Industrial robots are multi-joint mechanical arms or multi-degree-of-freedom robots designed for the industrial field.Industrial robots replace humans in production and are an important development trend in the future manufacturing industry, serving as the foundation for achieving intelligent manufacturing, as well as ensuring future industrial automation, digitization, and intelligence.The harsh production processing environment and the labor shortage caused by an aging population, along with high costs of human training, are driving the growth in demand for industrial robots.
Author and Source: Huashu Robot Technology Lecture Hall

Basic Components of Industrial Robots

Industrial robots consist of main body, drive system, control system as three basic components.
-
Main Body: This includes the base and the actuators, which consist of the arm, wrist, and hand; some robots also have a walking mechanism. The wrist part is also known as the end effector interface, where grippers, tools, sensors, etc., can be installed.
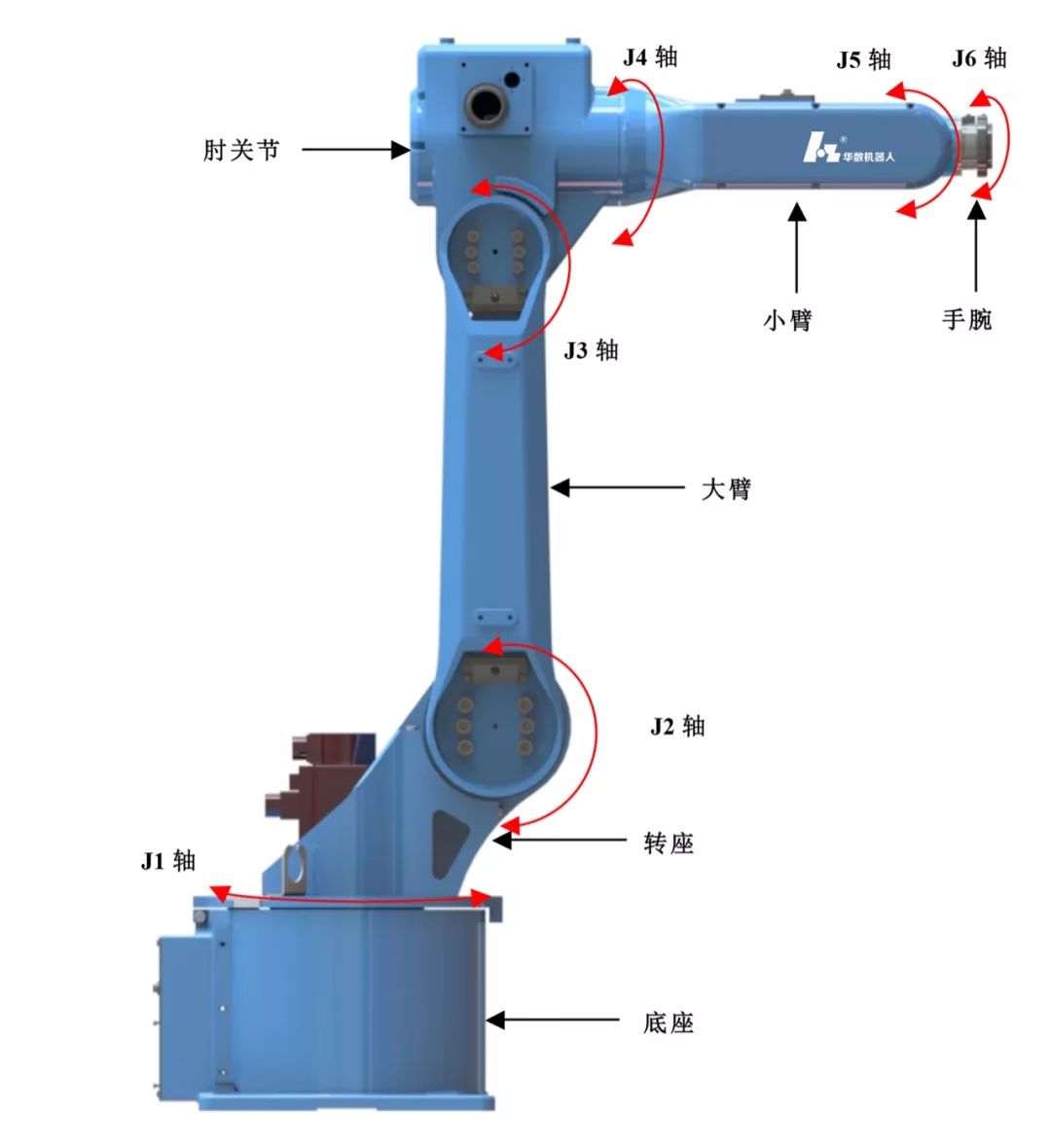
-
Drive System: This includes the power device and transmission mechanism, which enables the actuators to perform corresponding movements.
-
Control System: This issues command signals to the drive system and actuators according to the input program, controlling the industrial robot to act as required.
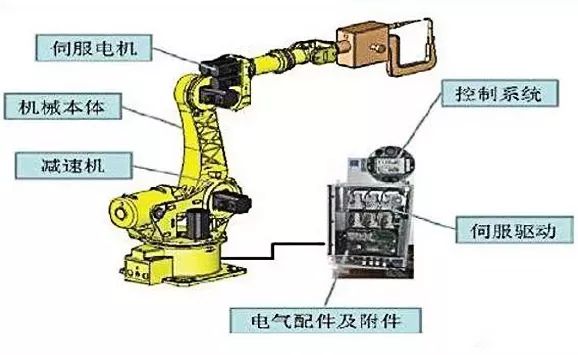

Classification of Industrial Robots

Classification by Joint Coordinate Form
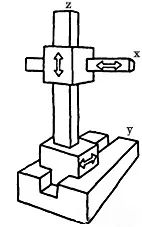
Rectangular Coordinate Robot (PPP)
The rectangular coordinate robot, also known as a single-axis manipulator, changes the spatial position of its end effector (hand) through the movement along three mutually perpendicular coordinates: x, y, and z axes.
Cylindrical Coordinate Robot (RPP)
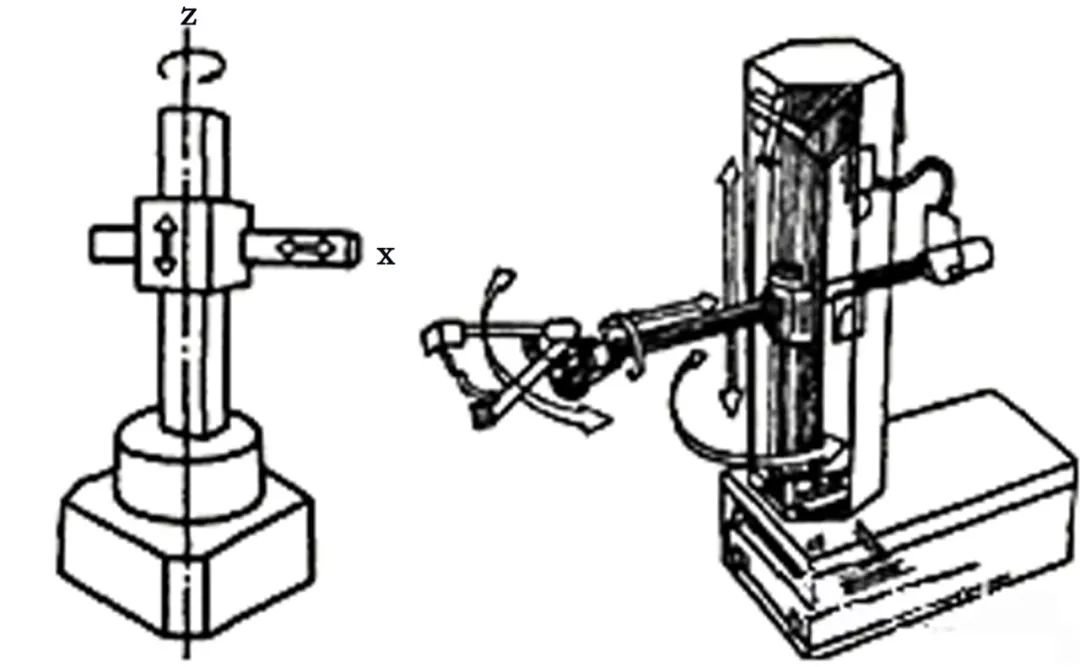
Spherical Coordinate Robot (RRP)
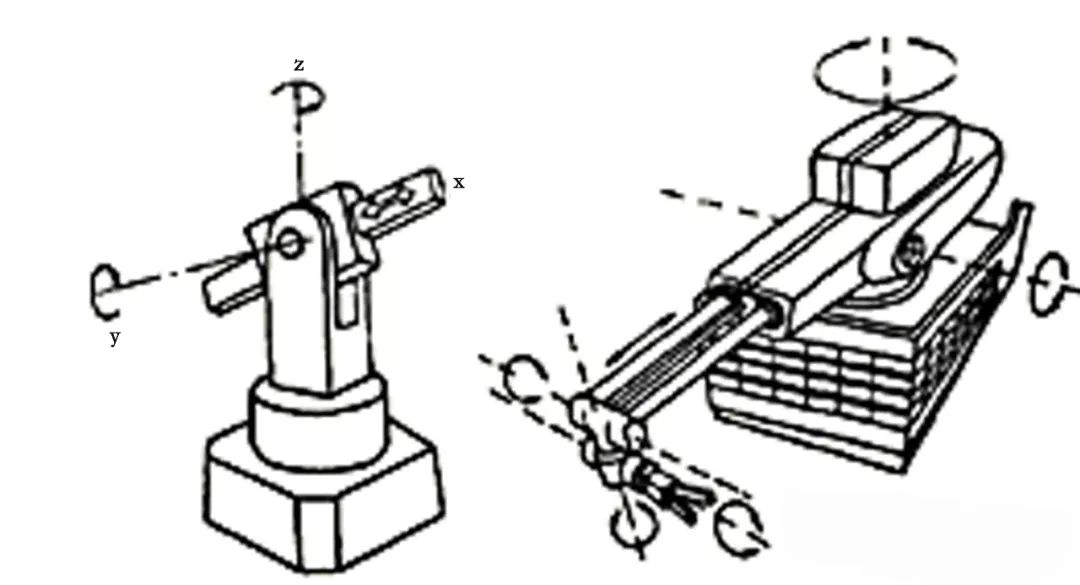
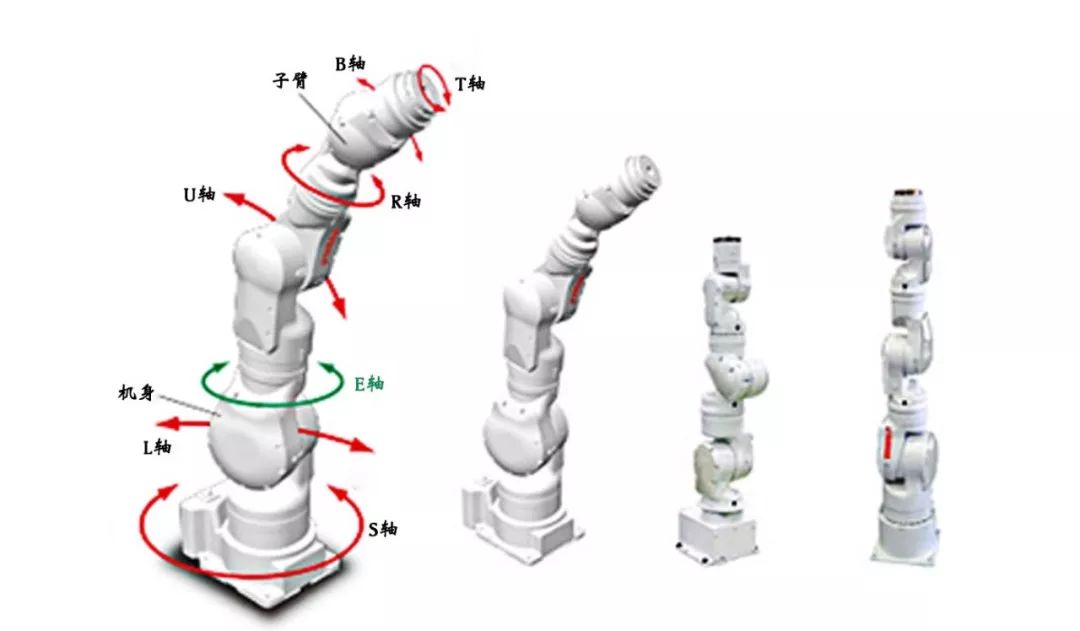
Joint Robot (RRR)

In addition, joint robots can also be classified according to their working nature, such as handling robots, palletizing robots, welding robots, painting robots, laser cutting robots, etc.
Classification by Number of Robot Axes
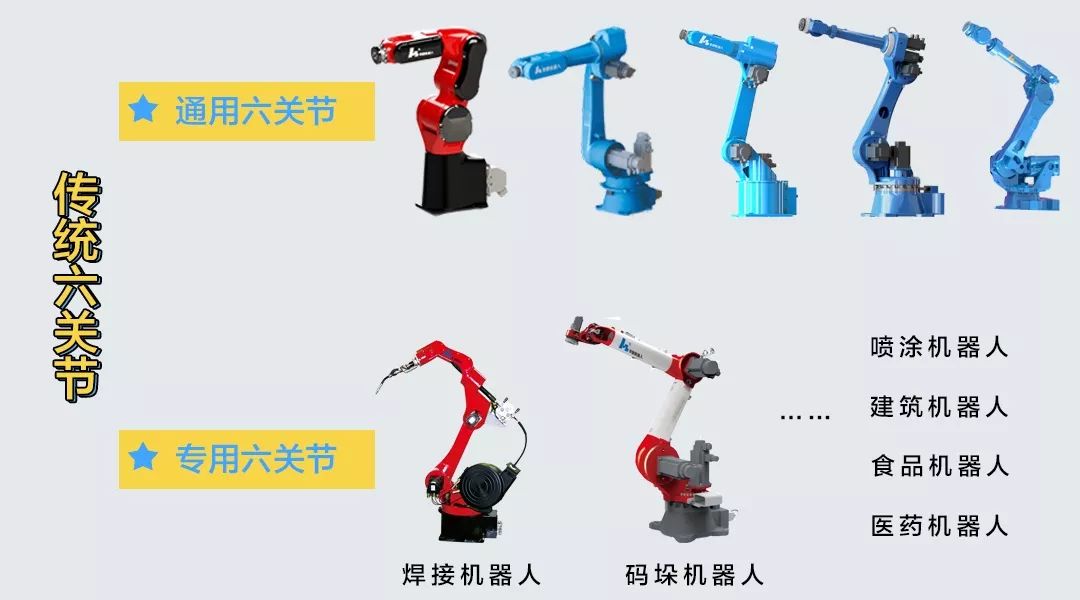
Traditional Six-Axis
Six-axis robots have six serial rotating joints, and traditional six-axis robots are divided into general-purpose six-axis robots and special-purpose six-axis robots.

Seven-Axis Robot
Also known as redundant robots. Compared to six-axis robots, the additional axis allows the robot to avoid certain specific targets, making it easier for the end effector to reach specific positions and adapt more flexibly to certain special working environments.
Collaborative Robot
Abbreviated as cobot or co-robot, it is a robot that can safely interact/contact directly with humans. Collaborative robots can combine the precision and repeatability of robots with the unique skills and capabilities of humans, where humans excel at solving imprecise and ambiguous problems, while robots have advantages in precision, strength, and durability.

Four-Axis/SCARA Robot
Four-axis robots refer to “Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm”. The arm of a four-axis robot can move freely in a geometric plane, i.e., it has translational degrees of freedom in the X, Y, Z directions and rotational freedom around the Z-axis.

Delta Parallel Robot
Delta robots are high-speed, lightweight parallel robots that typically capture target objects through teaching programming or vision systems, determining the spatial position of the tool center point (TCP) through three parallel servo axes, and performing operations such as transporting and processing target objects.
