Click the blue text
Follow us

The new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation represented by large models of artificial intelligence is advancing deeply, and various industries will face huge opportunities and disruptive challenges. In the industrial sector, artificial intelligence is a key variable in promoting new industrialization, and the implementation of industrial large models will provide a new path for manufacturing enterprises to explore new industrialization. In the future, AI large models may reshape the global manufacturing competition landscape from a new starting point. No matter what form of robot or terminal, its core competitiveness may lie in the intelligence level of the large model that drives it. This article explores the basic concepts of industrial robots, their relationship with large models, and the market impact that the application of generated code can bring to the industrial field.
According to the definition by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), industrial robots are multifunctional mechanical execution devices that can be automatically controlled and are programmable for repetitive tasks, equipped with three or more joint axes, and capable of handling various industrial automation applications through programmed instructions.Currently, industrial robots can be roughly divided into six types:
– Polar coordinate robots: Widely popular in the early days, they have a rotation axis set at the center of a pedestal, with the robotic arm rotating up and down and extending to perform tasks. Similar robots were also active on stage in the early days.
– Cylindrical coordinate robots: Also active in the early days, they use a rotation axis as the center and a mechanical arm that can move up and down and extend.
– Rectangular coordinate robots: They do not use a rotation axis but achieve three-dimensional movement through sliding in three orthogonal directions (length × width × height). They have a larger installation area but a simpler structure, making them easier to control.
– Vertical multi-joint robots: Currently the most widely used, they consist of a mechanical arm with multiple joints (axes) like a human arm and a rotation axis, active in various applications such as welding, palletizing, and assembly.
– Horizontal multi-joint robots: Composed of a horizontal rotation axis and a vertical linear axis. Since the front end moves horizontally while moving up and down, they are suitable for operations on stable work surfaces.
– Parallel robots: Best at fast operations, they achieve high-speed and precise actions through multiple joints configured in parallel, used for picking lightweight items on conveyor belts.
In recent years, as the demand for industrial automation has surged, global sales and revenue of industrial robots have continued to grow. According to the “2023 World Robot Report” released by the International Federation of Robotics, global industrial robot sales exceeded 500,000 units for the second consecutive year in 2022, a year-on-year increase of 5%. China is the world’s largest robot market, with industrial robot sales in the Chinese market accounting for more than half of the global total in 2022. The International Federation of Robotics predicts that by 2024, the global robot market size will reach 66 billion USD.
Currently, the global demand for industrial robots is mainly concentrated in countries with large manufacturing scales and relatively high automation levels. More than 70% of industrial robots are deployed in China, Japan, the USA, South Korea, and Germany. In 2022, the sales of industrial robots in these five major markets accounted for 79.1% of the global total. The report from the International Federation of Robotics shows that the number of newly installed industrial robots in factories worldwide in 2022 was 553,000 units, with Asia accounting for 73%, Europe for 15%, and the Americas for 10%. In terms of industry structure, more than half of the global demand for industrial robots comes from the automotive and electrical electronics industries. Additionally, industrial robots are also widely used in production lines of food, pharmaceuticals, etc., helping companies reduce costs and enhance competitiveness by improving production efficiency and accuracy.
With the rise of a new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation, the integration of new generation digital technologies such as artificial intelligence and sensing with the robotics industry is accelerating, driving technological innovation in the robotics industry, enhancing the performance of robots in existing application fields, and expanding new application areas. Li Xiaohua, a researcher at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, stated that early industrial robots mainly replaced workers in heavy physical labor or performed tasks in harsh environments, such as in automotive manufacturing, shipbuilding, and chemical industries, handling tasks like material handling, loading and unloading, welding, and spraying. With the development of artificial intelligence technology, the application fields of industrial robots have begun to expand into high-precision scenarios in industries such as computers, communications, and consumer electronics.
On one hand, interconnected robots are changing manufacturing, integrating more comprehensively into interconnected digital ecosystems and operating as an important part. Driven by advancements in digital technology, robot suppliers and system integrators are actively providing new applications and improving the speed and quality of existing applications. On the other hand, industrial robots have also become important carriers and platforms for emerging technologies, serving as prerequisites and foundations for the application of new generation digital technologies such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and big data in manufacturing processes. Industrial robots excel in handling complex environments, maintaining precise operations, working continuously, and achieving information interconnectivity, and have a huge potential for future development.
Specifically, the core value of AI large models is enabling natural language interaction between humans and devices. On one hand, generative AI and large model technologies can significantly enhance the autonomy and cognitive abilities of industrial robots, solving application challenges in complex scenarios. On the other hand, the entry barrier for using industrial robots can also be effectively lowered, attracting more high-end talent into this innovative field, thus stimulating industrial development. At the same time, AI large models are expected to enhance the core competitiveness of domestic industrial robot manufacturers in the global market, gaining more influence in the future development of the industry. As AI large models evolve towards multi-modal capabilities, future industrial robots may also achieve interactions in voice, video, and even between devices and their environments, breaking original application boundaries and entering more industrial scenarios.
For example, in palletizing, for most industrial handling scenarios, palletizing is an unavoidable and challenging task. With the synergy of AI large models and industrial robots, this task can be completed in just three steps:
– First is for industry experts to create a knowledge base for the scenario, including scene descriptions, SOP process flows, robot API documents, and reference codes, allowing the large model to automatically acquire knowledge related to the scenario.
– Then the staff can propose task requirements through natural language, and the large model will automatically generate executable code that can be used with minor adjustments.
– Finally, the workers on site only need to click the “Start” button, and the large model can automatically calculate the positions of different boxes, allowing the industrial robot to complete the palletizing automatically.
It can be said that the general large model acts like an excellent assistant to industrial robots, trained on a vast amount of publicly available internet data, solving 80% of routine problems in daily scenarios. However, due to the scattered nature of data across various links and the uniqueness of the process, specialized training in vertical fields is needed to better address the remaining 20% of specialized issues.
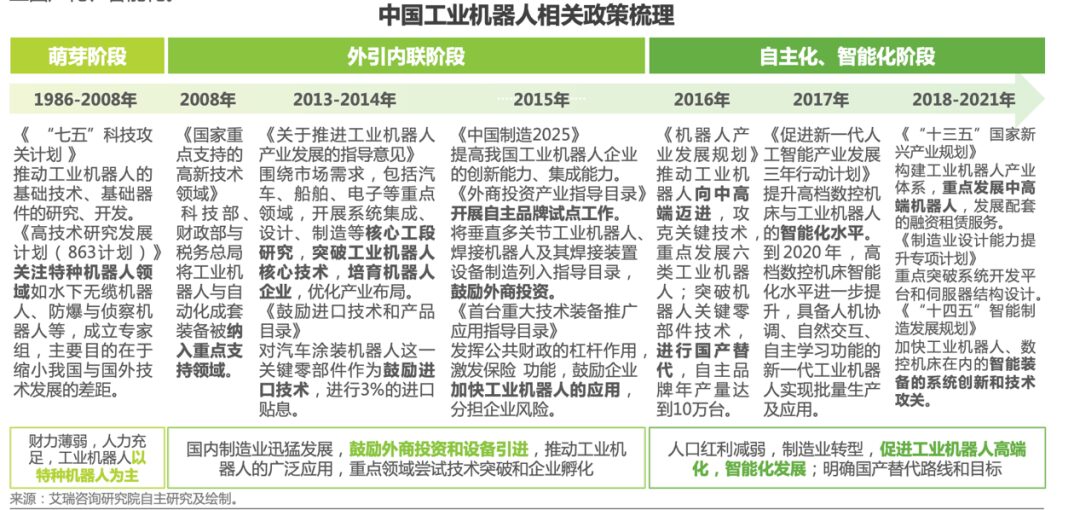
According to the latest data from the International Federation of Robotics, global industrial robot sales are expected to exceed 590,000 units in 2023. From 2023 to 2026, due to companies increasingly opting to utilize advanced robotic technologies to optimize production processes and enhance production efficiency and product quality, the global industrial robot market is expected to achieve an average annual compound growth rate of 7%, with sales expected to rise to 718,000 units, and the global robot market is expected to maintain a good growth trend. In the post-pandemic era, as the global economy gradually recovers, developed countries will place more emphasis on the robotics industry due to rising labor costs and improved robot usability and configuration efficiency.
Among them, China is the largest robot market in the world. The Chinese market has many industries and application scenarios yet to be developed, and there is considerable room for robot penetration in the future, making China a key support for global robot growth. Data shows that the application of industrial robots has covered 60 major categories of the national economy and 168 subcategories, and China has been the world’s largest industrial robot market for ten consecutive years. In 2022, the production of industrial robots in China reached 443,000 units, a year-on-year increase of over 20%, with installed units accounting for more than 50% of the global total. According to data from the International Federation of Robotics, approximately 290,000 units of industrial robots were installed in China in 2022, representing a year-on-year increase of 5%.
In recent years, global renowned robot companies such as ABB, Fanuc, and Yaskawa Electric have entered the Chinese market. In December 2022, ABB’s robot super factory officially commenced production in Shanghai’s Pudong New District, becoming ABB’s largest robot research, production, and application base globally. In 2022, China’s industrial robot market accounted for 52% of the global market. Notably, in the past decade, the number of domestically produced industrial robots in China has grown rapidly, with “ nearly half of the economic sectors having applications for domestic brand robots.” said Chen Dan, deputy secretary-general of the Robotics Branch of the China Machinery Industry Federation.
Moreover, with the rapid development of China’s industrial robot industry, more and more domestic industrial robot companies are accelerating their overseas expansion. Data from the International Federation of Robotics shows that in 2023, China’s industrial robot export volume reached a new high of 118,300 units. The overseas best-selling robot products are mainly used in home appliance manufacturing, automotive manufacturing, communications electronics, logistics and warehousing industries. Additionally, applications in the semiconductor and new energy sectors are also growing rapidly. The advantages of Chinese robots in application scenarios and practical settings lay a solid foundation for overseas cooperation.
However, the output growth rate of industrial robots among large-scale enterprises in China was-4.8% and-2.2%, contrasting sharply with the flourishing market. Due to high costs, lack of flexibility, safety concerns, and a shortage of skilled professionals, the application space for domestic industrial robots in China remains largely untapped. Therefore, the development of AI large models may become the key to breaking the deadlock for domestic industrial robots.
About Us
Tsinghua University Institute for AI International Governance (Institute for AI International Governance, Tsinghua University, THU I-AIIG) is a university-level research institution established by Tsinghua University in April 2020. Relying on Tsinghua University’s existing accumulation and interdisciplinary advantages in artificial intelligence and international governance, the institute conducts research on major theoretical issues and policy needs in AI international governance, aiming to enhance Tsinghua’s global academic influence and policy leadership in this field, and to provide intellectual support for China’s active participation in AI international governance.
Sina Weibo: @Tsinghua University Institute for AI International Governance
WeChat Video Account: THU-AIIG
Bilibili: Tsinghua University AIIG