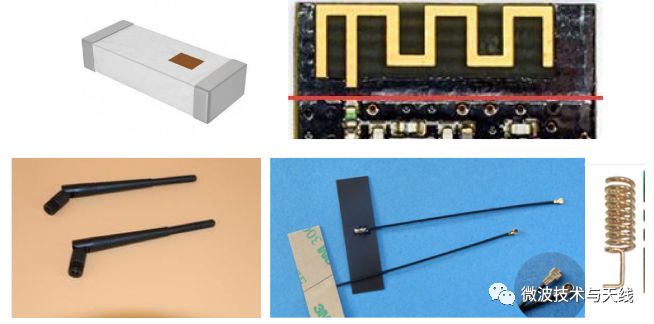
Common Types of Antennas
The common types of antennas for wireless modules can be simply divided into: ceramic antennas or LTCC antennas, onboard antennas, monopole antennas (commonly known as stick antennas), and FPC soft material antennas, as well as other types of antennas.
Ceramic Antennas
The ceramic antennas for wireless modules primarily use LTCC technology, and there are also pure block ceramic antennas, such as GPS ceramic antennas.

Block Ceramic Antennas and LTCC Technology Antennas
Block ceramic antennas are made by sintering a whole ceramic body at high temperatures and then printing the metal parts of the antenna on the surface of the ceramic block.
Multilayer antennas are manufactured using a low-temperature co-firing method (LTCC), where multiple ceramic layers are stacked and aligned before being sintered at high temperatures. Therefore, the metal conductors of the antennas can be printed on each layer of the ceramic dielectric layer according to design requirements. LTCC antennas utilize both high dielectric constant and multilayer characteristics, effectively reducing the size of the antennas. Since the dielectric constant of ceramics (generally between 9 and 16) is higher than that of PCB circuit boards (generally between 4 and 4.5), using ceramic antennas can effectively reduce antenna size.

TDK Multi-band Ceramic Antennas
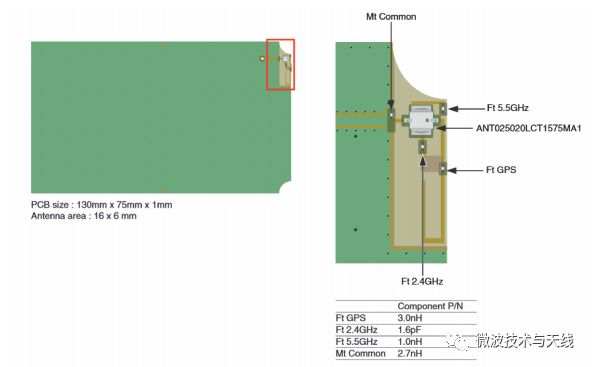
High requirements for PCB design during use
Onboard Antennas (PCB Antennas)
Onboard antennas directly utilize PCB as the medium, and the antennas are implemented through PCB technology, which can essentially be considered zero-cost. Additionally, assembly is simpler; however, the drawback is that the loss of the dielectric substrate is relatively large, leading to reduced efficiency. They are commonly found in wireless modules operating in the ISM 2.4GHz frequency band, such as Bluetooth, WIFI, and ZigBee.
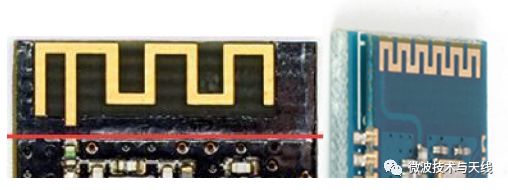
Inverted F antennas and monopole antennas, leaving a clearance area during design
External Antennas
External antennas are implemented by reserving RF connectors on the PCB. The advantage of external antennas is the variety of selectable antenna types, which allows for optimal product solutions by choosing different antenna forms. The benefits include guaranteed radiation patterns, high efficiency, strong anti-interference capability due to reduced interference from the motherboard, and minimal tuning required. However, the costs are higher, and assembly technology is involved, unlike the first two types, which can be directly handled through SMT or PCB.
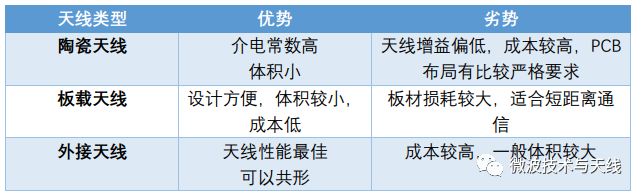
Advantages and Disadvantages of Various Antennas
If there are design and debugging needs for such antennas, please leave a message.