
Click the blue text above to follow us!
An Energy-Efficient Multi-Channel MAC Protocol for Linear Sensor Networks
Tong Fei1,2,3, Sui Rucong1, Chen Yu1, Su Heng1, Liu Hengrui1, Su Shangfeng1, Yan Yuke1
1. Southeast University, School of Cyberspace Security, Nanjing, Jiangsu 211189;
2. Jiangsu Provincial Ubiquitous Network Security Engineering Research Center, Nanjing, Jiangsu 211189; 3. Network Communication and Security Zijinshan Laboratory, Nanjing, Jiangsu 211111
Abstract:
Keywords:Linear Sensor Network; Redundant Node; Transmission Interference; Energy Hole; Duty-Cycling Scheduling; Multi-Channel
Citation Format:
Tong Fei, Sui Rucong, Chen Yu, et al. An energy-efficient multi-channel MAC protocol for linear sensor networks[J]. Chinese Journal on Internet of Things, 2022, 6(4): 27-40.
TONG F, SUI R C, CHEN Y, et al. An energy-efficient multi-channel MAC protocol for linear sensor networks[J]. Chinese Journal on Internet of Things, 2022, 6(4): 27-40.
1 Introduction
2 System Model
2.1 Network Topology
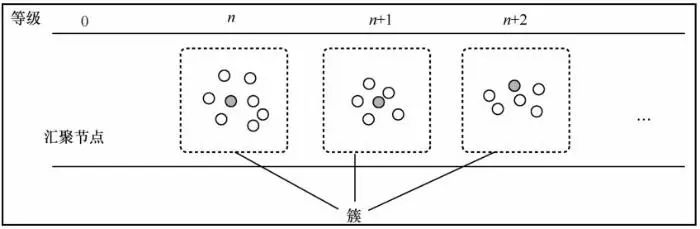
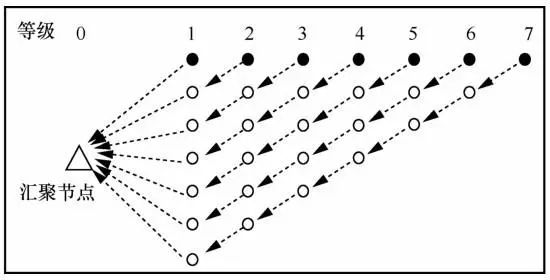
2.2 Pipelined Transmission on the Transmission Path
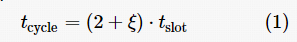
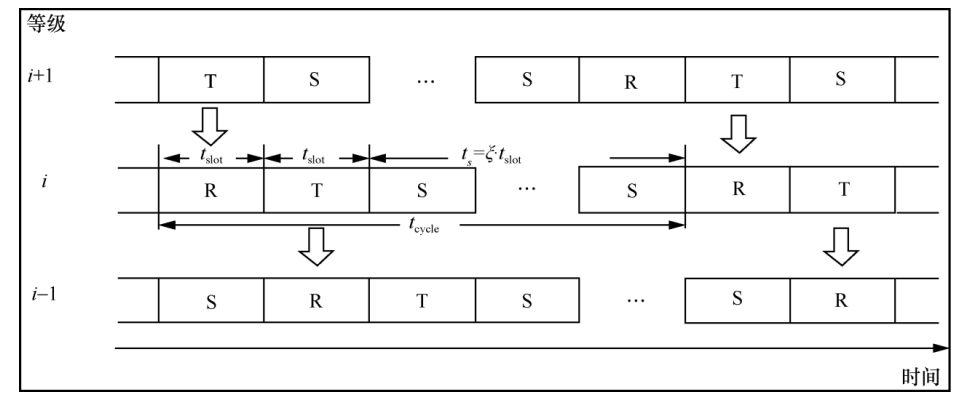
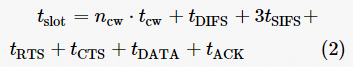
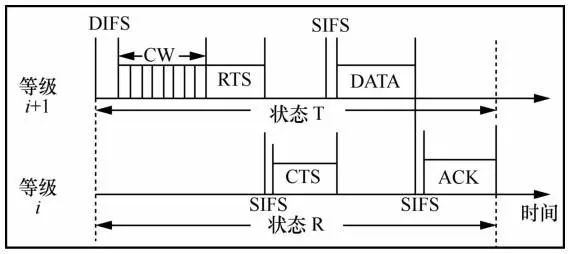
2.3 Multi-Channel Model
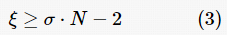
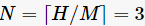 .
.
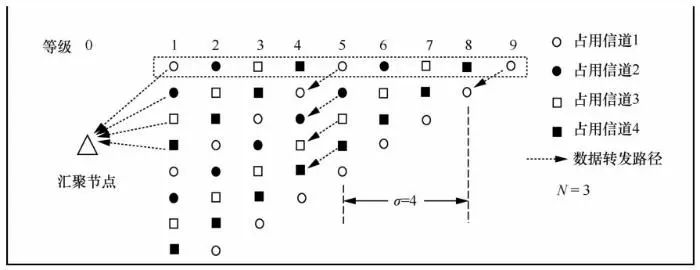
3 Implementation of MRPDC Protocol
3.1 Node Level Classification
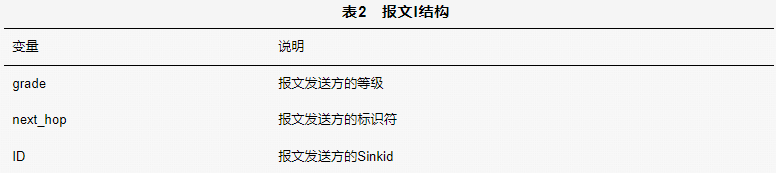
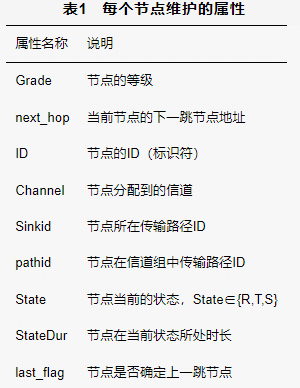
Nodes within one hop of the sink node (denoted as node) will receive message I, and the attributes of the nodes will be updated based on the information in message I as follows:


3.2 Channel Allocation
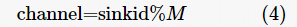
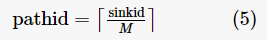
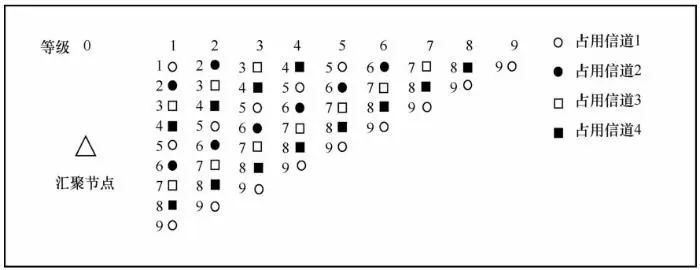
3.3 Establishment of Node Time Schedule

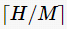 . The sink node broadcasts an IM message every σt slot interval, and the algorithm for constructing and broadcasting the IM data packet by the sink node is shown in Algorithm 1.
. The sink node broadcasts an IM message every σt slot interval, and the algorithm for constructing and broadcasting the IM data packet by the sink node is shown in Algorithm 1.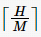 do
do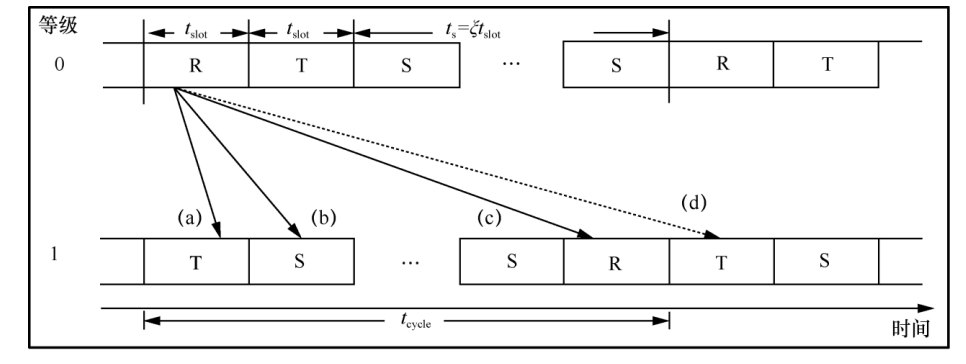
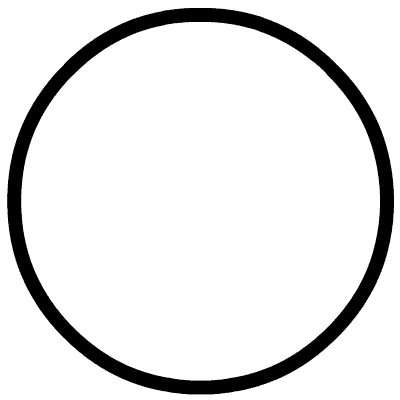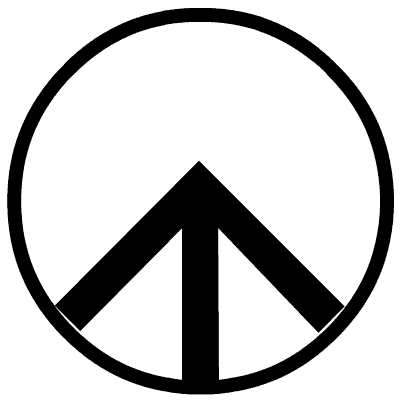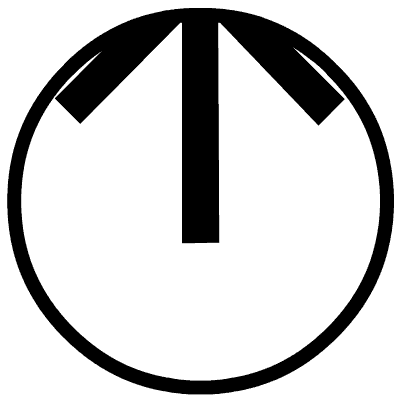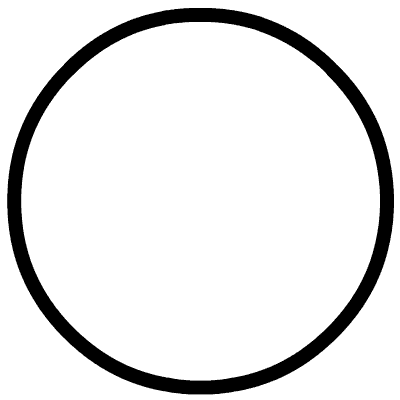
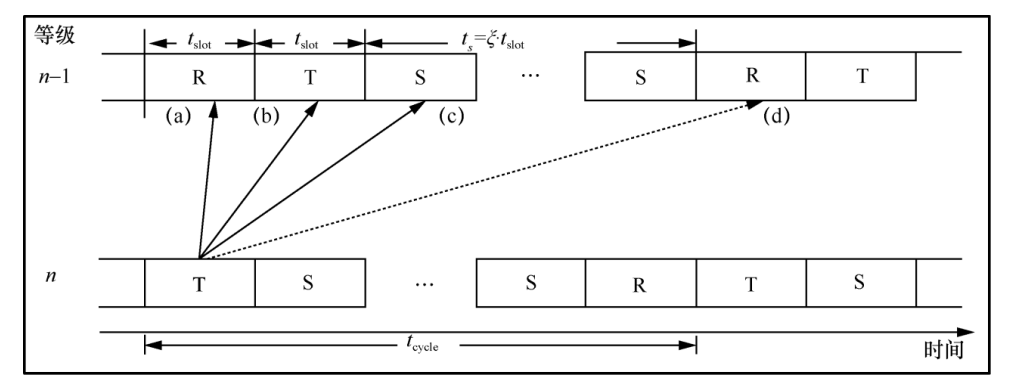
Figure 7 Four Situations When the Sink Node Sends IM Data Packet in R State
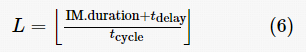
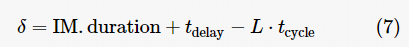
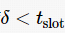 then
then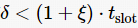 then
then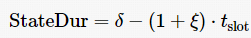
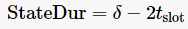
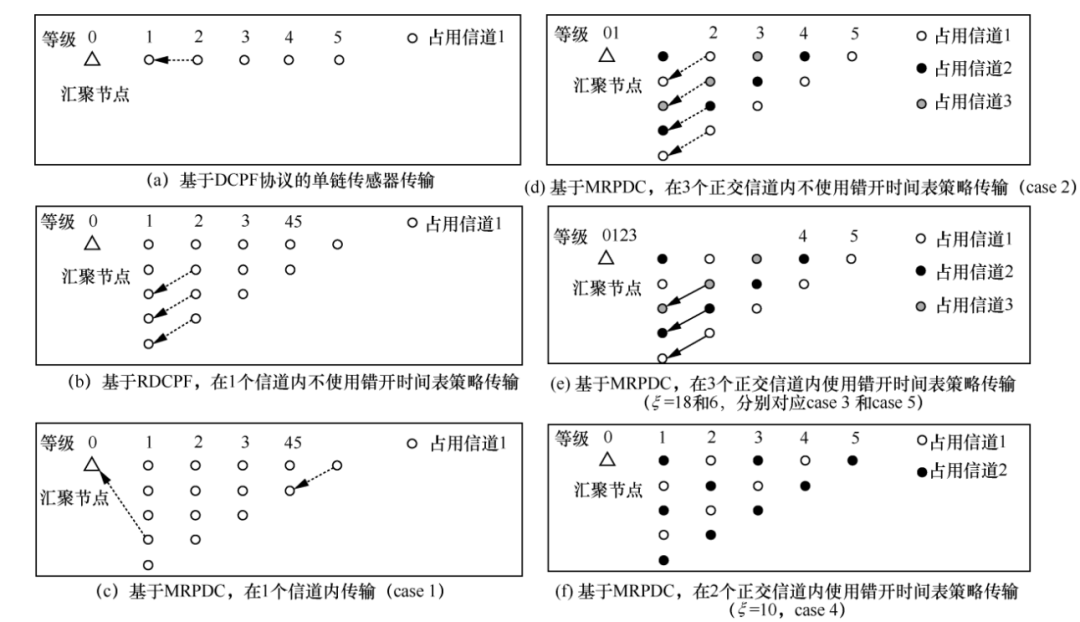
3.4 Data Transmission
3.5 Solutions for Redundant Node Failure
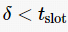 then
then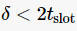 then
then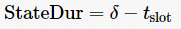
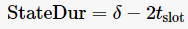
3.6 Number of Redundant Nodes
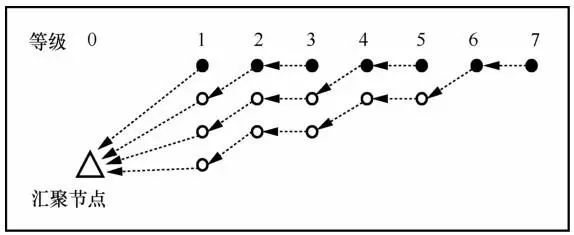
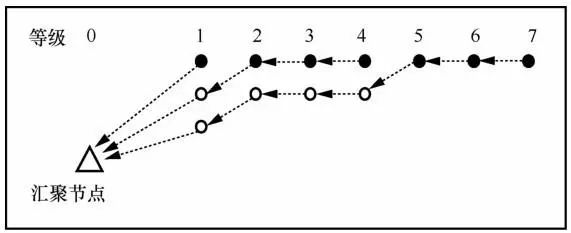
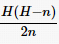 ; if H %n≠0, let
; if H %n≠0, let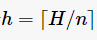 , the required number of redundant nodes is
, the required number of redundant nodes is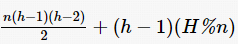 . When n=1, the maximum number of redundant nodes is needed, but the energy consumption among nodes in the network is the most balanced. As n increases, the required number of redundant nodes decreases, but the balance of energy consumption among nodes worsens. Particularly, when n=H, no redundant nodes need to be deployed, but energy consumption balance is the worst, and the energy hole problem is most severe. Therefore, network designers can decide the number of redundant nodes to deploy based on actual conditions.
. When n=1, the maximum number of redundant nodes is needed, but the energy consumption among nodes in the network is the most balanced. As n increases, the required number of redundant nodes decreases, but the balance of energy consumption among nodes worsens. Particularly, when n=H, no redundant nodes need to be deployed, but energy consumption balance is the worst, and the energy hole problem is most severe. Therefore, network designers can decide the number of redundant nodes to deploy based on actual conditions.4 Experimental Design and Analysis
4.1 Experimental Environment and Related Parameters
4.2 Experimental Results Analysis
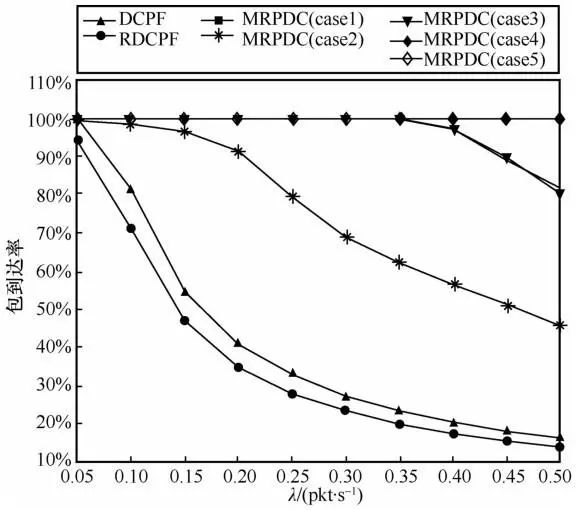
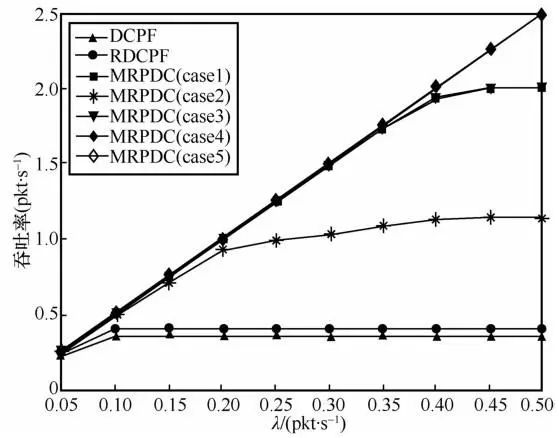
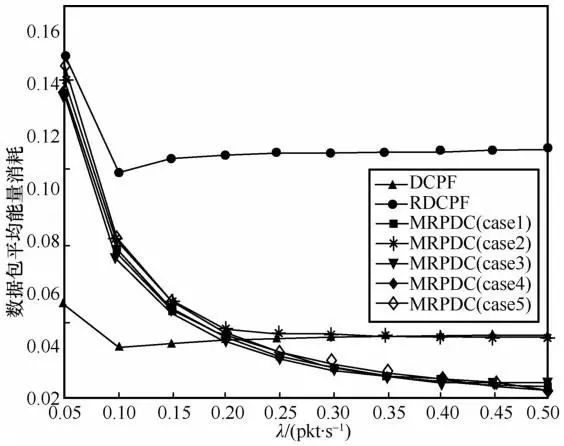
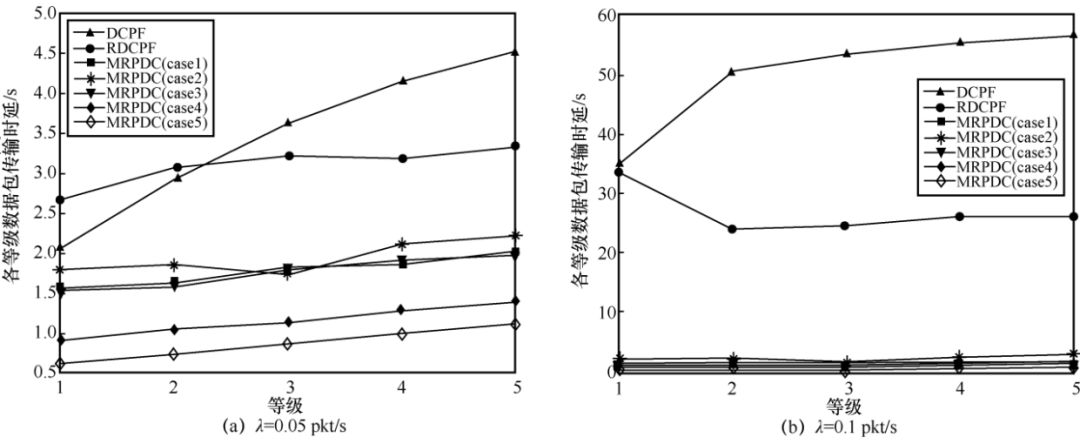
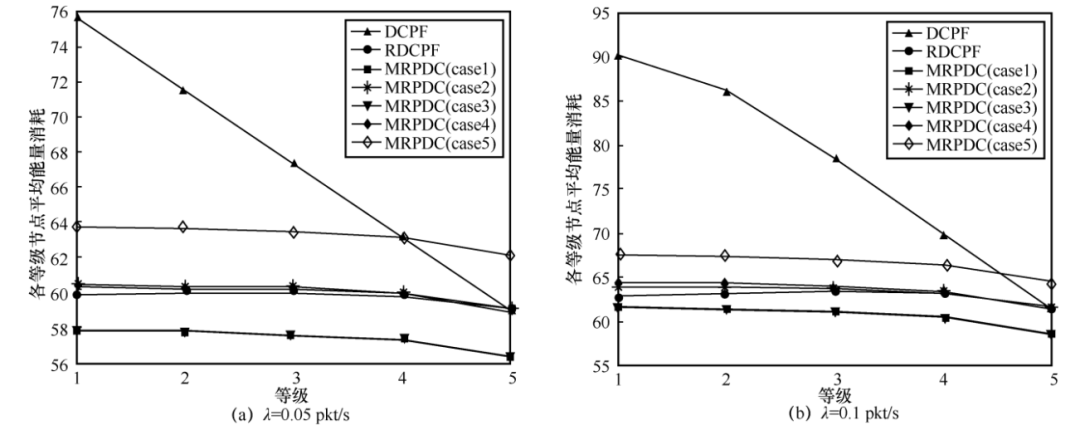
5 Conclusion
Author Information

Link to Previous Issue
Contents & Abstracts of IoT Journal 2022 Issue 4
Tel:010-81055691
E-mail:[email protected]
Scopus Indexed
Recommended Chinese Technology Journal by the China Communications Society (T1)
Recommended Chinese Technology Journal by the China Computer Society (T2)
Ulrichsweb Indexed
Journal Homepage
http://www.infocomm-journal.com/wlw/CN/2096-3750/home.shtml
Online Submission
http://cbpt.infocomm-journal.com/Journalx_wlw/authorLogOn.action

Long press or scan the QR code to follow us, all articles can be read online for free