
This article is sourced from: Global IoT Observation
This article will comprehensively review the core component of the Internet of Things, the wireless communication module, from the industrial chain to manufacturers and future trends.

Recently, the result of a tender for 500,000 units of the “Universe’s First Marker” was released, sparking heated discussions in the industry. As the core component for terminal access to the Internet of Things, wireless communication modules are rarely mentioned in the industry. Today, we are compiling three reports to discuss the industry’s matters.

Industrial Chain Analysis
Wireless communication modules are the key link connecting the perception layer and the network layer of the Internet of Things. They belong to the underlying hardware segment and possess irreplaceability. There is a one-to-one correspondence between wireless communication modules and IoT terminals.
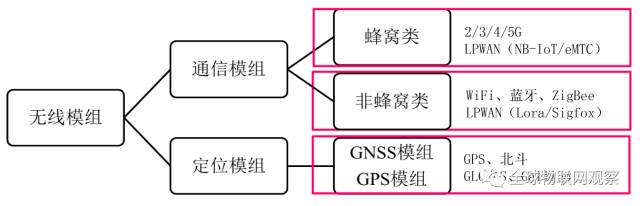
Classification of Wireless Modules
Wireless modules are classified into “communication modules” and “positioning modules” based on functionality. In comparison, communication modules have a broader application scope, as not all IoT terminals require positioning functionality.
Note: Since short-range wireless communication chips have been introduced previously, this article primarily focuses on cellular modules (2G/3G/4G/NB-IOT).
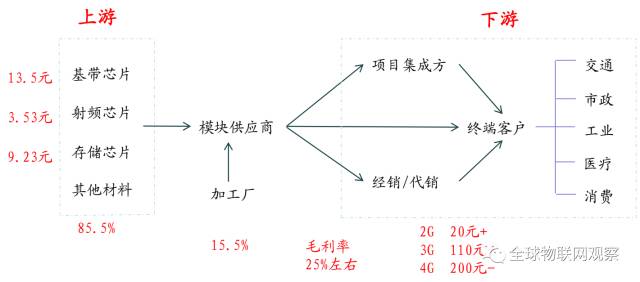
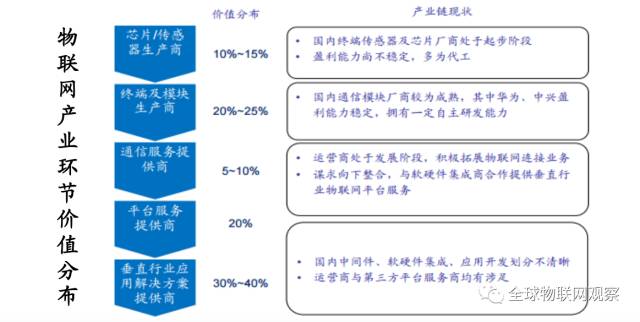
From the perspective of the industrial chain, the upstream of wireless communication modules is production materials such as baseband chips, which have a high degree of standardization. The downstream consists of various segmented application fields, which are extremely dispersed and often flow into various fields through intermediary distribution channels. The business model of module companies generally involves: procuring upstream materials themselves, being responsible for product design and sales, while outsourcing production to third-party processing plants.
In the upstream, baseband chips (communication chips) are core components, accounting for about 50% of material costs. The upstream has high technical barriers, and the industry is highly concentrated, with strong bargaining power among suppliers. Major suppliers include Qualcomm, Intel, MediaTek, RDA, Huawei, and ZTE.

Due to the wide application of the Internet of Things, the downstream industry is very dispersed. The downstream market is divided into large particle markets and small particle markets based on application market size. The large particle market (see below) has a high volume of IoT modules, high standardization, and fierce competition, suitable for generating high revenue and establishing a brand. The number of R&D personnel can be relatively small, but market development capabilities must be strong.

The small particle market (such as industrial IoT, asset tracking, environmental monitoring, etc.) has a low volume of IoT modules, high customization, and high profit margins, but requires significant R&D investment from suppliers.
The IoT module itself is positioned between standardized upstream chips and dispersed downstream vertical fields, needing to meet specific requirements for different customers and application scenarios. Its hardware structure design and customized software development become the value-added segments and the value of the industrial chain.
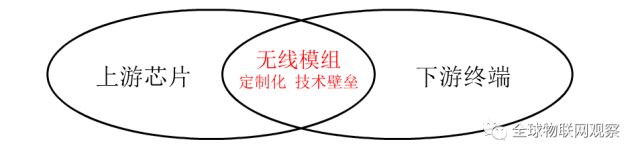
Value of the Industrial Chain:
1. Hardware integration and design, integrating various communication standards to meet environmental requirements in different application scenarios; stability and timeliness are core aspects;
2. Custom embedded software development, programming Linux/Android systems to meet different downstream application needs; mature application experience and solution capabilities are core aspects.
The wireless communication module market, is currently not highly concentrated, with the industry’s top tier occupying only about 30% of the global market share. With the rise of downstream applications and the expansion of the total market scale, a batch of quality module suppliers focusing on individual vertical application fields will begin to emerge.
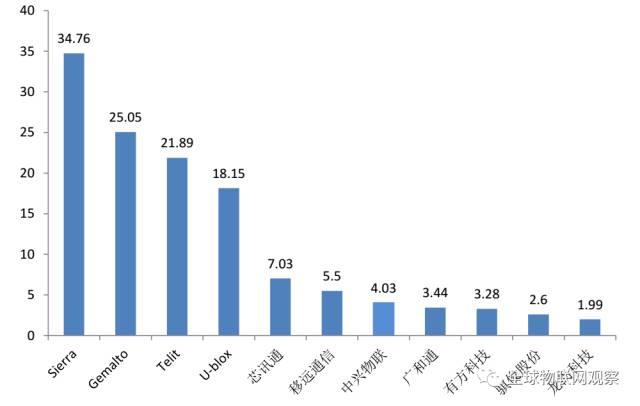
Global module supplier market share in 2015
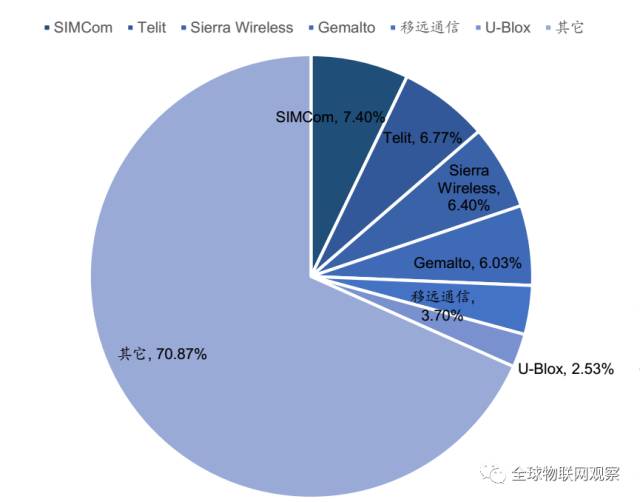
Data source: Guosen Securities Economic Research Institute
Overall, the industry is currently in a competitive landscape led by the first-tier players, with the domestic second-tier gradually strengthening. Global leading companies include Italy’s Telit, Canada’s Sierra Wireless, Switzerland’s u-blox, and the Netherlands’ Gemalto.
Overview of module revenues for industrial companies in 2016 (in billions)
“Market-Related” Companies
In the past year, domestic first-tier wireless communication module suppliers have been entering the A-share market through IPOs or acquisitions. Below are the main “market-related” companies. (Note: Rankings are not in order)

Headquarters: Shanghai
Introduction: Simcom is a subsidiary of Hong Kong-listed company Sim Technology Group, with its products holding a significant share in the smart POS, smart metering, and healthcare industries. Due to the traditional nature of Simcom’s wireless communication module business, it does not align with Sim Technology Group’s overall strategic direction towards high-margin service industries.
This January, Sim Technology Group planned to sell its wireless communication module assets (wholly-owned subsidiaries Shanghai Simcom and Simcom Wireless) for $52.5 million to Swiss u-blox. It is estimated that due to the disruption caused by Shanghai Wewi Communication, this acquisition did not reach consensus, and Sim Technology Group ultimately announced that Simcom would be sold to Wewi Communication and a company owned by its internal board member’s son, while another asset, Xintong Electronics, would also be packaged and sold.
According to Wewi Communication’s latest announcement, the Shenzhen Stock Exchange is still reviewing this transaction plan.
Website: www.simcomm2m.com

Headquarters: Shanghai
Introduction: Queclink was established in 2009, primarily focusing on positioning modules, and went public in January 2017. Queclink’s wireless communication module shipments surged to the global number one spot in 2015. If this acquisition is successful, Queclink will become the world’s largest IoT wireless communication company, cementing its monopoly position in the IoT communication terminal field.
Website: www.queclink.com
Headquarters: Shanghai
Introduction: Quectel was established in 2010 and has grown rapidly, with its products achieving significant success in the domestic smart POS market, overseas automotive pre-installation market, and carrier market. It has a leading position in the NB-IOT module field and is one of Huawei’s early partners in NB-IOT chip production. Quectel was previously listed on the New Third Board and is now planning to list on the A-share market, having submitted relevant materials to the Shanghai Regulatory Bureau.
Interestingly, the founders of Wewi and Quectel both come from Simcom. Wewi and Quectel were originally one company (Wewi), but they became independent due to different business development directions.
Website: www.quectel.com

Headquarters: Guangzhou
Introduction: Gosuncn is a provider of smart city IoT applications and services. In 2016, it acquired ZTE’s wireless communication module subsidiary, ZTE IoT. ZTE IoT focuses on the enterprise-level market and has deep experience in automotive networking and satellite communication applications.
Website: www.gosuncn.com

Headquarters: Shenzhen
Introduction: Fibocom was established in 1999 and is an established company. Initially, it provided OEM services for Motorola. In 2008, Telit acquired Motorola’s mobile communications division, nullifying all contracts with Fibocom. Subsequently, Fibocom transformed into its own brand, successfully entering the high-margin electronic consumer markets such as laptops and tablets after receiving investment from Intel. In April of this year, Fibocom successfully went public.
Website: www.fibocom.com

Headquarters: Xiamen
Introduction: Cheerzing was established in 2012 and obtained production qualification for live broadcasting satellite set-top box positioning modules recognized by the State Administration of Radio, Film and Television in 2013. Its products are used by nearly thirty enterprises, including Haier, Hisense, Changhong, TCL, and Konka, capturing a significant portion of the domestic set-top box positioning terminal market.
Website: www.cheerzing.com

Headquarters: Shenzhen
Introduction: Sunsea is the largest supplier of physical connection devices for communication networks in China. In September, Sunsea acquired the leading 4G wireless communication module company Longshang Technology, along with its previous investment in Aila IoT, achieving a layout of IoT cloud platform + modules. While providing cloud platforms for traditional enterprises, it can also directly package modules for integrated sales of products.
Website: www.sunseagroup.com
Future Trends
For IoT terminals to achieve networking or positioning functionality, they require wireless modules. Typically, for each additional terminal, 1-2 wireless modules need to be added, indicating a vast market. Of course, this is the future direction; in the short term, the prices of 4G modules are rapidly declining, and the shipment volume is expected to see significant growth.
Price trend of Fibocom’s 2G/3G/4G modules
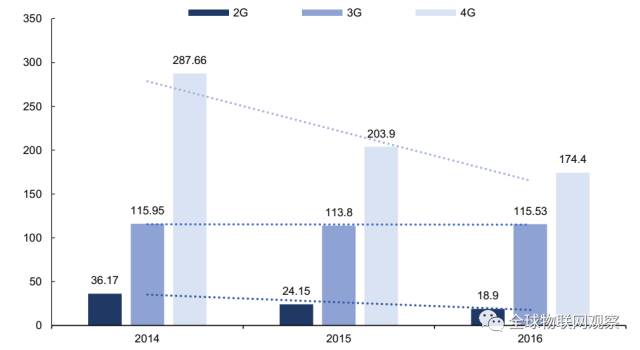
Currently, domestic wireless communication module suppliers are focusing more on the module business itself. However, the standardized nature of pure module business leads to high price transparency and limited premium space. International leading companies have begun to explore new directions for module business development, which is worth learning from for newcomers.
Canada’s Sierra Wireless, established in 1993, is the world’s first cellular communication module supplier, offering a full product line including 2G, 3G, 4G, LPWA modules, Bluetooth, WiFi, and GNSS. Its module business has become an undisputed industry leader.
To improve overall business profitability and open up growth spaces, Sierra Wireless has been building an “end + cloud + application” one-stop solution service through self-research and acquisitions.
Sierra’s recent acquisition events

Based on its hardware business (modules), the company launched the AirVantage Cloud platform, and in 2014 introduced the Linux-based open-source embedded platform LegatoTM, followed by the open-source hardware design project MangOH in 2015. Using these two service platforms along with the AirVantage cloud platform, the company can provide complete IoT platform service capabilities.
Alongside communication modules, Sierra Wireless has launched a series of smart routers and gateways, as well as management tools and applications, providing cellular connectivity services based on specific customer requirements. All cellular gateways can be remotely monitored, managed, and controlled via the AirVantage Cloud platform.
In specific vertical application fields, the company entered the vehicle networking market by acquiring GenX in 2016, completing the full business extension of the “end + cloud + application” solution.
Sierra’s business layout

How is the transformation going? From Sierra Wireless’s financial reports, it can be seen that the introduction of the IoT platform has steadily improved its gross margin level, and the company believes that the platform business will continue to play an important role, expecting to contribute about 70% of revenue by 2021.
From the industrial chain to manufacturers and future trends, seeing this, I believe you now have a comprehensive understanding of the wireless communication module industry.
Note: The relevant data for this article is sourced from:
1.07-20 Guosen Communication — “IoT Discussion II: Communication Modules in Shared Bicycles”
2.08-29 CITIC Construction Investment — “IoT Deep Report Series V: Wireless Modules, Enabling Connectivity and Positioning for Everything”
3.09-22 Guosen Securities — “Research and Reflection on the Wireless Communication Module Industry”
Previous Recommendations
-
Alibaba and several smart lock giants released a white paper stating: By 2020, China’s smart lock industry scale will reach 32 million units (full text attached)
-
IoT Chips Overview: Industry Scale and Global Chip Suppliers
-
Four Questions You Need to Know About IoT Projects!
-
Still obsessed with unmanned retail? Unmanned warehousing is the new blue ocean
-
What to do if elevators malfunction? The IoT provides solutions
