Follow+Top Public Account, don’t miss out on exciting content

Materials Needed
-
PCB -
ESP8266 or NodeMCU -
Jumper wires -
Soldering tools
Step 1: Preparation


Step 2: Create a 7-segment display using Neo Pixel LED



<span>DOUT</span> to the second panel’s<span>DIN</span>.Step 3: Connect the dashboard


<span>Dash</span>, which contains 2 LEDs as binary digits that light up once every second.Step 4: Introduction to NodeMCU/ESP8266

Step 5: Supported functions in the code

-
Temperature and humidity display using tactile switch
-
Brightness control using LDR sensor on pin A0

Step 6: Video demonstration
Step 7: 7-segment clock
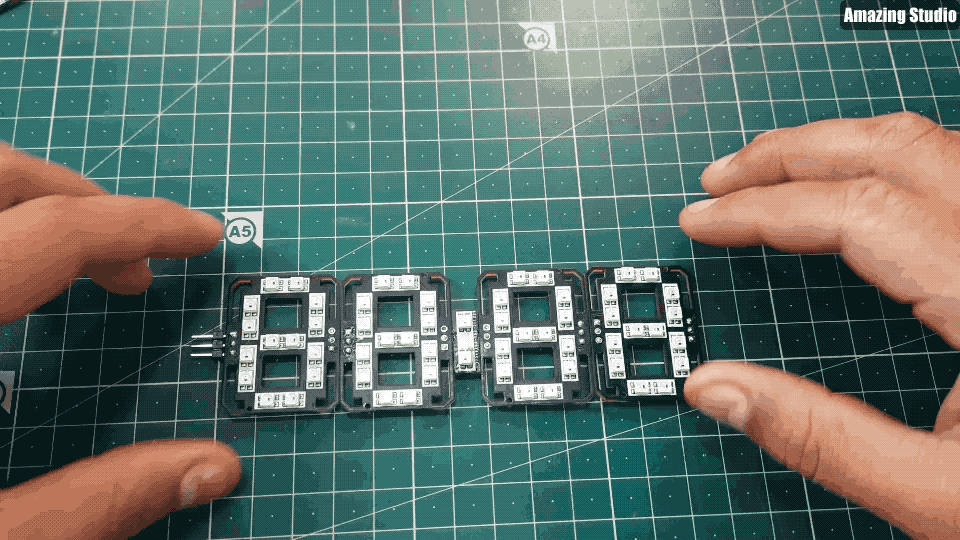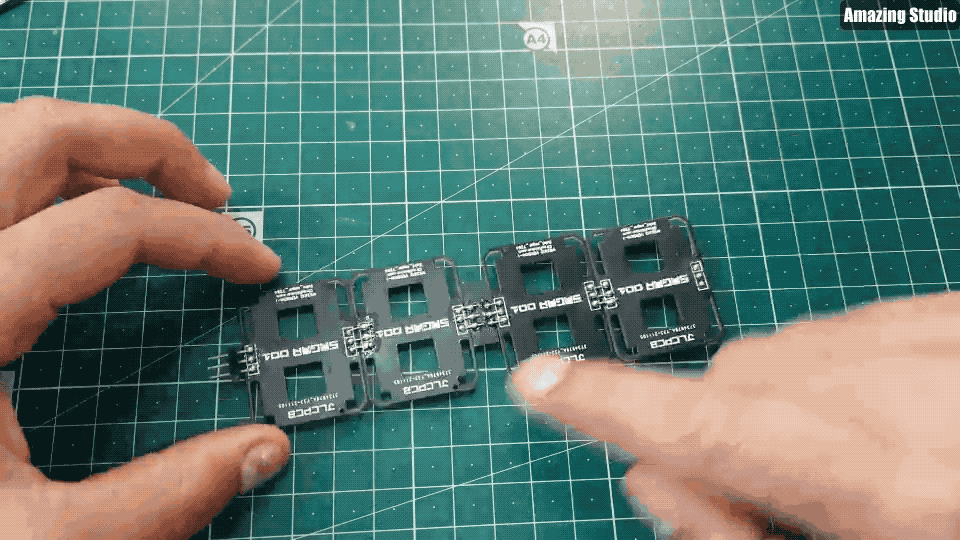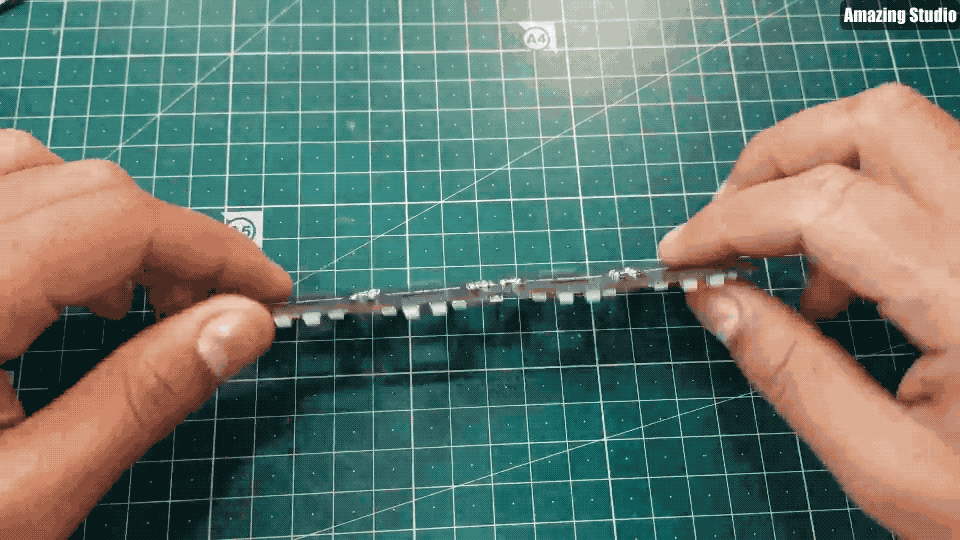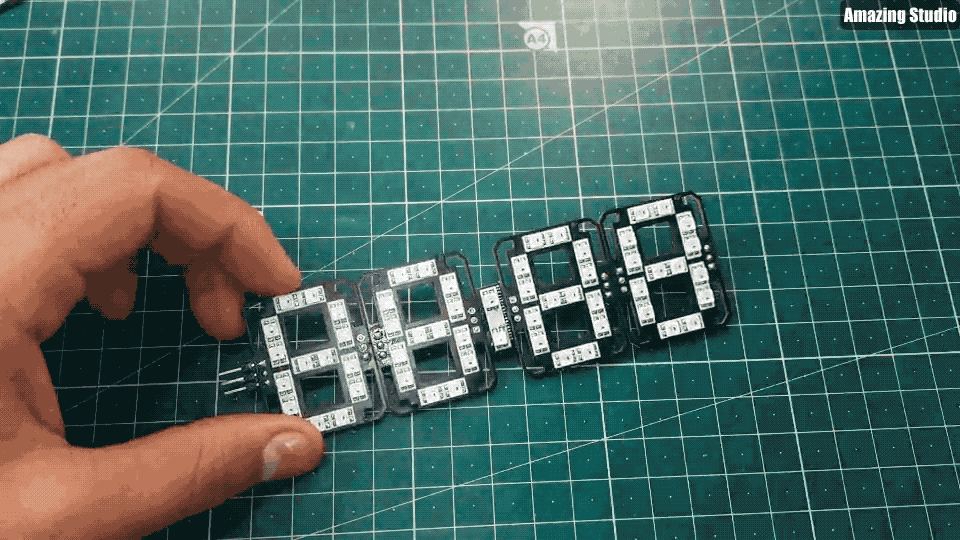

Step 8: Code
-
First, use libraries to initialize the code:
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#include <WiFiUdp.h>
#include <NTPClient.h>
#include <TimeLib.h>
#include <DHT.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
-
Define all pixels, I/O pins, and sensor pins:
#define PIXEL_PER_SEGMENT 2 // Number of LEDs in each Segment
#define PIXEL_DIGITS 4 // Number of connected Digits
#define PIXEL_PIN 2 // GPIO Pin
#define PIXEL_DASH 1 // Binary segment
#define LDR_PIN A0 // LDR pin
#define DHT_PIN 13 // DHT Sensor pin
#define BUTTON_PIN 12 // Button pin
3. For time format, connect ESP8266 to the internet via Wi-Fi:
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Connecting.");
while ( WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED )
-
Time setting:
void disp_Time() {
clearDisplay();
writeDigit(0, Hour / 10);
writeDigit(1, Hour % 10);
writeDigit(2, Minute / 10);
writeDigit(3, Minute % 10);
writeDigit(4, Second / 10);
writeDigit(5, Second % 10);
disp_Dash();
5. Color settings on the panel:
if (index == 0 || index == 1 ) color = strip.Color(0, Brightness, 0);
if (index == 2 || index == 3 ) color = strip.Color(0, Brightness, 0);
if (index == 4 || index == 5 ) color = strip.Color(Brightness, 0, 0);
Step 9: Complete code
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#include <WiFiUdp.h>
#include <NTPClient.h>
#include <TimeLib.h>
#include <DHT.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#define PIXEL_PER_SEGMENT 2 // Number of LEDs in each Segment
#define PIXEL_DIGITS 4 // Number of connected Digits
#define PIXEL_PIN 2 // GPIO Pin
#define PIXEL_DASH 1 // Binary segment
#define LDR_PIN A0 // LDR pin
#define DHT_PIN 13 // DHT Sensor pin
#define BUTTON_PIN 12 // Button pin
// Uncomment the type of sensor in use
#define DHT_TYPE DHT11 // DHT 11
//#define DHT_TYPE DHT22 // DHT 22 (AM2302)
//#define DHT_TYPE DHT21 // DHT 21 (AM2301)
#define TIME_FORMAT 12 // 12 = 12 hours format || 24 = 24 hours format
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel((PIXEL_PER_SEGMENT * 7 * PIXEL_DIGITS) + (PIXEL_DASH * 2), PIXEL_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
DHT dht(DHT_PIN, DHT_TYPE);
// set Wi-Fi SSID and password
const char *ssid = "Hackster";
const char *password = "Sainisagar7294";
WiFiUDP ntpUDP;
// 'time.nist.gov' is used (default server) with +1 hour offset (3600 seconds) 60 seconds (60000 milliseconds) update interval
NTPClient timeClient(ntpUDP, "time.nist.gov", 19800, 60000); //GMT+5:30 : 5*3600+30*60=19800
int period = 2000; //Update frequency
unsigned long time_now = 0;
int Second, Minute, Hour;
// set default brightness
int Brightness = 40;
// current temperature, updated in loop()
int Temperature;
bool Show_Temp = false;
//Digits array
byte digits[12] = {
//abcdefg
0b1111110, // 0
0b0110000, // 1
0b1101101, // 2
0b1111001, // 3
0b0110011, // 4
0b1011011, // 5
0b1011111, // 6
0b1110000, // 7
0b1111111, // 8
0b1110011, // 9
0b1001110, // C
0b1000111, // F
};
//Clear all the Pixels
void clearDisplay() {
for (int i = 0; i < strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, strip.Color(0, 0, 0));
}
strip.show();
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
strip.begin();
strip.show();
dht.begin();
pinMode(BUTTON_PIN, INPUT);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Connecting.");
while ( WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED ) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("connected");
timeClient.begin();
delay(10);
}
void loop() {
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED) { // check WiFi connection status
int sensor_val = analogRead(LDR_PIN);
Brightness =40;
timeClient.update();
int Hours;
unsigned long unix_epoch = timeClient.getEpochTime(); // get UNIX Epoch time
Second = second(unix_epoch); // get seconds
Minute = minute(unix_epoch); // get minutes
Hours = hour(unix_epoch); // get hours
if (TIME_FORMAT == 12) {
if (Hours > 12) {
Hour = Hours - 12;
}
else
Hour = Hours;
}
else
Hour = Hours;
}
if (digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN) == LOW) {
Show_Temp = true;
}
else
Show_Temp = false;
if (Show_Temp) {
Temperature = dht.readTemperature();
Serial.println(Temperature);
clearDisplay();
writeDigit(0, Temperature / 10);
writeDigit(1, Temperature % 10);
writeDigit(2, 10);
strip.setPixelColor(28, strip.Color(Brightness, Brightness, Brightness));
strip.show();
delay(3000);
clearDisplay();
Show_Temp = false;
}
while (millis() > time_now + period) {
time_now = millis();
disp_Time(); // Show Time
}
}
void disp_Time() {
clearDisplay();
writeDigit(0, Hour / 10);
writeDigit(1, Hour % 10);
writeDigit(2, Minute / 10);
writeDigit(3, Minute % 10);
writeDigit(4, Second / 10);
writeDigit(5, Second % 10);
disp_Dash();
strip.show();
}
void disp_Dash() {
int dot, dash;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
dot = 2 * (PIXEL_PER_SEGMENT * 7) + i;
for (int j = 0; j < PIXEL_DASH; j++) {
dash = dot + j * (2 * (PIXEL_PER_SEGMENT * 7) + 2);
Second % 2 == 0 ? strip.setPixelColor(dash, strip.Color(0,Brightness ,0)) : strip.setPixelColor(dash, strip.Color(0, Brightness,0));
}
}
}
void writeDigit(int index, int val) {
byte digit = digits[val];
int margin;
if (index == 0 || index == 1 ) margin = 0;
if (index == 2 || index == 3 ) margin = 1;
if (index == 4 || index == 5 ) margin = 2;
for (int i = 6; i >= 0; i--) {
int offset = index * (PIXEL_PER_SEGMENT * 7) + i * PIXEL_PER_SEGMENT + margin * 2;
uint32_t color;
if (digit & 0x01 != 0) {
if (index == 0 || index == 1 ) color = strip.Color(Brightness, 0, Brightness);
if (index == 2 || index == 3 ) color = strip.Color(Brightness, 0,Brightness);
if (index == 4 || index == 5 ) color = strip.Color(Brightness, 0, 0);
}
else
color = strip.Color(0, 0, 0);
for (int j = offset; j < offset + PIXEL_PER_SEGMENT; j++) {
strip.setPixelColor(j, color);
}
digit = digit >> 1;
}
}
Step 10: Complete circuit diagram


Step 11: PCB Design (Panel part)

Main PCB design for displaying numbers and other letters.
Step 12: PCB Design (Dash part)


Step 13: Troubleshooting
-
<span>DIN</span>must always be connected in series with<span>DOUT</span>; if connected incorrectly or disconnected from anywhere, the entire device will stop working; -
Connect the Dash as shown above;
-
Ensure all connections are soldered well; poor soldering can lead to data value and color changes;
-
When soldering, do not heat the printed circuit board too much; keep the temperature below 300 degrees.
Step 14: Complete showcase


Hope you all enjoy this project!
Click the public account below and reply with the keyword “020” to get the relevant source files and high-definition images
Original link: https://www.instructables.com/RGB-7-Segment-Clock-Using-ESP8266/
Original author: sainisagar7294 Translated first published in:DF Maker Community