Automotive sensors are one of the key components of the automotive electronic control system and the main source of information in the automotive electronic control system. With the rapid development of technology, the cost proportion of electrical and electronic equipment in automobiles is increasingly high, and the number of sensors in cars is also rising. Currently, an ordinary family car has about dozens to nearly a hundred sensors, while luxury cars can have up to two hundred sensors.
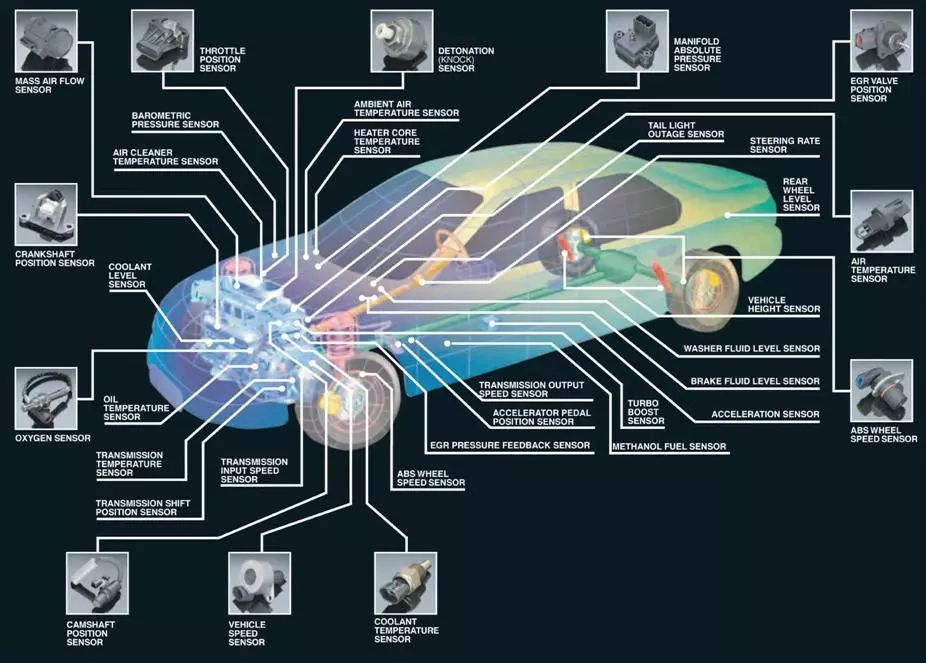
The main function of automotive sensors is to measure or detect the working parameters of related components in various operating states of the vehicle and convert them into standard electrical signals sent to the Electronic Control Unit (ECU). The ECU processes this information and issues commands to control the actuators in a timely manner. Automotive sensors are mainly used in the engine control system, chassis control system, and body control system.
1. Main Types of Automotive Sensors
There are many types of automotive sensors, and sometimes different types of sensors can be used to measure the same parameter. Similarly, the same type of sensor can often measure multiple parameters. Automotive sensors are generally classified according to the measured parameters: mainly including temperature, pressure, speed and acceleration, position, flow, liquid level, gas concentration, etc. The corresponding sensors for the measured parameters in automobiles are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Types of Common Automotive Sensors
|
Serial No. |
Type |
Measured Parameter |
|
1 |
Flow Sensor |
Intake flow, fuel flow, refrigerant flow, exhaust recirculation flow, etc. |
|
2 |
Pressure Sensor |
Intake manifold pressure, fuel pressure, automatic transmission oil pressure, brake fluid pressure, tire pressure, etc. |
|
3 |
Position and Angle Sensor |
Cylinder position, camshaft position, throttle position, steering wheel angle, accelerator pedal position, front and rear suspension height, vehicle height, etc. |
|
4 |
Temperature Sensor |
Coolant temperature, exhaust temperature, intake temperature, fuel temperature, hydraulic oil (automatic transmission) temperature, inside and outside air temperature, etc. |
|
5 |
Speed and Acceleration Sensor |
Cylinder speed, vehicle speed, wheel speed, acceleration, etc. |
|
6 |
Liquid Level Sensor |
Fuel level, coolant level, oil level, electrolyte level, windshield washer fluid level, brake fluid level, etc. |
|
7 |
Gas Concentration Sensor |
Oxygen concentration, carbon dioxide concentration, lean mixture concentration, smoke concentration, NOx concentration, etc. |
|
8 |
Other Sensors |
Engine knock, collision, air humidity, light intensity, raindrop detection, etc. |
(1) Air Flow Sensor
The function of the air flow sensor is to detect the amount of air intake into the engine and convert this information into an electrical signal input to the ECU, allowing the ECU to determine the optimal fuel injection amount and ignition timing. It is usually installed between the air filter and the throttle. Currently, common types include: vane type, Karman type, hot wire type, and hot film type.
Figure 1 shows the composition and working principle of the vane type air flow meter. Figure 2 shows the composition and working principle of the optical Karman vortex air flow meter.
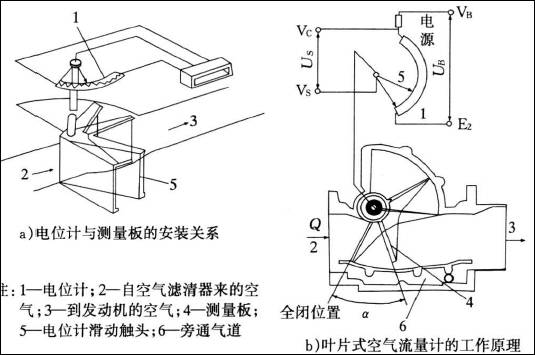 ▲ Figure 1: Composition and Working Principle of Vane Type Air Flow Meter
▲ Figure 1: Composition and Working Principle of Vane Type Air Flow Meter
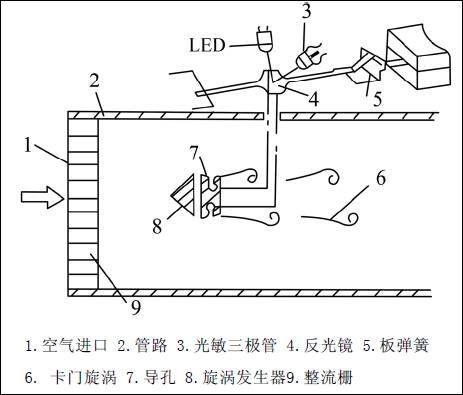 ▲ Figure 2: Composition and Working Principle of Optical Karman Vortex Air Flow Meter
▲ Figure 2: Composition and Working Principle of Optical Karman Vortex Air Flow Meter
(2) Pressure Sensor
The main function of the pressure sensor is to detect the pressure of gases or liquids and convert these pressure signals into voltage signals. Common pressure sensors in automobiles include intake manifold pressure sensors, engine oil pressure sensors, tire pressure sensors, etc. Figure 3 shows the composition of the tire pressure monitoring system.
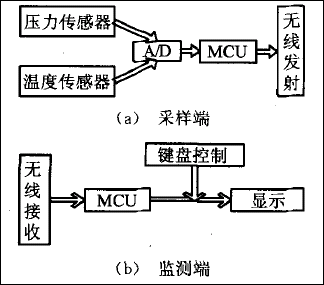
▲ Figure 3: Composition of Tire Pressure Monitoring System
(3) Position and Angle Sensor
Sensors that detect position and angle in automobiles mainly include crankshaft position sensors, throttle position sensors, liquid level sensors, vehicle height sensors, etc. Figure 4 shows the working principle of the magnetic induction crankshaft position sensor. Figure 5 shows the working principle of the Hall effect crankshaft position sensor.
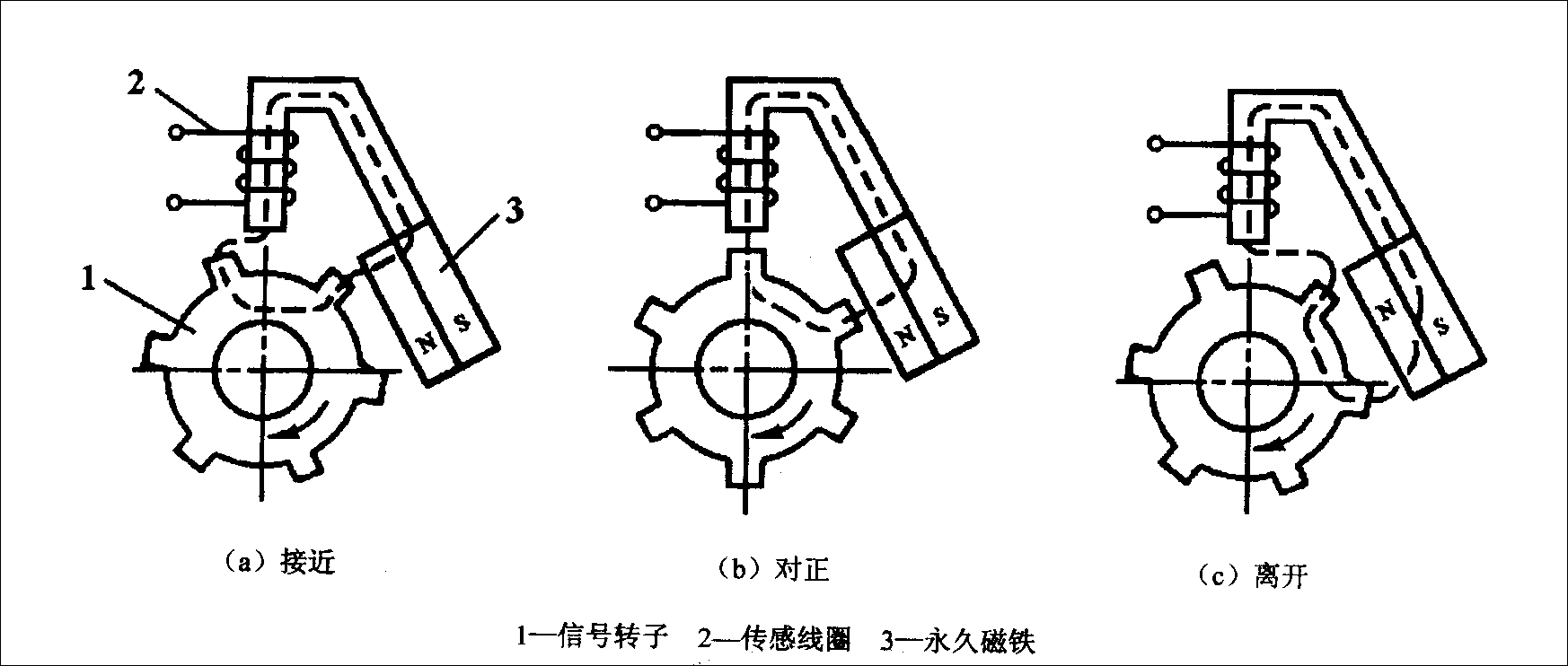 ▲Figure 4: Working Principle of Magnetic Induction Crankshaft Position Sensor
▲Figure 4: Working Principle of Magnetic Induction Crankshaft Position Sensor
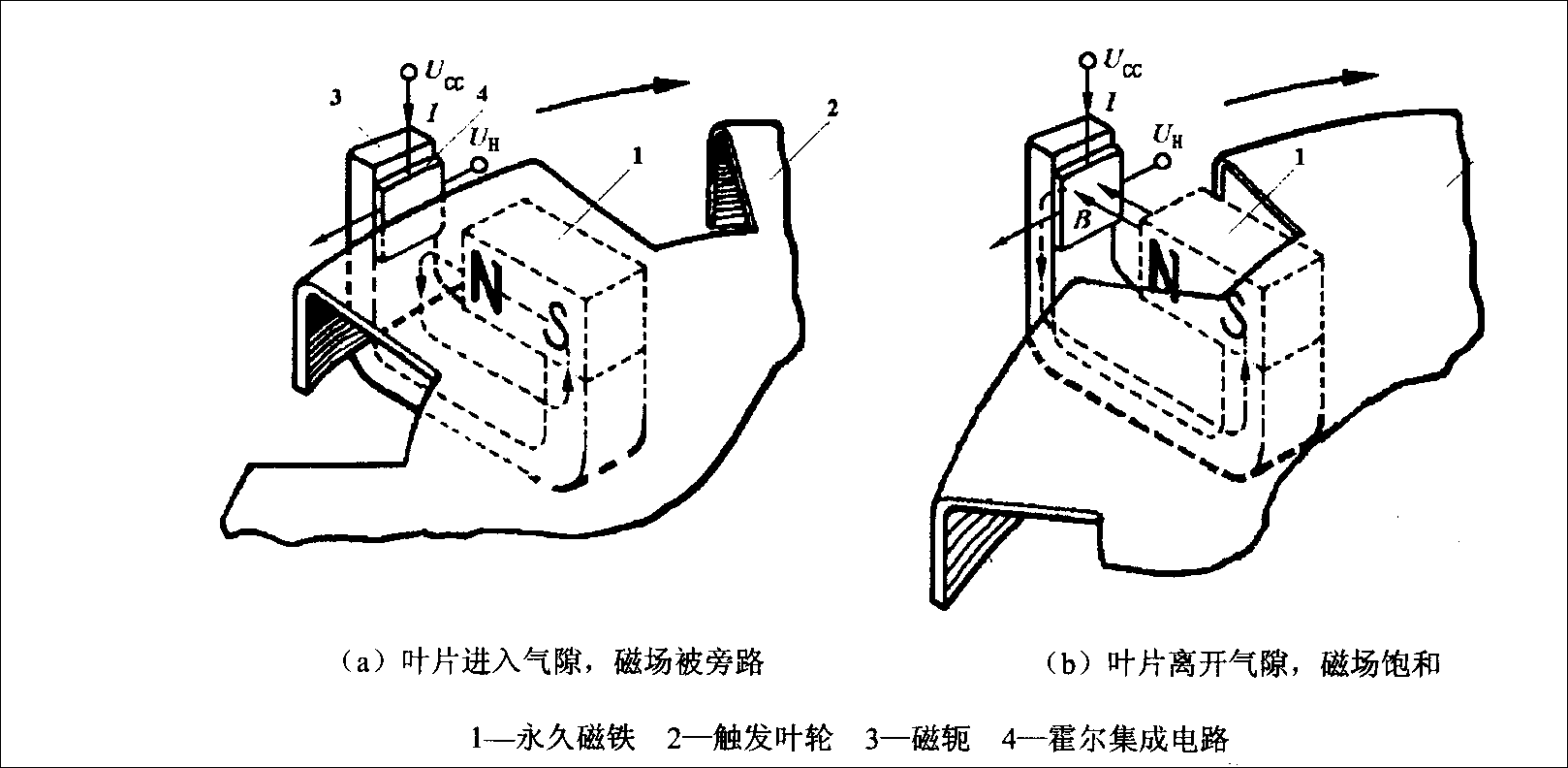 ▲ Figure 5: Working Principle of Hall Effect Crankshaft Position Sensor
▲ Figure 5: Working Principle of Hall Effect Crankshaft Position Sensor
(4) Temperature Sensor
Currently, temperature sensors in automobiles mainly include thermistor type and thermoelectric type. The thermistor type is widely used, such as coolant temperature sensors installed on coolant pipelines, air temperature sensors inside (installed under the windshield) and outside (installed in the front bumper), intake temperature sensors in the intake manifold, and exhaust temperature sensors on the three-way catalytic converter; the thermoelectric type is mainly used for controlling the cooling fan of the radiator.
(5) Speed and Acceleration Sensor
Speed sensors in automobiles mainly include engine speed sensors and vehicle speed sensors. Acceleration sensors detect negative acceleration (deceleration) and are mainly used to detect the deceleration of the vehicle during braking. Figure 6 shows the working principle of the variable reluctance speed sensor.
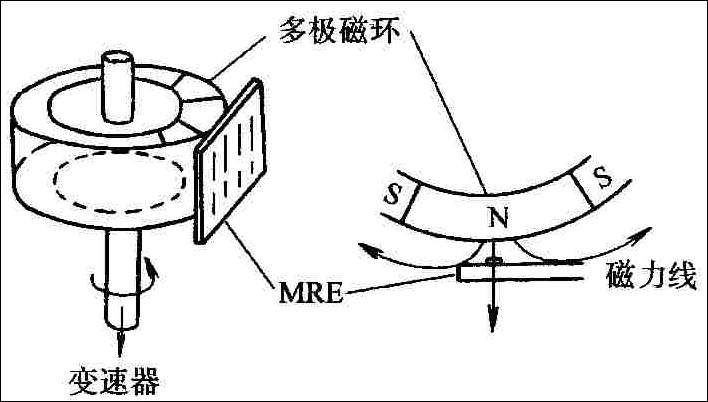 ▲Figure 6: Working Principle of Variable Reluctance Speed Sensor
▲Figure 6: Working Principle of Variable Reluctance Speed Sensor
(6) Knock and Collision Sensors
Knock sensors are primarily used to detect engine knock conditions.
Collision sensors are generally used in airbag systems and are the main signal input device in airbag systems. When a collision occurs, the detected collision intensity signal is sent to the airbag ECU, which determines whether to trigger the gas generator to inflate the airbag based on this signal.
(7) Gas Concentration Sensors
Gas concentration sensors in automobiles mainly include oxygen sensors and lean mixture sensors.
The function of the oxygen sensor is to detect the oxygen content in the exhaust after combustion in the engine, usually installed on the exhaust pipe of the engine.
The lean mixture sensor is used in the feedback control system of the engine’s lean combustion air-fuel ratio. Its function is to measure the oxygen concentration in the exhaust using zirconia elements to determine the air-fuel ratio, enabling feedback control of the air-fuel ratio under ultra-lean combustion conditions, thereby reducing fuel consumption and harmful gas emissions.
2. Classification of Common Automotive Sensors
Common sensor product information, recommended tax numbers, and classification criteria are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 is lengthy; please click the link at the bottom Read Original to view.
(Download link: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1mhfD6Ve)
The above views are for reference only; please correct any inaccuracies.
Author: Wen Chaozhu, Shanghai Customs College
Editor and Publisher: Dai Jun

