1.What is aBSPEngineer?
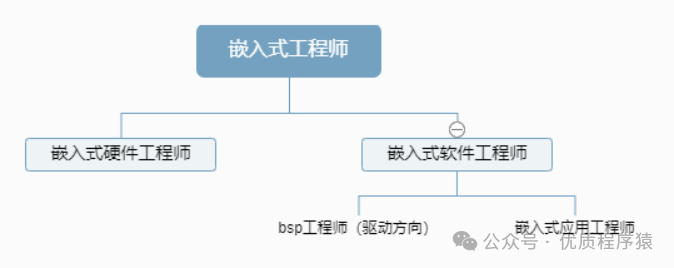
BSP, short for Board Support Package, refers to the software that supports the hardware of a specific board. A BSP engineer is a technical professional responsible for the development, debugging, and maintenance of the board support package, which is a subfield of embedded software engineering.So, what is a board support package? It is a layer between the mainboard hardware and the operating system’s driver layer, generally considered part of the operating system. Its main function is to support the operating system and provide a function package for upper-leveldrivers to access hardware device registers, enabling better operation on the hardware mainboard.
1. Industry Driving Factors
² Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing: Embedded systems are at the core of IoT devices. With the proliferation of 5G/6G and AIoT, fields such as smart homes, Industrial IoT (IIoT), and smart cities will require more BSP engineers for low-level driver development and hardware adaptation.
² Automotive Electronics and Autonomous Driving: New energy vehicles and autonomous driving technologies rely on high-performance ECUs (Electronic Control Units) and SoCs (such as Qualcomm and NXP chips). BSP engineers need to customize operating systems (like QNX and Linux Auto) for these platforms.
² AI Hardware Acceleration: The integration of AI chips (such as NPUs and GPUs) requires BSP engineers to optimize the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) to ensure efficient operation of AI frameworks (TensorFlow Lite, ONNX).
² Rise of the RISC-V Ecosystem: The popularity of the open-source RISC-V architecture will create new BSP demands, requiring engineers to adapt RTOS or Linux to customized RISC-V chips.
2. Technical Skill Requirements
Core Competencies:
² Proficient inC/C++ and assembly language (ARM/RTOS scenarios).
² Familiar with Linux kernel driver development, Device Tree, and U-Boot porting.
² Knowledgeable in hardware debugging tools (JTAG, oscilloscopes, logic analyzers).
Bonus Skills:
² Experience with real-time operating systems (FreeRTOS, Zephyr, VxWorks).
² Low-power optimization (for battery-operated devices) and security (Secure Boot, TrustZone).
² Understanding of heterogeneous computing (such as CPU+GPU+NPU collaborative scheduling).
3. Job Market Trends
Growing Job Areas::
² Semi-conductor Companies (such as NVIDIA, TI, Renesas): require BSP teams to support reference designs for their chips.
² Consumer Electronics / Automotive Tier 1 (Huawei, DJI, Bosch): rapid hardware product iterations, stable BSP demand.
² Startups: Small companies in fields like AIoT and robotics tend to prefer full-stack embedded talent.
² Salary Competitiveness: According to 2023 data, the annual salary for mid-level BSP engineers in first-tier cities is around 250,000 to 500,000 RMB, while senior experts (such as Linux kernel contributors) can earn over 800,000 RMB, with potential further increases by 2026.
4. Skill Requirements
² To become a BSP engineer, one needs to master the following skills:
² Familiarity with computer principles, Linux operating systems, processor architectures, and other foundational knowledge.
² Proficient in C language and some assembly language.
² Able to read and understand hardware schematics, modifying reference code based on schematics.
² Familiar with kernel porting, trimming, and other techniques.
² Master common interface protocols, such as I2C, SPI, UART, USB, etc.
5. Potential Challenges
² Impact of Automation Tools:
Some low-level development may be assisted by AI code generation tools (such as GitHub Copilot), but complex hardware adaptation still requires manual debugging.
² High Industry Barriers:
Requires knowledge of both hardware (circuit principles, timing analysis) and software (operating system principles), with talent supply growth potentially lagging behind demand.
² Fragmented Technology Stack:
Different manufacturers’ chips (such as STM32 vs. Allwinner) and RTOS version differences may lead to high skill transfer costs.
2.BSP Engineer Job Analysis
l No experience required:
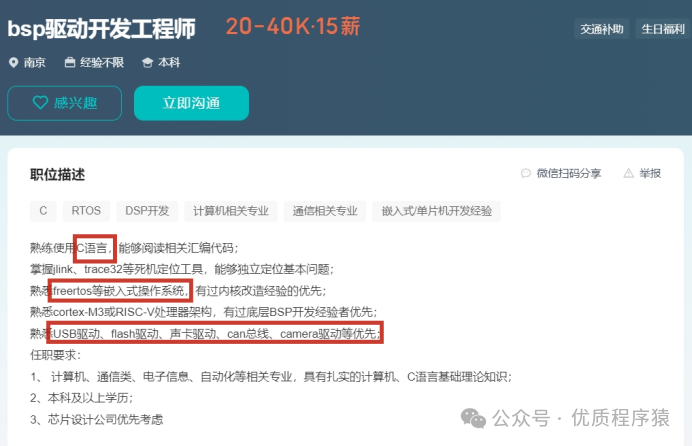
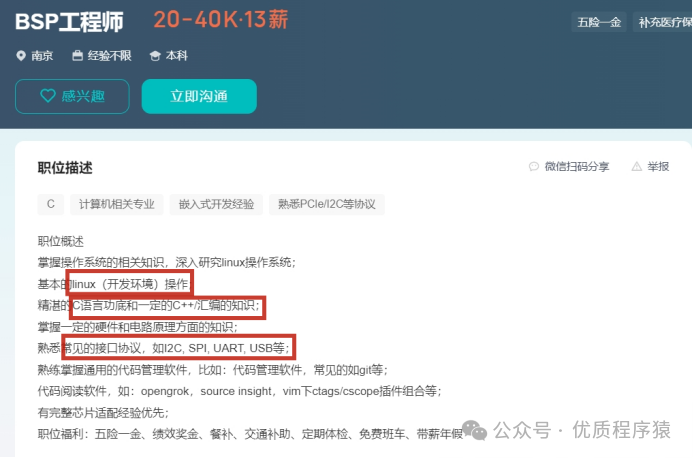

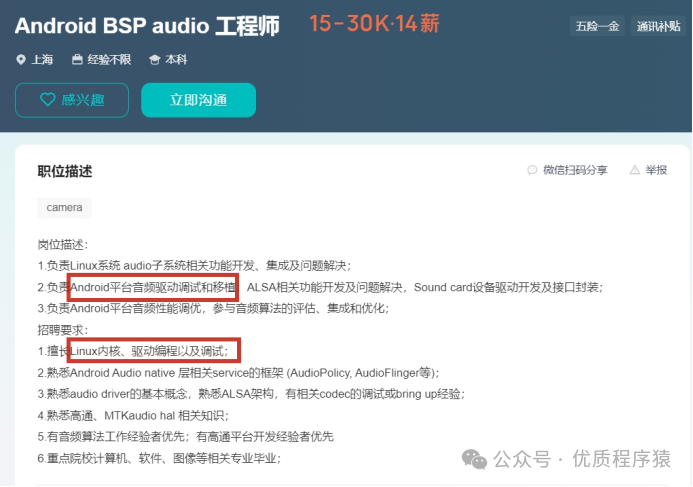
Salary situation: average around 20k
Knowledge to learn: C language, Linux, FreeRTOS, ARM development, common interface protocols, etc.
l 1-3 years of experience

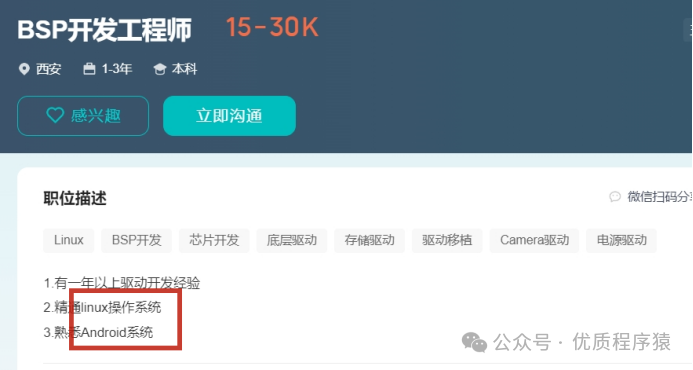
Salary situation: average around 25k
Knowledge to learn: Linux, Android system-related knowledge (the two found here are both Android-oriented, indicating that combining Linux and Android knowledge will significantly increase competitiveness).
l 3-5 years of experience

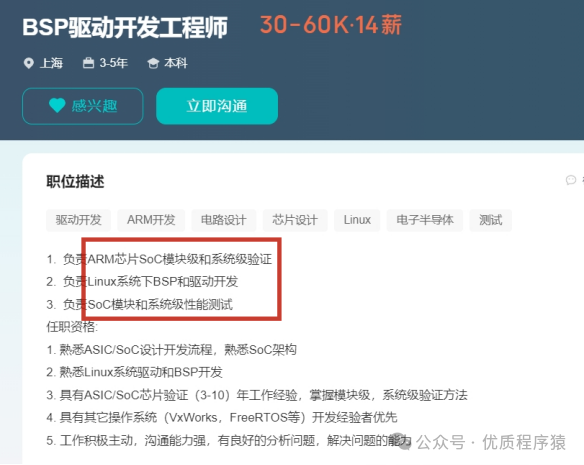
Salary situation: average around 30k
Knowledge to learn: Linux, Android, ARM, SoC, FreeRTOS, etc. (the two found here are more chip-oriented; students interested in the BSP chip direction can follow this path to learn).
l 5-10 years of experience
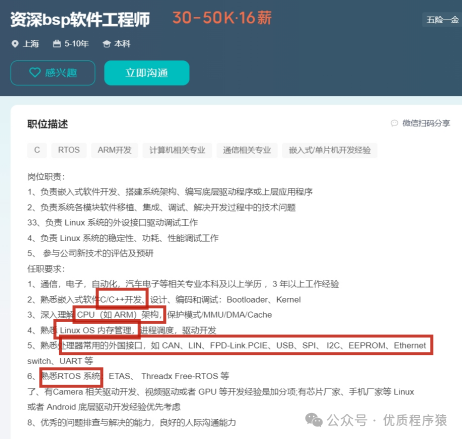
Salary situation: average around 35k
Knowledge to learn: C/C++, ARM, Linux, CAN/USB and various interface protocols, RTOS, etc.
l 10+ years of experience

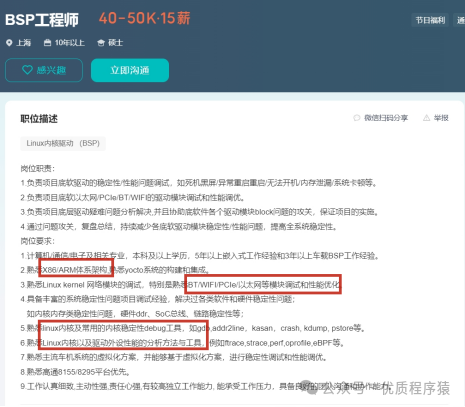
Salary situation: average around 40k
Knowledge to learn: C/C++, Linux, Android, ARM, debugging various modules such as WIFI.
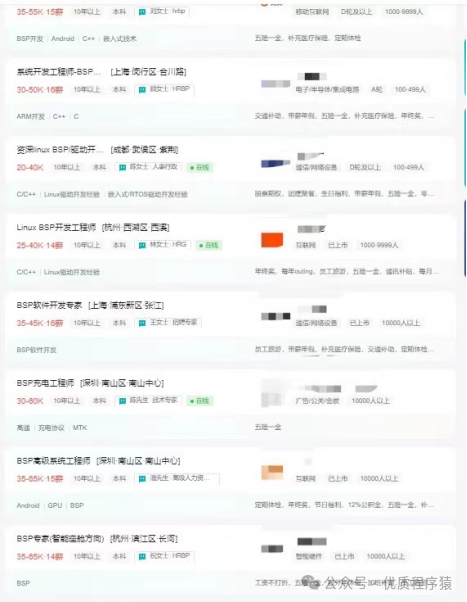
From this chart, it can be seen that there is still a high demand for positions with over 10 years of experience, and the offered salaries are quite attractive, so there is no need to worry too much about the so-called 35-year crisis.
3.Summary
Career Development Suggestions
² Vertical Deepening: Choose high-value areas (such as automotive functional safety ISO 26262, industrial-grade Linux Yocto projects).
² Horizontal Expansion: Learn FPGA collaborative design (Xilinx Vitis), wireless protocol stacks (BLE/Wi-Fi 6), to enhance system-level capabilities.
² Community Participation: Contributing to open-source projects (such as Zephyr OS, Linux kernel drivers) can enhance competitiveness.
In summary:
1. The BSP engineer position generally requires a bachelor’s degree or higher, so choosing this direction with only a diploma is quite risky.
2. Salary levels are also proportional to experience growth, and the salary situation during the zero-experience period is already quite considerable.
3. To engage in this position, it is crucial to focus on Linux, C language, ARM, and RTOS. One must study diligently. For those interested in specific subfields, such as Android, it is essential to study Android system knowledge; for those interested in chip directions, it is important to study ARM chips and SoC module-level knowledge; for those interested in automotive directions, it is important to study automotive electronics.

Learning Consultation

 Share
Share Collect
Collect View
View Like
Like