▍Data Security in the Internet of Vehicles
Enterprises should implement a series of security guarantees and support measures based on data security laws and regulations to ensure data security and personal information protection within smart connected vehicles, IoV platforms, and in-vehicle application services.
1. Classification and Grading of IoV Data
To conduct IoV data security protection activities more efficiently, enterprises should inventory their data for classification and grading, and clarify the security protection requirements for different categories and levels of data.
To have a clearer and more intuitive understanding of IoV data processing activities, targeted risk assessments, audits, and security management should be conducted, and the IoV data processing situation should be presented in plain, readable form to national regulatory authorities. Enterprises should inventory IoV data, clarifying the basic situation of data assets and the flow of data throughout its lifecycle, including but not limited to the following:
Data Fields: Clearly define the business processes related to the IoV, and organize the data fields involved in each IoV business process and their respective systems through technical scans and document reviews, forming a catalog.
Data Quantity: Identify and clarify the number of personal information subjects involved and the storage volume of important data.
Data Lifecycle Flow: Clarify the source of the data, storage location, processing methods and purposes, receiving parties, retention periods, and destruction methods.
(2) Classification and Grading of IoV Data
Enterprises should classify IoV data based on the results of the IoV data inventory, considering the attributes of IoV data and specific business scenarios. They should also grade IoV data according to the potential impact of unauthorized disclosure on the enterprise. Additionally, enterprises should label core and important data in accordance with relevant national laws and regulations.
(3) Lifecycle Security Management of IoV Data
Enterprises should define security management requirements for the entire lifecycle of IoV data based on different categories and levels, and carry out corresponding security management work.
Data Collection and Generation: Enterprises must adhere to the principles of legality and legitimacy, and must not collect data through theft or other illegal means.
Data Storage: Enterprises should store IoV data in accordance with legal and regulatory requirements and agreements with data subjects, employing security measures such as encryption, access control, and backups.
Data Processing: Enterprises should ensure the security of the IoV data processing process through measures such as access control and data backup and recovery.
Data Transmission and Provision: Enterprises should develop corresponding secure transmission strategies based on the type, level, and application scenario of the data being transmitted, such as encrypting the transmission of personal information and important data. If there is a need to provide data to third parties, enterprises should clarify their relationship with the data receiving party and specify the scope of IoV data provided to third parties, as well as the data security management responsibilities of both parties through contracts and agreements.
Data Disclosure: Enterprises should analyze whether disclosing IoV data would impact national security or public interest. If there are significant impacts, enterprises must not disclose IoV data.
Data Deletion: When the retention period for IoV data expires, enterprises should carry out data deletion activities and keep records of the deletion process.
2. Protection of Personal Information in IoV
Enterprises should ensure the protection of personal information in IoV in accordance with the Personal Information Protection Law and other relevant regulatory requirements.
Lifecycle Management of Personal Information: Enterprises should clarify the security requirements for personal information at each stage of its lifecycle in IoV, establishing differentiated control requirements and technical protection measures for different categories of personal information.
Exercising the Rights of Personal Information Subjects: Enterprises should establish convenient channels for personal information subjects in IoV to exercise their rights and complaints, and create internal response procedures to ensure that they can exercise their rights to know, decide, review, copy, transfer, correct, supplement, delete, and retain relevant processing records.
Impact Assessment of Personal Information Protection: Enterprises should conduct impact assessments for specific scenarios defined by law, such as processing sensitive personal information, cross-border transfer of personal information, automated decision-making based on personal information, entrusting the processing of personal information, and sharing with other personal information processors. The assessment should evaluate the legality, legitimacy, necessity of processing activities, and whether the protective measures are commensurate with the level of risk.
3. Data Security in IoV Applications
Assessment of IoV Data Security Protection Capabilities: Enterprises should assess their data security protection capabilities from multiple perspectives, including technology, management, and personnel capabilities, focusing on the confidentiality, integrity, availability of data, authentication and authorization, security monitoring, and response.
Data De-identification for IoV Application Services: Enterprises can use techniques such as de-identification, data encryption, data masking, data truncation, and data obfuscation to carry out data de-identification for IoV application services.
4. Cross-border Data Transfer in IoV
Enterprises should provide security protection for data collection and processing activities related to specific IoV applications, including the following:
For identified cross-border data transfer scenarios, enterprises should conduct a risk self-assessment before providing data to overseas parties. Based on the self-assessment results, enterprises should carry out security assessments for cross-border data transfers as necessary. Moreover, in accordance with relevant regulatory requirements, for scenarios requiring security assessments for cross-border data transfers, enterprises should report to the national cyberspace department through their provincial cyberspace department for approval of the security assessment of cross-border IoV data transfer.
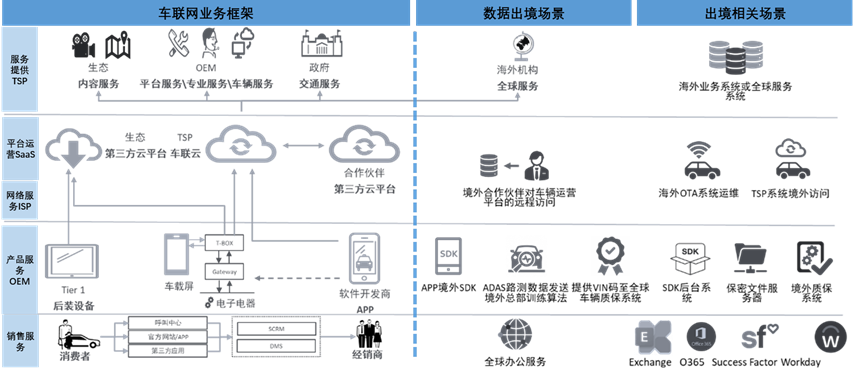
Common Cross-border Scenarios for Foreign and Joint Venture IoV Enterprises
▍Security of IoV Application Services
Enterprises should establish security requirements for IoV service platforms and applications, as well as security requirements for typical business application service scenarios, including platform security, application security, and service security.
1. Security of IoV Applications
Enterprises should conduct security assessments of IoV apps, including privacy statement assessments, penetration testing, and technical testing; based on the results of the security assessments, reasonable measures should be taken to address the security risks identified in IoV apps, thereby enhancing the overall security capability of the IoV apps and effectively preventing sensitive data within the apps from being tampered with, destroyed, disclosed, or illegally obtained and utilized.
Compliance Testing Framework for Mobile Apps by the Communications Authority
2. Security of IoV Services and Platforms
Enterprises should take necessary technical measures to enhance the security of IoV service platforms, including but not limited to:
Security for platform access for smart connected vehicles, roadside devices, and other platform facilities, as well as security for mainframes, data storage systems, and other platform application security protection capabilities;
Strengthening security and vulnerability detection for online upgrade services (OTA), remote information services for electric vehicles, etc.;
Properly classify the network security protection levels for IoV-related platforms, preventing risks such as network intrusion, data theft, and remote control.
At the same time, enterprises should protect services conducted in typical IoV business scenarios, including the security of interactions between IoV service platforms and in-vehicle terminals, network security for remote diagnostic services for IoV vehicles, network security for interactions between advanced driver-assistance systems and remote platforms, and network security for IoV vehicle-road collaboration services.
▍Security of IoV Communication
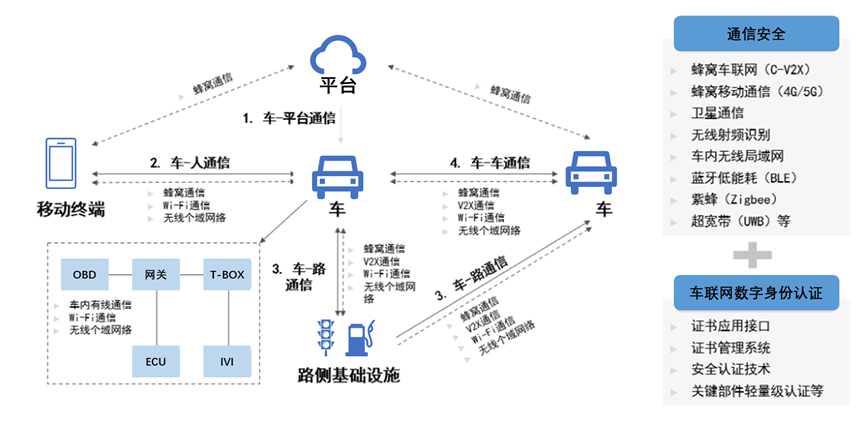
Enterprises should implement technical measures such as encryption, identity authentication, and data verification for communication connections, protocols, transmissions, and interfaces, to ensure the security of various communications within the vehicle, between the vehicle and the platform, between vehicles, and between the vehicle and the road, as well as between the vehicle and people, such as cellular networks, V2X, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, UMB, WPAN, etc., preventing risks such as communication information forgery, data tampering, and replay attacks.
Common Communication Networks in Smart Connected Vehicles
▍Network Security for IoV Terminals and Facilities
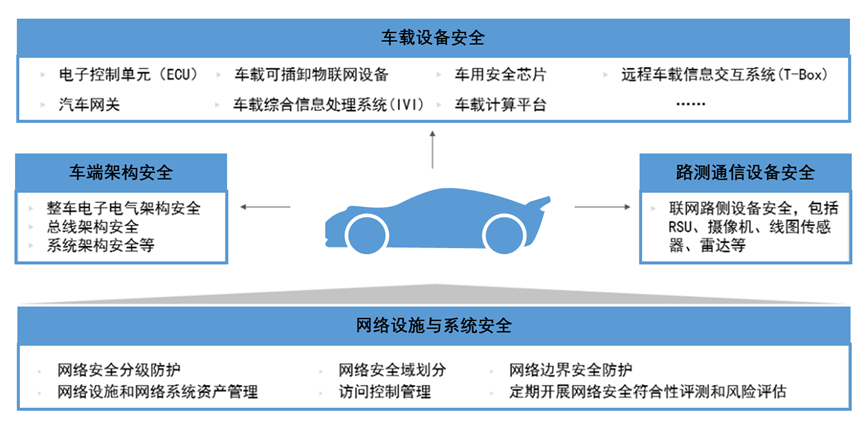
Enterprises should establish network security requirements for IoV terminals and infrastructure, including network security for in-vehicle devices, vehicle-side network security, roadside communication devices, and network facilities and systems.
1. Network Security for In-vehicle Devices
Enterprises should enhance the security protection and detection of key intelligent devices and components in smart connected vehicles, including automotive gateway security, electronic control unit (ECU) security, security for automotive security chips, network security for in-vehicle computing platforms, security for removable IoT devices, security for in-vehicle integrated information processing systems (IVI), and security for remote in-vehicle information interaction systems (T-Box).
2. Vehicle-side Network Security
Enterprises should enhance vehicle-side network security protection and detection, including security for electronic and electrical architecture, bus architecture, and system architecture.
3. Network Security for Roadside Communication Devices
Enterprises should enhance network security protection and detection for roadside communication devices in the IoV, including roadside units (RSU), cameras, LiDAR sensors, radars, etc.
4. Network Facility and System Security
Enterprises should enhance security protection and detection for IoV network facilities and systems, including implementing graded protection for network security, rationally dividing network security domains, ensuring network boundary security, strengthening asset management for network facilities and systems, managing network access control, and taking technical measures to prevent threats such as Trojan viruses, network attacks, and intrusions that endanger IoV security.
The automotive industry in China is rapidly developing, facing challenges from domestic new forces and new consumer demands. For foreign and joint venture enterprises, smart connectivity is a new competitive landscape and a key element for establishing a foothold in the Chinese market.
Ensuring compliance with cybersecurity and data security is fundamental for the long-term and stable development of competitive capabilities in smart connected vehicles. Enterprises should build and continuously improve the IoV security system, achieving a robust security framework across various levels including network security for IoV terminals and facilities, communication security, application service security, data security, and security guarantees and support, forming a continuous supervision and optimization mechanism to meet regulatory compliance requirements and effectively enhance IoV security protection capabilities.
Open and Inclusive, Hand in Hand Cooperation
Share Opportunities and Achievements of Industrial Transformation
Beijing High-level Autonomous Driving Demonstration Zone
Office: 010-67865603
Industry Policy and Scenario Implementation: [email protected]
Vehicle Testing and Regulation: 010-67865636
Media Cooperation: [email protected]