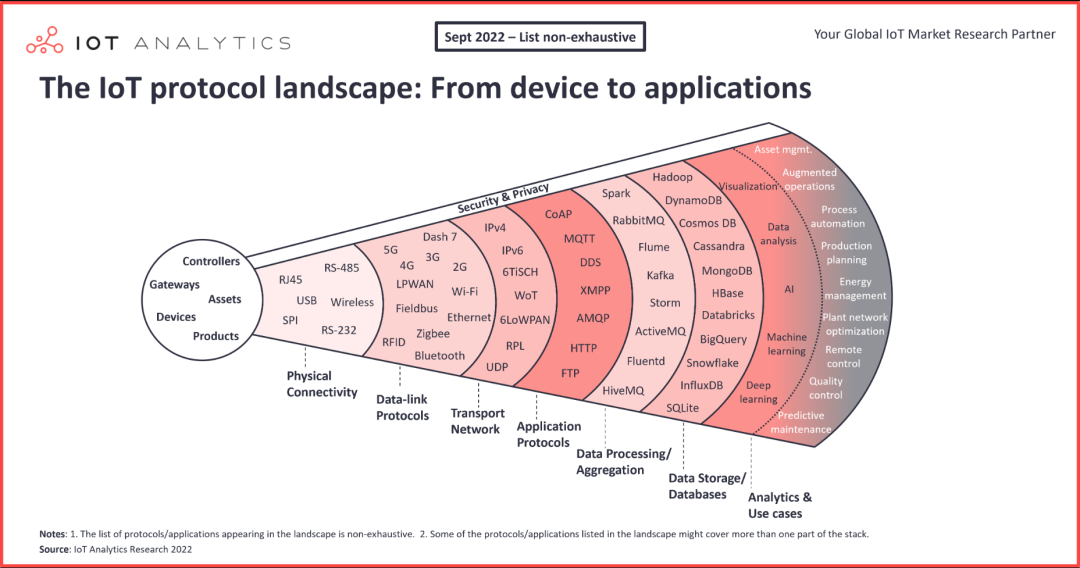
(Image source: IoT-Analytics)
| Common IoT Protocols List | ||
| Type | Protocol Code | Description and Scenario |
| General Protocol | MQTT | Protocol Description:MQTT is a lightweight publish-subscribe messaging protocol based on TCP/IP, characterized by compact messages, lightweight reliability, and support for QoS, etc. Application Scenario: Recommended protocol for the IoT industry, widely used in smart hardware, vehicle networking, energy, power, and other scenarios. |
| Modbus TCP | Protocol Description:Modbus is an application layer message transmission protocol that includes three message types: ASCII, RTU, and TCP. This protocol allows controllers to communicate with each other and with other devices over a network (e.g., Ethernet). Application Scenario: Widely used in the industrial sector. | |
| HTTPS | Protocol Description:HTTP is a hypertext transfer protocol that transmits data based on a request/response model. Application Scenario: Suitable for scenarios with abundant hardware and network bandwidth for devices. | |
| CoAP | Protocol Description:CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) is a web-like protocol for the IoT world, using a request/response interaction model. The protocol is designed to be compact and uses the UDP protocol for data transmission, suitable for resource-constrained low-power devices, especially those using NB-IoT. Application Scenario: Widely used in resource-constrained low-power devices such as water meters and electricity meters. | |
| UDP | Protocol Description:UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a connectionless protocol that does not provide reliability and flow control for data transmission but has lower latency and overhead. Application Scenario: Mainly used for real-time data transmission and quick communication between devices, including real-time video and audio streaming, sensor data collection, control signal transmission, broadcasting, and multicasting. Due to its low latency, low overhead, and no need for connection establishment, UDP can meet the high demands for rapid transmission and real-time performance in IoT applications. | |
| TCP | Protocol Description: Standards developed and adopted internally by vendors. Private protocols offer flexibility, often used within a company or organization, customizable, easy to upgrade, and highly flexible. Specific implementations require manual deployment by the customer. | |
| GB/T28181 | Protocol Description:The national standard GB/T 28181-2016 “Technical Requirements for Information Transmission, Exchange, and Control of Public Safety Video Surveillance Networking Systems” is a national standard in the field of video surveillance. Application Scenario: Video networking transmission and device control. | |
| OPC-UA | Protocol Description:OPC Unified Architecture (OPC-UA) is an open-source, platform-independent standard protocol; through this protocol, devices using different systems can communicate by sending messages over the network between clients and servers. Application Scenario: Suitable for manufacturing software applications in fields such as field devices, control systems, manufacturing execution systems, and enterprise resource planning systems. | |
| OPC-DA | Protocol Description:Compared to OPC-UA, OPC-DA is more suitable for single-system data access. OPC-DA is a real-time data access specification that defines standards related to data values, update times, and data quality information. Application Scenario: Suitable for data exchange between devices from multiple vendors and control applications. | |
| LoRa | Protocol Description:LoRa is a low-power local area network wireless standard developed by Semtech, solving the technical problem of achieving longer transmission distances under the same power conditions compared to other wireless methods, realizing the unification of low power consumption and long distance. Application Scenario: Mainly used in smart cities, smart buildings, smart homes, smart agriculture, and wireless industrial sectors. | |
| Industry Protocol | JT/T 808 | Protocol Description:The “Satellite Positioning System Terminal Communication Protocol and Data Format for Road Transport Vehicles” is mainly used for “two passengers and one dangerous” vehicles. Application Scenario: Applications in the transportation industry. |
| HJ212 | Protocol Description:The “Standard for Data Transmission of Pollutants Online Monitoring (Monitoring) Systems” is a data transmission standard protocol used in the environmental protection industry. Application Scenario: Environmental protection industry. | |
| SL651 | Protocol Description:The “Hydrological Monitoring Data Communication Protocol” is a standard that hydrological monitoring equipment must follow. Application Scenario: Hydrological monitoring. | |
| GB3761 | Protocol Description:A national standard electric meter protocol plugin that uses new data collection technology to convert real-time operational data of electric meters into electrical signals for the metering system, allowing for real-time recording, statistics, meter reading, and settlement of electric energy, etc. Application Scenario: Electric meters. | |
| IEC104 | Protocol Description:The IEC104 protocol was established by the International Electrotechnical Commission. The IEC104 protocol transmits the application service data unit (ASDU) of IEC101 using the TCP/IP network protocol, providing a communication protocol basis for the network transmission of remote information. By combining the ASDU of the 104 protocol with the 101 protocol, it can ensure the standardization of the protocol and the reliability of communication. Application Scenario: Power, urban rail transit. | |
| DL645 | Protocol Description:DL/T 645 is the standard and specification for physical connections and protocols for data exchange between multifunctional electric meters and data terminal devices. This device uses the DL/T 645-2007 standard protocol proposed by the China Electricity Council to achieve information communication between devices and multifunctional electric meters. Application Scenario: Electric meters. |
Previous Exciting Recommendations
-
Open Source IoT Platform: ThingsBoard
-
FluxMQ: Java-Based IoT Access Service Platform
-
DC3 Open Source IoT Platform: Open Source, Distributed IoT Platform Based on SpringCloud