5. Short Circuit of CAN L to Power (Positive)



6. Open Circuit of CAN H
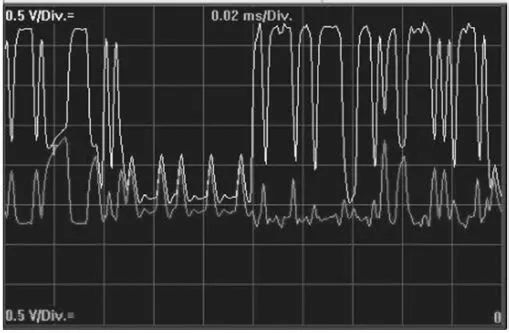
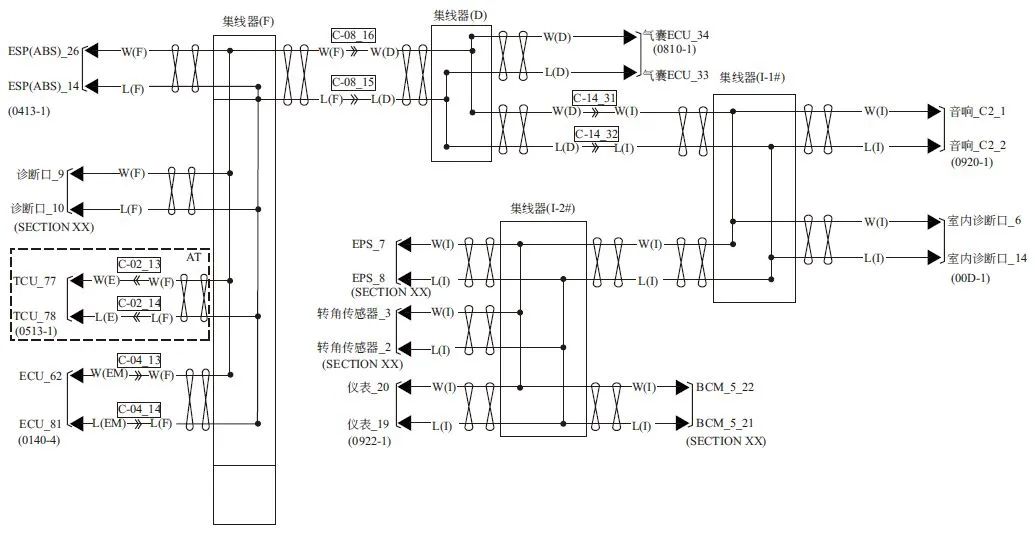
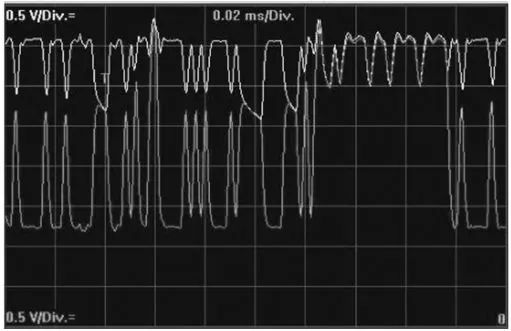
7. Open Circuit of CAN L
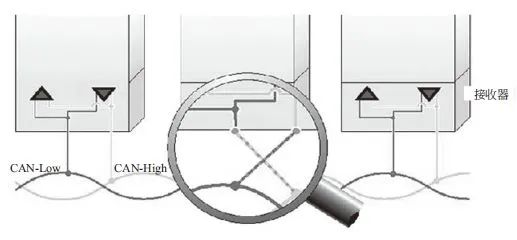
Source | Wiring Engineer
Click the mini-program below to see more repair cases








Source | Wiring Engineer
Click the mini-program below to see more repair cases
