required for edge computing business operation management, such as providing edge application service portals, business orchestration management, business policy management, FCAPS management, lifecycle management, and virtual resource management.
Related Reading:
High-Performance Computing Technologies, Solutions, and Industry Overview (Second Edition)InfiniBand Architecture and Technical Practical Summary (Second Edition)RDMA Principle Analysis, Comparison, and Technical Implementation Analysis
Complete Technical Data Package for All Stores (Complete)
Reprint Statement: Please indicate the author and source when reprinting articles from this account. If there are copyright issues with articles published by this account, please leave a message for processing. Thank you.
Recommended Reading
For more architecture-related technical knowledge summaries, please refer to the “Architect’s Complete Technical Data Package” related e-books (37 books technical data package summary details can be obtained through “Read the original text“.
All store content is continuously updated. Now order the “Architect’s Complete Technical Data Package Summary (Complete)“, and you can enjoy the “free” reading of all store content updates later, priced at only 198 yuan (original total price 350 yuan).
Warm Reminder:
Scan the QR code to follow the public account, click the mini program link to obtain the “Architect’s Technical Alliance Bookstore“ e-book data details.