10 to 20 years ago, µCOS was the first choice for many beginners. Ten years later, FreeRTOS has become the preferred choice for many newcomers.Why was µCOS so popular in the past, but now it receives little attention?As a once “popular” RTOS, although µCOS is not as focused on by newcomers today, its coding style is still worth learning and understanding for beginners.Today, I will compare the coding standards of these two RTOS (taking uC/OS-III V3.08.02 and FreeRTOS V10.5.1 as examples).
Coding Standards
Both uC/OS and FreeRTOS adhere to the MISRA C coding standard and support PC-Lint static analysis, as stated in their official documentation.
Note:The MISRA C standard refers to the C language development standard for automotive applications. You can refer to the previously shared article:MISRA C: What is the 2012 Standard?
1. uC/OS
The uC/OS documentation clearly states adherence to the MISRA C:2012 standard and supports PC-Lint static analysis.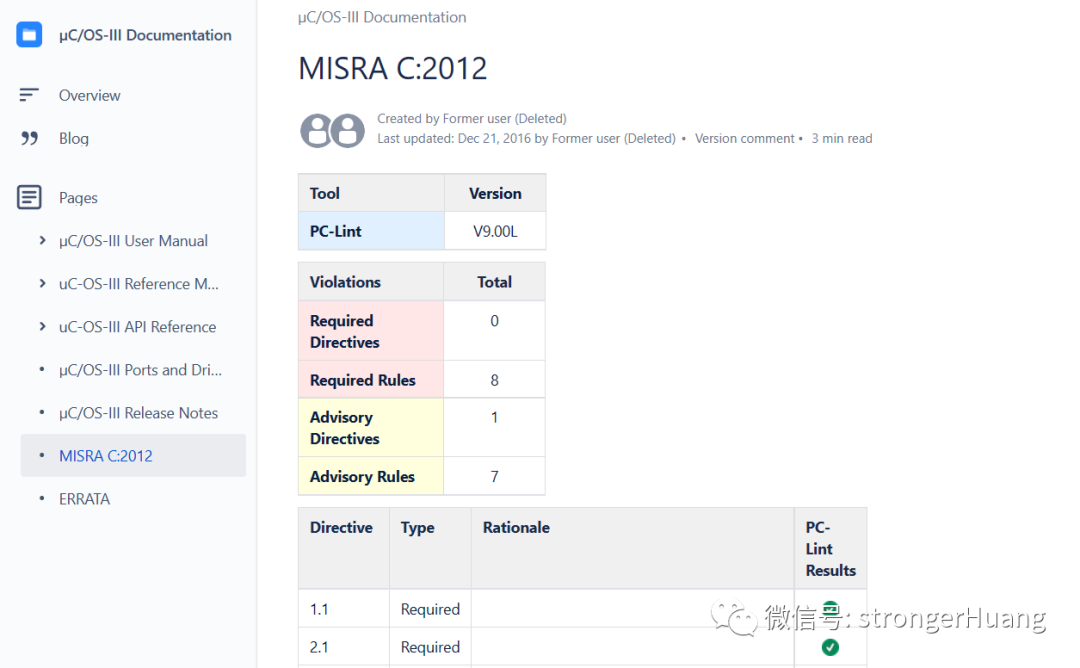
2. FreeRTOS
FreeRTOS also clearly states that it adopts the MISRA C coding standard, but does not support standards after C99, and supports PC-Lint static analysis.
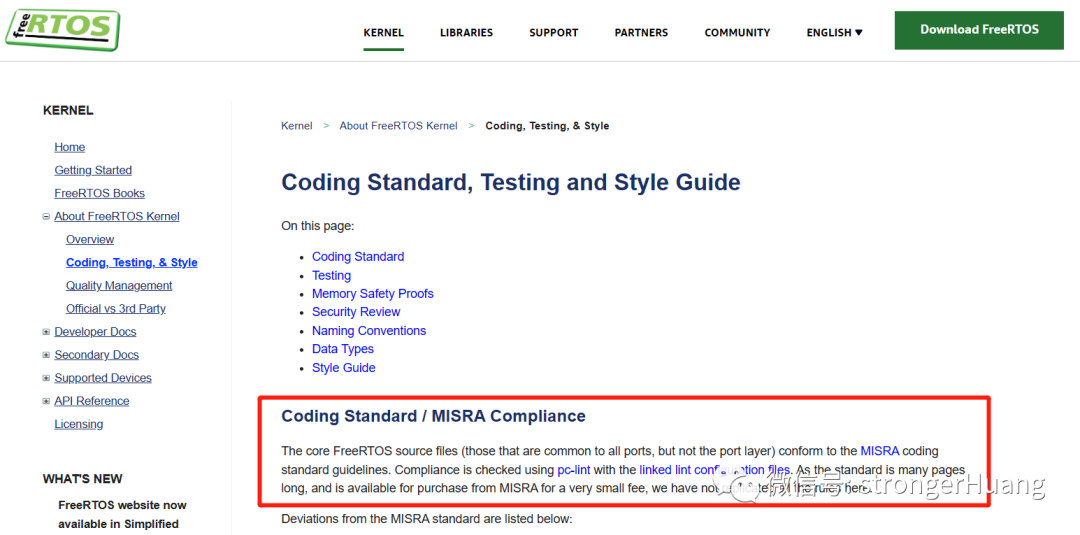
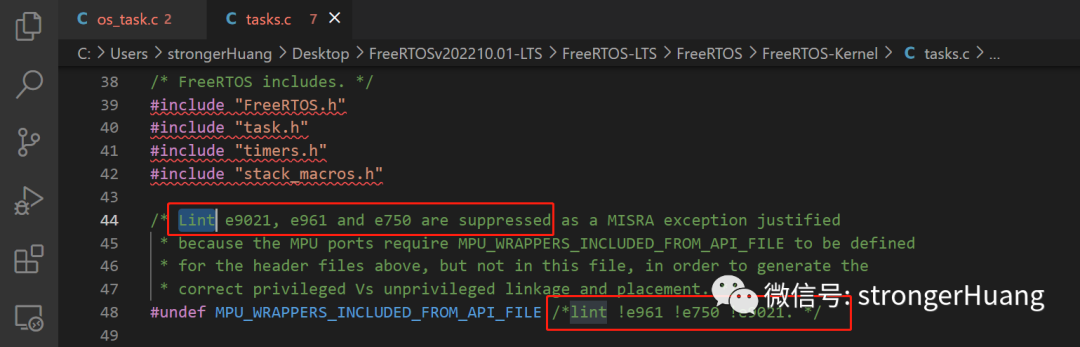
FreeRTOS contains a large number of comments in its source code regarding code that may cause exceptions during PC-Lint static analysis, which is not present in the uC/OS source code.
For example:
Configuration Files
The configuration files (also known as “trimming” files) for both RTOS are somewhat similar in content and are categorized.
However, the categorization and comments in uC/OS are more user-friendly and easier for beginners to understand.
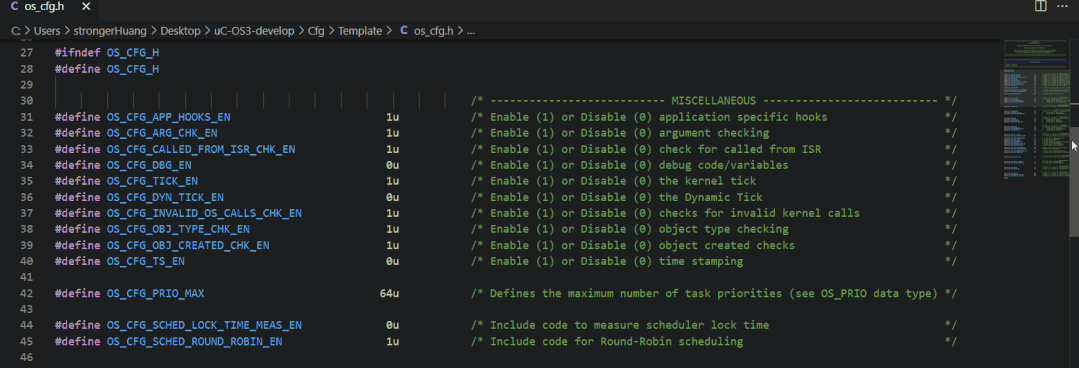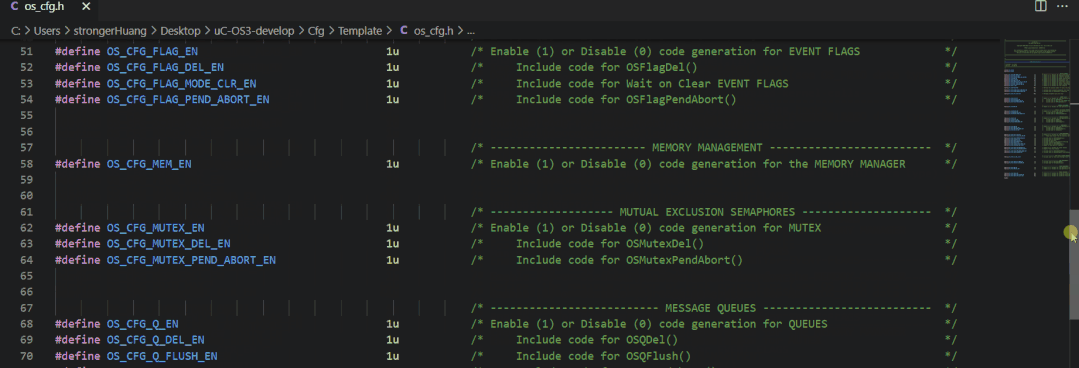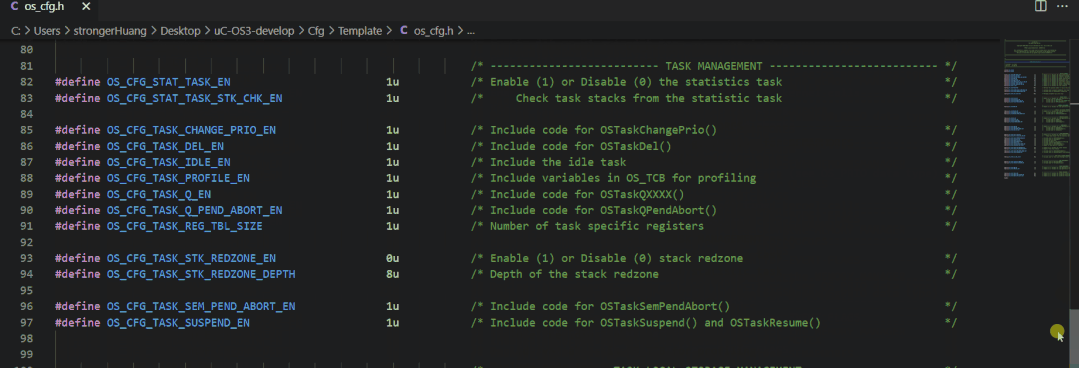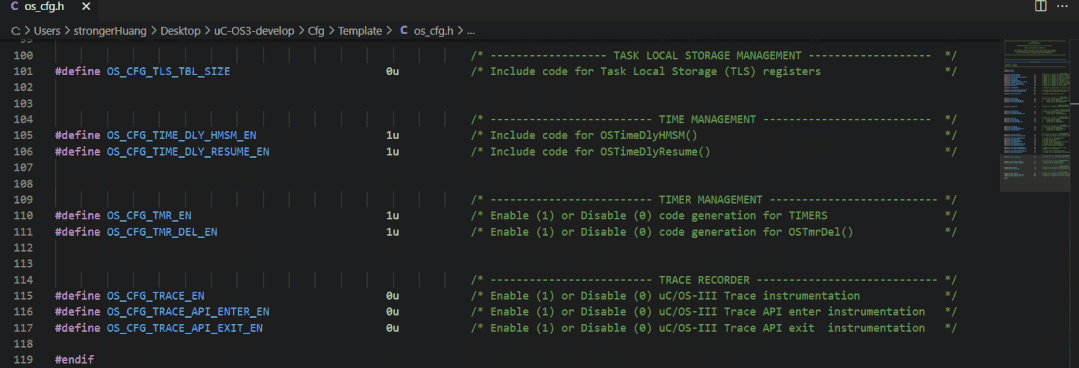
1. uC/OS
The configuration file for uC/OS is typically:os_cfg.h
2. FreeRTOS
The configuration file for FreeRTOS is typically:FreeRTOSConfig.h
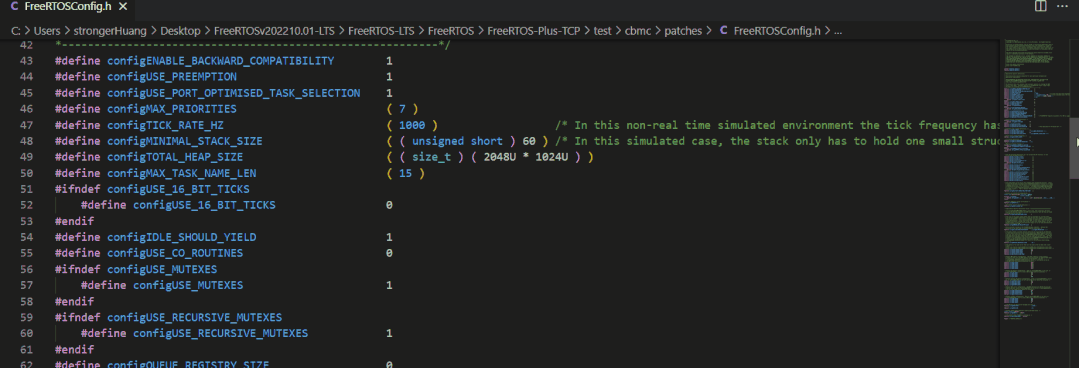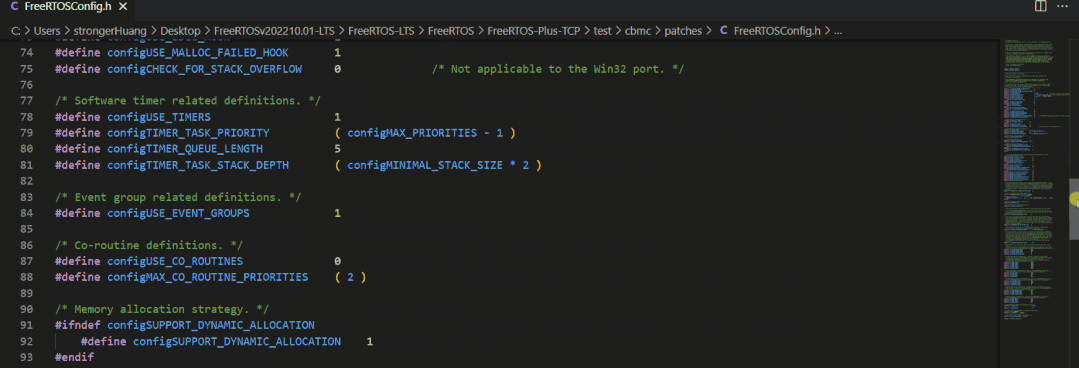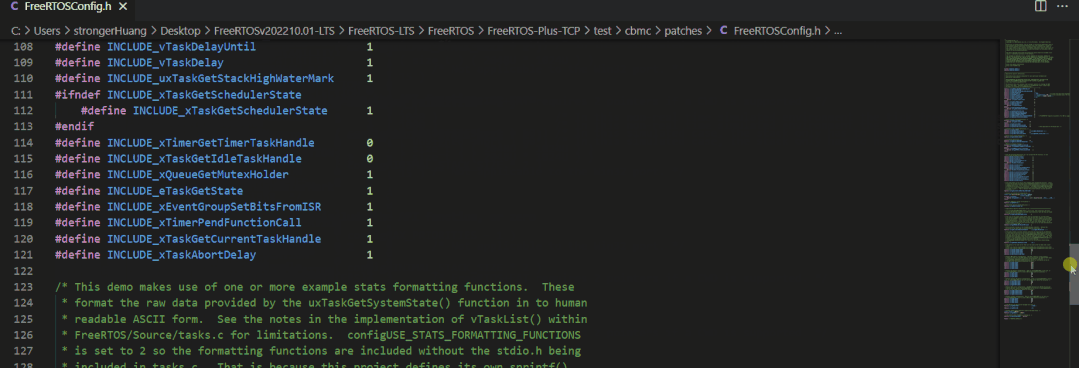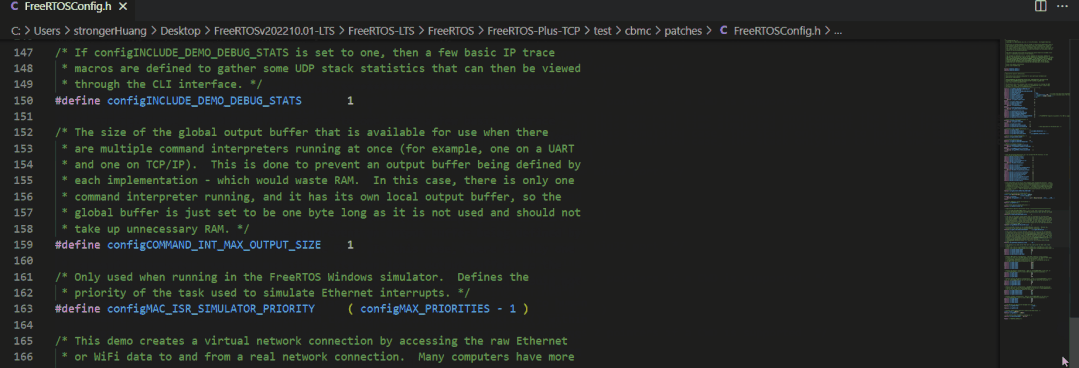
Headers
The content of the headers for both RTOS is somewhat similar, with one being centered and the other left-aligned.
1. uC/OS
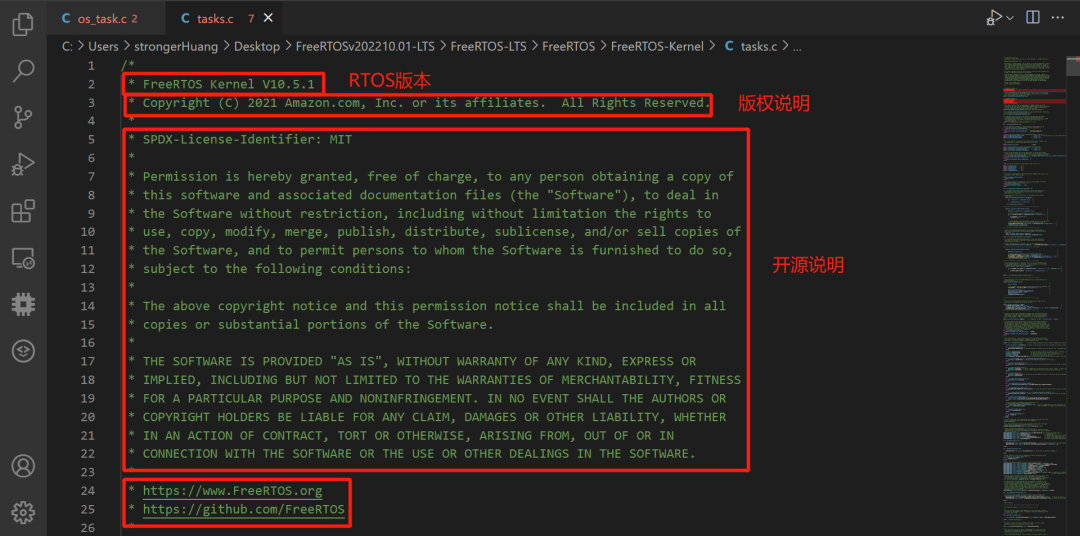
Includes RTOS version, copyright information, open-source license information, etc.:
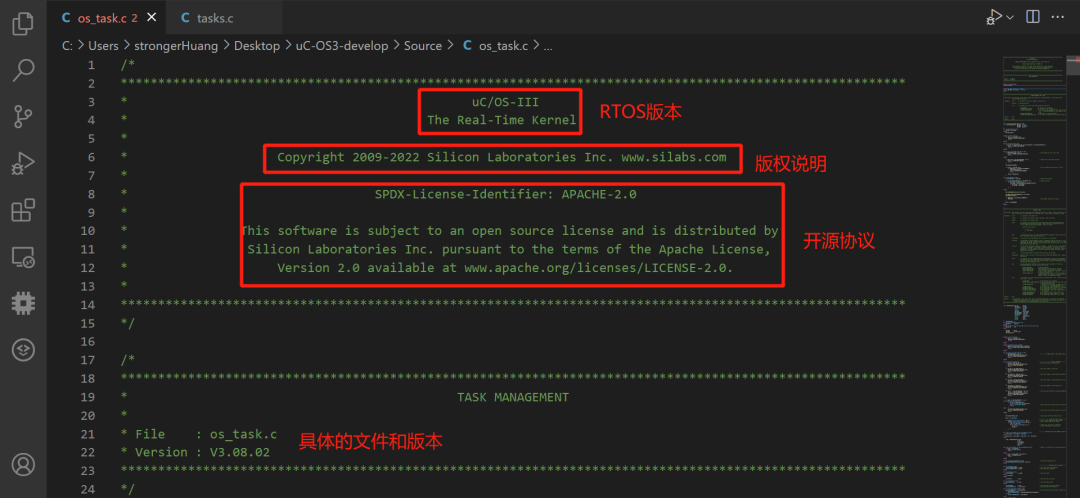
2. FreeRTOS
Includes RTOS version, copyright information, open-source license information, website, etc., similar to uC/OS.
Naming
The naming conventions for both RTOS differ significantly, but both adhere to conventional coding naming rules.
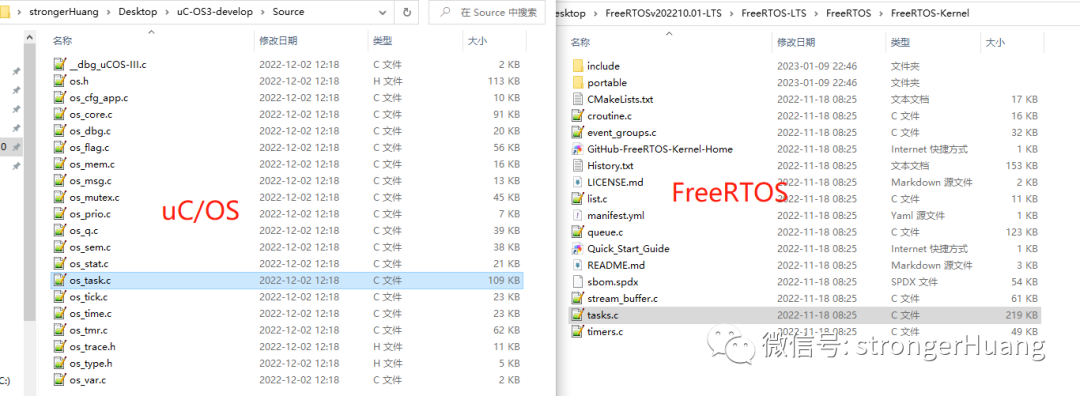
1. File Names
uC/OS uses the format 【os_ system file】, which appears more standardized (reflecting modularity).
FreeRTOS is more straightforward, which may be due to a lack of long-term planning during naming, and it has continued to be used for compatibility. (This can lead to file name collisions.)
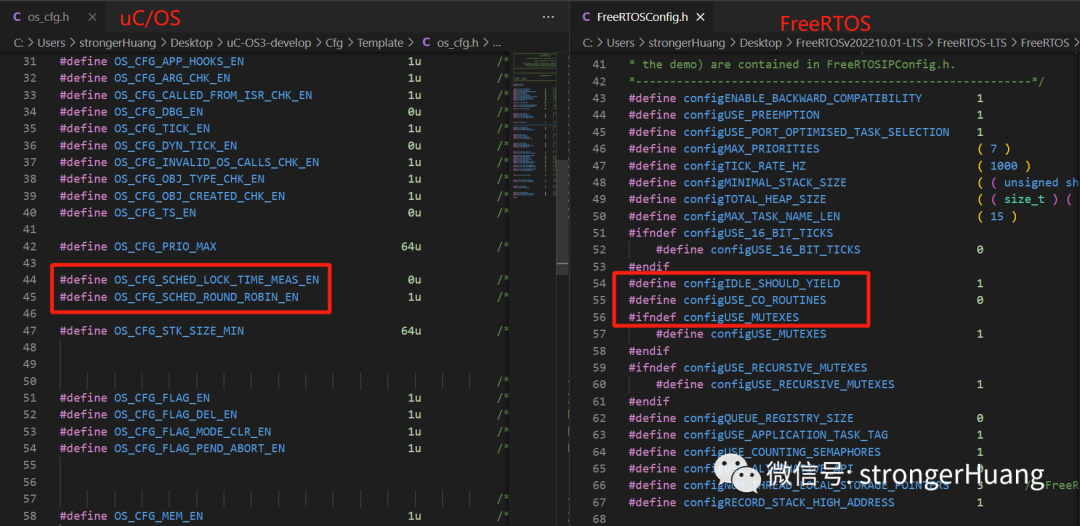
2. Macros
Both have similarities: uppercase letters are separated by underscores, but the prefixes differ.
For example, for “configuration files”: uC/OS starts with 【OS_CFG_】, while FreeRTOS starts with 【config】.
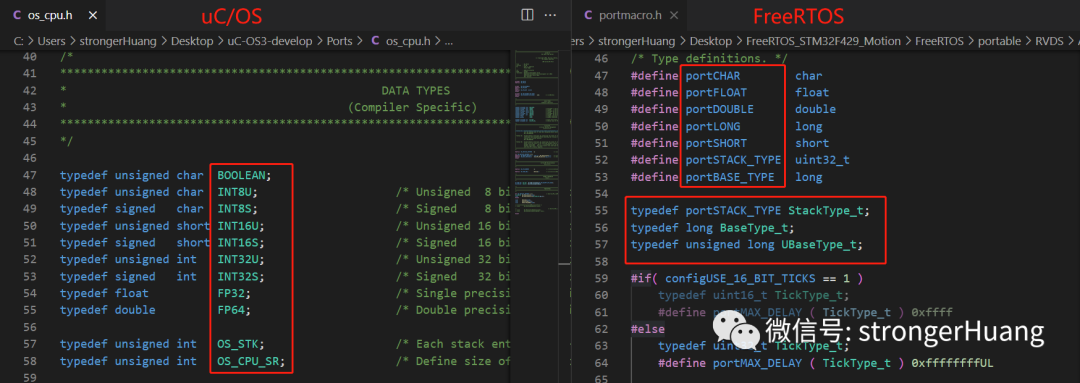
3. Data Types
Data types defined by uC/OS are relatively more common and suitable for beginners.
Data types defined by FreeRTOS are more “systematic” and suitable for experienced users, making them less friendly for beginners.
4. Function Names
Both are somewhat similar, with different prefixes, and both distinguish with 【uppercase letters at the beginning】.
For example, the function name for creating tasks:
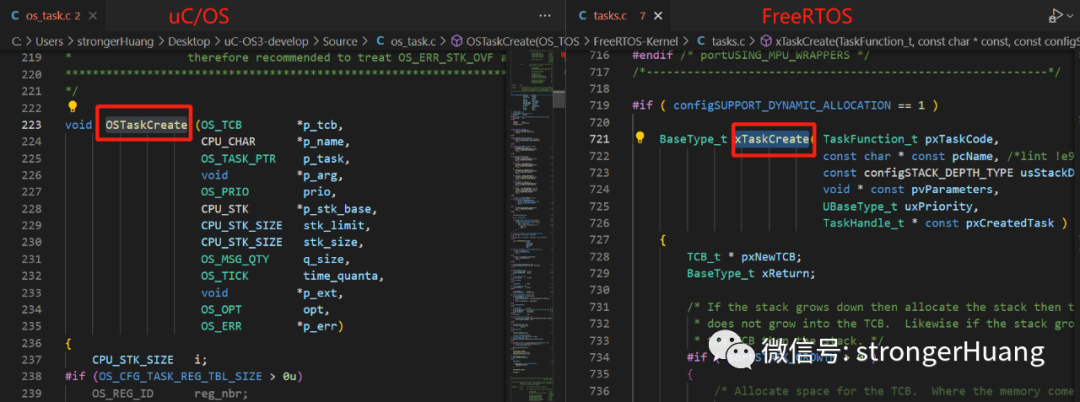
The official description of FreeRTOS prefixes is as follows:
-
Static functions are prefixed with prv, for example: the prvIdleTask function.
-
API functions are prefixed with their return type, with void types prefixed with v. For example: the vTaskDelete function.
Comments
// /* */ are the two most common methods of commenting, but these two RTOS primarily use 【/* */】 comments.
The position of comments is also important, usually one line above the line of code or at the end of the line of code.
It is important to note that FreeRTOS does not have comments in the code regarding function functionality, parameters, return values, etc.
Taking the “create task” function as an example:
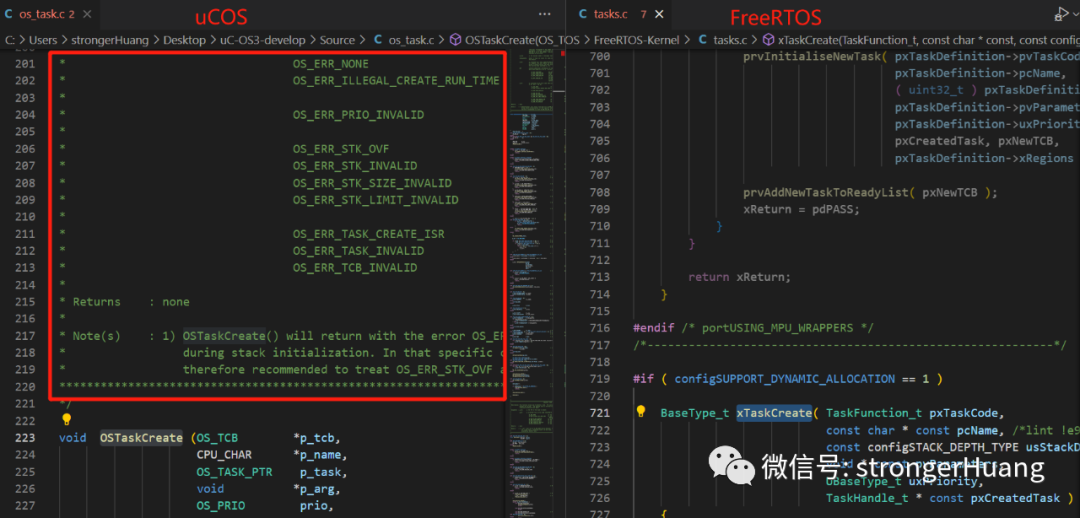
Of course, the function comment information for FreeRTOS is described in detail in the manual.
Indentation
Both RTOS use the same indentation style, which is 4 spaces:
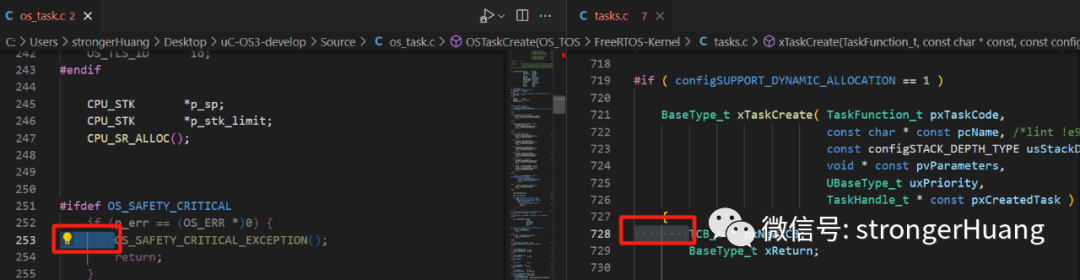
It is important to remember not to mix tabs and spaces, otherwise the code will become chaotic. (This often occurs in many beginners or junior engineers, making the code difficult to read).
Abbreviations
Different fields have different ways of abbreviating words. In RTOS, there are also some common abbreviations, such as:
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| Addr | Address |
| Blk | Block |
| Chk | Check |
| Clr | Clear |
| Cnt | Count |
| Ctr | Counter |
| Ctx | Context |
| Cur | Current |
| Del | Delete |
| Dly | Delay |
| Err | Error |
| OS | Operating System |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
That concludes this article. The above only lists some typical coding styles; for more details, you can take the time to study them yourself.
END
Source:strongerHuang
Copyright belongs to the original author. If there is any infringement, please contact for removal..▍Recommended ReadingOverview of job positions and salary status at Zhihui Jun CompanyA guide to writing embedded driver programs (based on timing diagrams)Why is hardware harder than software, yet hardware engineers earn less than software engineers?→ Follow for more updates ←