Nowadays, high-speed, large-capacity microSD and SD cards have become the most popular storage products for every imaging worker and digital photography user. As the school season approaches, many people’s vlogging cameras and DSLRs need new cards. So, what specifications of SD cards should you buy?

Three Sizes, Five Classes
All SD cards (Secure Digital) use one or two small NAND chips (similar to those found in USB drives and solid-state drives) and a microprocessor (similar to the controller in SSDs) to manage data flow and commands.
There are three standard sizes of cards: standard SD card 32 x 24 x 2.1-1.4 mm, miniSD card 21.5 x 20 x 1.4 mm, and microSD (TF) card 15 x 11 x 1 mm. Currently, the most common are standard SD cards, primarily used in digital imaging devices, and microSD cards, mainly used in smartphones.
Within the size classifications, there are five categories, representing the card’s connection system and data capacity, which you must have often seen on e-commerce platforms:
SD or SDSC (Secure Digital Standard Capacity): maximum storage capacity of 2 GBSDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity): storage capacity from 2 GB to 32 GBSDXC (Secure Digital Extended Capacity): storage capacity from 32 GB to 2 TBSDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity): storage capacity from 2 TB to 128 TBSDIO (Secure Digital Input Output): not only includes storage functions but also has an additional device that provides extra functionalities like Bluetooth, WIFI, or GPS receivers.

SDSC is limited to FAT12, FAT16, and FAT16B partition formats, suitable for older digital devices. SDHC is mostly FAT32, providing the best read-write compatibility. SDXC/HC versions use exFAT file format, which is specifically designed for NAND flash storage, but there are minor compatibility issues across multiple systems.
Speed: A Variety of Standards Reflecting Manufacturer Strength
All SD cards use small brass contacts at the card’s end to send and receive data. The interface between the card and the reading device evolves with each specification revision; in some cases, the updated standard simply runs faster, but in other cases, manufacturers often provide more data channels by adding extra contacts.
Ultimately, these differences are categorized into the four most mainstream speed classes, each represented by peak bus throughput (i.e., the maximum number of bytes that can be transferred per second between the SD card and the host device).
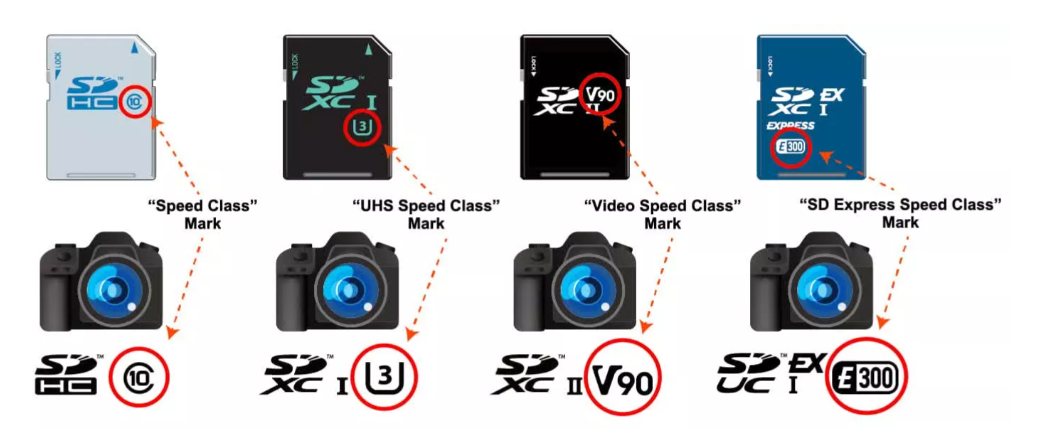

You may have seen on the card surface, numbers like “class10/C10”, “U3”, “V900”, “E300”, which are actually indicators of these currently mainstream speed classes.

The SD Association has established a speed classification system to help distinguish which card is best suited for which purpose. The numbers are the most direct indicators of SD card speed; Class 2 indicates a read and write speed of 2 MB/s, which is the lowest in the standard. The commonly used Class 10 on smartphones indicates a read and write speed of 10 MB/s, sufficient for recording or playing back up to 4K video, although the frame rate is not very high.
Some SDHC and SDXC storage cards also support Ultra High Speed (UHS) classification, which can enhance data transfer rates. This system has three versions, with the earliest (UHS-I and UHS-II) providing two speed modes: U1 and U3. The former is essentially the same as C10, but U3’s throughput is three times higher than C10, reaching 30 MB per second, enough for shooting high frame rate 4K videos. This is where the U-marked SD cards come from.

UHS-I cards only have one set of contacts for sending and receiving information, so when running at higher speeds, the bus operates in a so-called half-duplex mode: the SD card can only receive or send data at any one time. Later versions of UHS added extra contacts, allowing for full-duplex communication (sending and receiving simultaneously); however, in UHS-II, this caused the bus to operate at lower speeds. UHS-III and SD Express do not have this issue and always operate in full duplex mode.
In SD Specification 5.0, the SD Association introduced another rating system: video speed. This is the origin of the SD cards marked with a V, which better conveys usage information, for instance, Video Class 10 (V10) is suitable for a minimum continuous write speed of 10 MB/s, up to Video Class 90 (V90 = 90 MB/s) storage cards. At this speed, 8K video can be recorded and played back at 60 to 120 fps.

Later, the SD Association released the SD Express specification, which uses up to 2 PCI Express lanes, significantly increasing throughput. Thus, ultra-high-speed cards emerged, marked with the letter E.
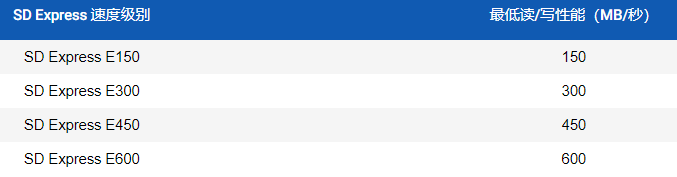
Regarding read and write speed class indicators and corresponding video shooting capabilities, you can refer to the table below.
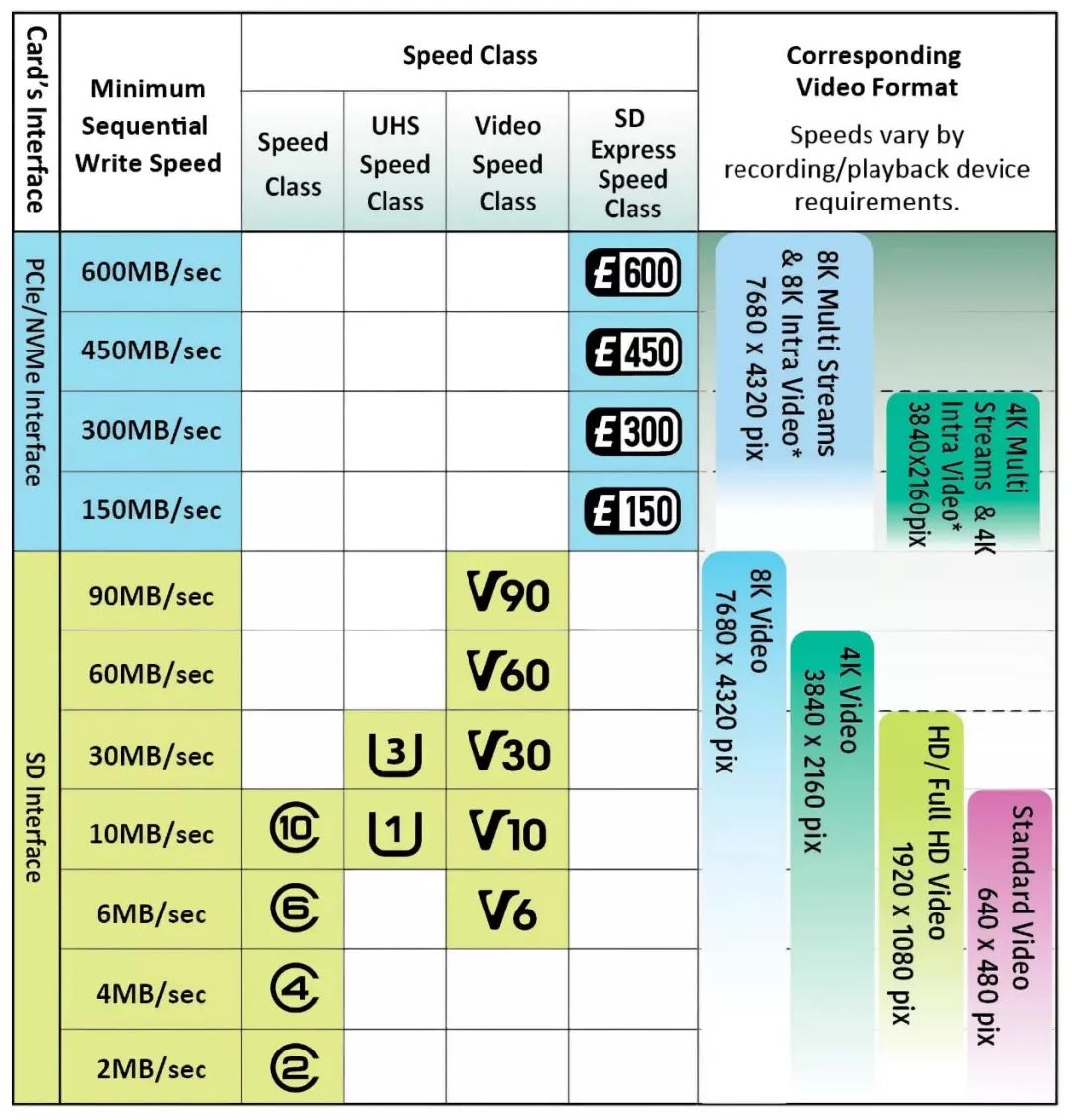
Therefore, a high-end card will often have all the applicable standards printed from high to low for promotional purposes, along with some actual performance metrics like XXXMB/s.

Finally, for cards that require frequent read and write operations, similar to those used as SSDs, such as various development boards, industrial computers, microcontrollers, Raspberry Pi, etc., the SD Association has also established a rating for random read/write IO performance: A1 and A2. A1 cards have a random read performance of 1500 IOPS and a random write performance of 500 IOPS, while A2 cards have significantly improved random read and write performance of 4000/2000 IOPS. However, their sustained continuous write speeds are only comparable to V10. But due to the niche market, it is generally hard to find cards labeled A1/A2 for sale in retail markets.

How Should I Choose a Card?
For most users, a cost-effective C10/U1/U3 level storage card is fast enough and has ample storage space. However, for more professional uses, ensure you purchase the best-performing storage card suitable for the corresponding tasks.
If you only occasionally shoot photos or videos, then buying mainstream brand C10 or higher SDHC cards will suffice.
If you want to provide fast storage and editing capabilities for your smartphone or tablet, you should focus more on fast random access and simultaneous reading of small files, which is IO performance. Consider purchasing products with A2 level IO performance and read/write performance above 100MB, such as SanDisk Extreme Pro 256 GB card, A2 level IO performance (4000/2000 IOPS), continuous read speed of 200 MB/s, and write speed of 140 MB/s.

To record videos on devices like drones and DSLRs, a mainstream resolution and frame rate require a storage card that meets UHS-II V60 specifications, with the SONY TOUGH series being one of the representatives and having certain rugged features.

If you want the best performance on full-size SD cards, then top SD cards like Lexar 2000x can achieve read speeds of up to 300 MB/s, with better sustained write speeds at larger sizes.

Editor: Xiong Le
·END·