
Since the last issue, we have entered the detailed analysis phase of the “Judgement and Reasoning” module in the civil service exam, so that students can supplement and deepen their knowledge based on a systematic understanding. This issue will specifically introduce the reasoning judgment module of the civil service exam, mainly covering the subdivision of question types, problem-solving ideas, and answering methods.
First, it is important to clarify that preparing for the civil service written exam is a relatively long-term process, usually requiring three to four months. I hope students can develop a good review plan based on their understanding of the exam questions and their own situation, and execute it diligently, making full use of this time!

1. Civil Service Exam Question Types
In the third issue, it was mentioned that the civil service exam is mainly divided into five modules: Common Sense Judgement (20 questions), Language Comprehension (40 questions), Quantitative Relationships (10-15 questions), Judgement and Reasoning (40 questions), Data Analysis (20 questions).
The judgement and reasoning module of the civil service exam is mainly divided into graphic reasoning, analogy reasoning, deductive reasoning, and scientific reasoning. These four types of questions have distinct styles, and everyone can focus on reviewing the weaker types.

2. Graphic Reasoning
2.1 Characteristics of Question Types
Graphic reasoning refers to deducing a type of rule based on several existing graphics. Due to the variety of rule types, graphic reasoning involves many knowledge points, and the difficult problems are highly comprehensive. The types of graphic rules can be divided into: positional, stylistic, quantitative, attribute, planar combination, and spatial (including views, hexahedrons, tetrahedrons, spatial combinations, and sectional diagrams).
2.2 Preparation Methods
List each type of rule from general to specific in a table or mind map format to establish a knowledge framework for graphic reasoning. The focus should be on question type characteristics, key points, and knowledge difficulties. The difficulty of graphic reasoning lies in identifying and finding the rules, so this systematic sequential judgment method can help us quickly locate the problem-solving points to avoid being at a loss when facing questions.
2.3 Problem-Solving Techniques
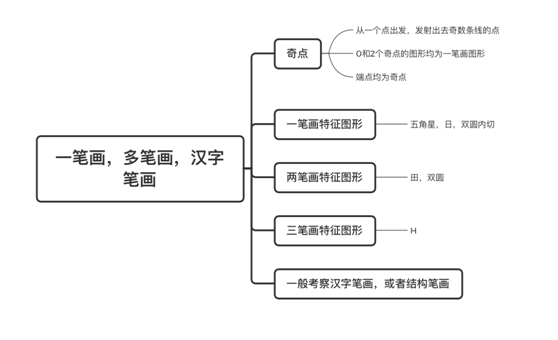
As shown in the figure below, taking the stroke question in the quantitative category as an example, if elements like pentagrams, sun characters, and double circles appear in the question, we can judge that this question tests the stroke question in the one-stroke category. Then we think about whether the figure can be drawn in one stroke, so we only need to find the figure that can be drawn in one stroke from the options.

3. Analogy Reasoning
3.1 Characteristics of Question Types
Analogy reasoning questions are a must-have question type every year. The stem is concise, often consisting of two or three commonly used words or idioms. The focus is still on finding the logical relationship between the stems, and the knowledge points tested mainly include four aspects: the extension and connotation relationships from a logical perspective, and the grammatical and semantic relationships from a linguistic perspective.
3.2 Preparation Methods
Fewer words in the stem also mean less information, making it easy to be unclear about the logical relationship being tested. Therefore, it is necessary to memorize the commonly tested logical relationships in analogy reasoning, which can be divided into the following four aspects:
1. Extension Relationship: The extension of a concept reflects the “quantity” of that concept, i.e., how many items conform to this concept. This means whether the two in the stem are in a contradictory relationship; for example, the “on: off” of a switch is a contradictory relationship, and there cannot be a third situation.
2. Connotation Relationship: The connotation of a concept reflects its “quality”, meaning the essence of a certain concept. For example, “cake: sweet” can be understood as the cake itself being sweet, while in “weather: sunny”, sunny is not a necessary attribute of weather, hence not the essence of this concept.
3. Grammatical Relationship: The relationship between verb and object, subject and predicate, and modifying phrases.
4. Semantic Relationship: Synonyms, antonyms, commendatory words, derogatory words, neutral words, metaphorical meanings, and symbolic meanings.
3.3 Problem-Solving Techniques
First, determine the logical relationship in the stem, which is one of the relationships mentioned above. Then, use the options to solve the problem; whether the direct relationships of the four options are the same as the stem needs to exclude incorrect or similar logical relationships. When encountering common sense questions, you can also use sentence construction methods to judge whether the structure is smooth and reasonable.

4. Deductive Reasoning
4.1 Characteristics of Question Types
Deductive reasoning mainly involves necessary reasoning and possible reasoning. Necessary reasoning includes translation reasoning, true-false reasoning, and analytical reasoning. Possible reasoning includes premise assumptions, strengthening arguments, weakening arguments, argument flaws, parallel structures, cause explanations, and inductive reasoning.
4.2 Preparation Methods
1. Necessary Reasoning: The focus is on identifying common contradictory relationships and opposing relationships in true-false reasoning, using methods like keyword extraction, listing, maximum information, determining information, and elimination to arrive at the correct answer after excluding incorrect options, avoiding spending too much time on forced reasoning without looking at the options. Additionally, it is essential to study the translation and reasoning techniques for sufficient and necessary conditions.
2. Possible Reasoning: The focus is on mastering the extraction techniques of reasoning structures in parallel structures, including letter substitution and translation methods, while also mastering methods for finding arguments and evidence in arguments, and analyzing models for strengthening, weakening, and flaws in arguments.
4.3 Problem-Solving Techniques
In the following example, first identify the question type, which asks for the “most effective explanation”; therefore, it is a possible reasoning cause explanation. Then analyze the stem; it can be seen that “logical thinking ability is one of the most important abilities of a person” contradicts “most schools do not offer specialized courses to cultivate logical thinking ability”. Therefore, using the elimination method, we sequentially judge the correctness of the options. A’s “some teachers do not have a clear understanding of how to cultivate logical thinking ability” and B’s “people’s logical thinking ability often improves naturally with knowledge and social experience” are unrelated to “there are no relevant courses”, so they are excluded. C contradicts the information in the stem, so it is excluded. D explains why there are no specialized courses to cultivate logical thinking by referring to “the core of most course designs”; therefore, it aligns with the question.
Example question: Logical thinking ability is one of the most important abilities of a person, but most schools do not offer specialized courses to cultivate logical thinking ability. Which of the following options, if true, most effectively explains this phenomenon?
A. Some teachers do not have a clear understanding of how to cultivate logical thinking ability
B. People’s logical thinking ability often improves naturally with knowledge and social experience
C. Most universities offer public elective courses on logical thinking ability
D. The core of most courses in schools is to enhance students’ logical thinking ability
[Answer] D

5. Scientific Reasoning
5.1 Characteristics of Question Types
Scientific reasoning mainly tests scientific knowledge, involving physics, chemistry, biology, and geography. Among them, physics is tested relatively frequently.
5.2 Preparation Methods
For this type, preparation is a process of literacy improvement; everyone needs to review based on the characteristics of the exam in their target province. The following are common test points:
1. Physics: Motion of objects (Newton’s laws of motion in kinematics, common motions, work and energy), mechanics (basics of force, balance of forces, buoyancy), electricity (basic formulas, circuit analysis, circuit design), optics (reflection and refraction in optics), acoustics, work and mechanical energy, pressure and stress
2. Chemistry: Classification of substances, chemical properties and composition of substances, properties and uses of common gases and solutions, common chemical reactions and phenomena, etc.
3. Biology: Cell biology, ecosystems, photosynthesis and respiration, genetics, etc.
4. Geography: Earth information, atmospheric movement, differences in natural environments, etc.
| Huazhong University of Science and Technology 2022 Employment Group |
Comprehensive: 689981660
Manufacturing: 801639514
Construction: 103969453
Information: 723040544
2023 Internship Group: 477814911
Doctoral Employment Exchange Group: 985746529
Source | Huazhong University of Science and Technology Career Guidance and Service Center
Editor | Ding Minghui
Reviewer | Zhang Jiaqi
