
Source: https://blog.csdn.net/XR528787067/article/details/52822377
Recently, a friend of mine was communicating with a peripheral using a microcontroller, and the peripheral returned a series of data formatted as follows:
AA AA 04 80 02 00 02 7B AA AA 04 80 02 00 08 75 AA AA 04 80 02 00 9B E2 AA AA 04 80 02 00 F6 87 AA AA 04 80 02 00 EC 91
Where AA AA 04 80 02 is the data validation header, and the next three bytes are the valid data. He asked me how to extract the valid data from the continuously returned data from the peripheral.
The most straightforward approach to this problem is to use a flag to indicate which byte of the current frame of data is being parsed, and then check if the currently received data matches the validation data. If it matches, increment the flag; otherwise, reset the flag to zero and start over. The code for parsing data using this method is as follows:
if(flag == 0)
{
if(tempData == 0xAA)
flag++;
else
flag = 0;
}
elseif(flag == 1)
{
if(tempData == 0xAA)
flag++;
else
flag = 0;
}
elseif(flag == 2)
{
if(tempData == 0x04)
flag++;
else
flag = 0;
}
elseif(flag == 3)
{
if(tempData == 0x80)
flag++;
else
flag = 0;
}
elseif(flag == 4)
{
if(tempData == 0x02)
flag++;
else
flag = 0;
}
elseif(flag == 5 || flag == 6 || flag == 7)
{
data[flag-5] = tempData;
flag = (flag == 7) ? 0 : flag+1;
}This method is the simplest and most intuitive approach. A quick search on Baidu shows that most similar methods for data parsing use this approach. However, this method has several drawbacks:
1. It involves a lot of conditional checks, which can lead to logical confusion.
2. The code has a high degree of repetition and low abstraction. As seen in the code above, a large amount of code is simply checking different data values, while the rest of the code remains identical.
3. The code has poor reusability. The written code cannot be used for other similar peripherals, and if there are multiple peripherals, multiple similar codes need to be written.
4. It has low extensibility. If the peripheral has a data validation tail that needs to be checked or if the data validation header changes, multiple checks need to be rewritten, making it impossible to extend the existing code.
5. It is prone to misjudgment.
To address these issues, I propose a new solution that can be generalized for all similar data parsing scenarios. The principle is as follows:
Use a fixed-capacity queue to cache the received data, with the queue capacity equal to the size of one frame of data. Each time data is received, it is added to the queue. When a complete frame of data is received, all data in the queue represents a complete frame. Therefore, we only need to check if the head of the queue matches the data validation header and if the tail of the queue matches the data validation tail to determine if a complete frame has been received. The schematic is as follows:
Each time data is received, it is added to the queue:
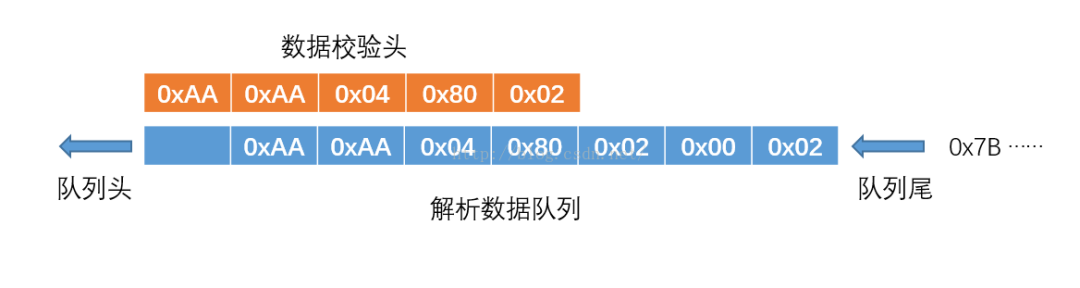
When a complete frame of data is received, the head of the queue coincides with the data validation header:

At this point, we only need to extract the valid data from the queue.
If there is a data tail check, we only need to add a validation tail, as shown in the following diagram:

Alright, the analysis is complete, let’s start coding.
First, we need a queue. To ensure generality, the queue will be implemented using a doubly linked list (though an array implementation is also possible). The encapsulated structure will include queue capacity, queue size, front node, and back node. The operations to be implemented include queue initialization, data enqueue, data dequeue, clearing the queue, and releasing the queue. The specific code is as follows:
/* queue.h */
#ifndef _QUEUE_H_
#define _QUEUE_H_
#ifndef NULL
#define NULL ((void *)0)
#endif
typedef unsigned char uint8;
/* Queue Node */
typedef struct Node
{
uint8 data;
struct Node *pre_node;
struct Node *next_node;
} Node;
/* Queue Structure */
typedef struct Queue
{
uint8 capacity; // Total capacity of the queue
uint8 size; // Current size of the queue
Node *front; // Front node of the queue
Node *back; // Back node of the queue
} Queue;
/* Initialize a queue */
Queue *init_queue(uint8 _capacity);
/* Enqueue data */
uint8 en_queue(Queue *_queue, uint8 _data);
/* Dequeue data */
uint8 de_queue(Queue *_queue);
/* Clear the queue */
void clear_queue(Queue *_queue);
/* Release the queue */
void release_queue(Queue *_queue);
#endif/* queue.c */
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "parser.h"
/**
* Initialize a queue
*
* @_capacity: Total capacity of the queue
*/
Queue *init_queue(uint8 _capacity)
{
Queue *queue = (Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
queue->capacity = _capacity;
queue->size = 0;
return queue;
}
/**
* Enqueue data
*
* @_queue: Queue
* @_data: Data
**/
uint8 en_queue(Queue *_queue, uint8 _data)
{
if(_queue->size < _queue->capacity)
{
Node *node = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = _data;
node->next_node = NULL;
if(_queue->size == 0)
{
node->pre_node = NULL;
_queue->back = node;
_queue->front = _queue->back;
}
else
{
node->pre_node = _queue->back;
_queue->back->next_node = node;
_queue->back = _queue->back->next_node;
}
_queue->size++;
}
else
{
Node *temp_node = _queue->front->next_node;
_queue->front->pre_node = _queue->back;
_queue->back->next_node = _queue->front;
_queue->back = _queue->back->next_node;
_queue->back->data = _data;
_queue->back->next_node = NULL;
_queue->front = temp_node;
}
return _queue->size-1;
}
/**
* Dequeue data
*
* @_queue: Queue
*
* @return: Dequeued data
*/
uint8 de_queue(Queue *_queue)
{
uint8 old_data = 0;
if(_queue->size > 0)
{
old_data = _queue->front->data;
if(_queue->size == 1)
{
free(_queue->front);
_queue->front = NULL;
_queue->back = NULL;
}
else
{
_queue->front = _queue->front->next_node;
free(_queue->front->pre_node);
_queue->front->pre_node = NULL;
}
_queue->size--;
}
return old_data;
}
/**
* Clear the queue
*
* @_queue: Queue
*/
void clear_queue(Queue *_queue)
{
while(_queue->size > 0)
{
de_queue(_queue);
}
}
/**
* Release the queue
*
* @_queue: Queue
*/
void release_queue(Queue *_queue)
{
clear_queue(_queue);
free(_queue);
_queue = NULL;
}
Next, we need a parser. The encapsulated structure will include the data parsing queue, data validation header, data validation tail, parsing results, and a pointer to the parsing results. The operations to be implemented include parser initialization, adding data for parsing, retrieving parsing results, resetting the parser, and releasing the parser. The specific code is as follows:
/* parser.h */
#ifndef _PARSER_H_
#define _PARSER_H_
#include "queue.h"
typedef enum
{
RESULT_FALSE,
RESULT_TRUE
} ParserResult;
/* Parser Structure */
typedef struct DataParser
{
Queue *parser_queue; // Data parsing queue
Node *resule_pointer; // Pointer to parsed result data
uint8 *data_header; // Data validation header pointer
uint8 header_size; // Data validation header size
uint8 *data_footer; // Data validation tail pointer
uint8 footer_size; // Data validation tail size
uint8 result_size; // Size of parsed data
ParserResult parserResult; // Parsing result
} DataParser;
/* Initialize a parser */
DataParser *parser_init(uint8 *_data_header, uint8 _header_size, uint8 *_data_footer, uint8 _foot_size, uint8 _data_frame_size);
/* Add data to the parser for parsing */
ParserResult parser_put_data(DataParser *_parser, uint8 _data);
/* Retrieve parsing results from the parser after successful parsing */
int parser_get_data(DataParser *_parser, uint8 _index);
/* Reset the parser */
void parser_reset(DataParser *_parser);
/* Release the parser */
void parser_release(DataParser *_parser);
#endif/* parser.c */
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "parser.h"
/**
* Initialize a parser
*
* @_data_header: Data header pointer
* @_header_size: Data header size
* @_data_footer: Data tail pointer
* @_foot_size: Data tail size
* @_data_frame_size: Size of a complete frame of data
*
* @return: Parser
*/
DataParser *parser_init(uint8 *_data_header, uint8 _header_size, uint8 *_data_footer, uint8 _foot_size, uint8 _data_frame_size)
{
if((_header_size+_foot_size) > _data_frame_size || (_header_size+_foot_size) == 0)
return NULL;
DataParser *parser = (DataParser *)malloc(sizeof(DataParser));
parser->parser_queue = init_queue(_data_frame_size);
parser->resule_pointer = NULL;
parser->data_header = _data_header;
parser->header_size = _header_size;
parser->data_footer = _data_footer;
parser->footer_size = _foot_size;
parser->result_size = _data_frame_size - parser->header_size - parser->footer_size;
parser->parserResult = RESULT_FALSE;
while(_data_frame_size-- > 0)
{
en_queue(parser->parser_queue, 0);
}
return parser;
}
/**
* Add data to the parser for parsing
*
* @_parser: Parser
* @_data: Data to be parsed
*
* @return: Current parsing result, returning RESULT_TRUE indicates successful parsing of a frame of data
*/
ParserResult parser_put_data(DataParser *_parser, uint8 _data)
{
uint8 i;
Node *node;
if(_parser == NULL)
return RESULT_FALSE;
en_queue(_parser->parser_queue, _data);
/* Validate data tail */
node = _parser->parser_queue->back;
for(i = _parser->footer_size; i > 0; i--)
{
if(node->data != _parser->data_footer[i-1])
goto DATA_FRAME_FALSE;
node = node->pre_node;
}
/* Validate data header */
node = _parser->parser_queue->front;
for(i = 0; i < _parser->header_size; i++)
{
if(node->data != _parser->data_header[i])
goto DATA_FRAME_FALSE;
node = node->next_node;
}
if(_parser->resule_pointer == NULL && _parser->result_size > 0)
_parser->resule_pointer = node;
if(_parser->parserResult != RESULT_TRUE)
_parser->parserResult = RESULT_TRUE;
return _parser->parserResult;
DATA_FRAME_FALSE:
if(_parser->resule_pointer != NULL)
_parser->resule_pointer = NULL;
if(_parser->parserResult != RESULT_FALSE)
_parser->parserResult = RESULT_FALSE;
return _parser->parserResult;
}
/**
* Retrieve parsing results from the parser after successful parsing
*
* @_parser: Parser
* @_index: The _index-th data in the parsing result set
*
* @return: Retrieved parsed data, returning -1 indicates data retrieval failure
*/
int parser_get_data(DataParser *_parser, uint8 _index)
{
Node *node;
if(_parser == NULL
|| _parser->parserResult != RESULT_TRUE
|| _index >= _parser->result_size
|| _parser->resule_pointer == NULL)
return -1;
node = _parser->resule_pointer;
while(_index > 0)
{
node = node->next_node;
_index--;
}
return node->data;
}
/**
* Reset the parser
*
* @_parser: Parser
*/
void parser_reset(DataParser *_parser)
{
uint8 _data_frame_size;
if(_parser == NULL)
return;
_data_frame_size = _parser->parser_queue->size;
while(_data_frame_size-- > 0)
{
en_queue(_parser->parser_queue, 0);
}
_parser->resule_pointer = NULL;
_parser->parserResult = RESULT_FALSE;
}
/**
* Release the parser
*
* @_parser: Parser
*/
void parser_release(DataParser *_parser)
{
if(_parser == NULL)
return;
release_queue(_parser->parser_queue);
free(_parser);
_parser = NULL;
}
Next, let’s write some test code to test it:
/* main.c */
#include <stdio.h>
#include "parser.h"
int main()
{
uint8 i;
// Data header
uint8 data_header[] = {0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02};
// Data to be parsed, for testing
uint8 data[] = {
0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x00, 0x02, 0x7B, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80,
0x02, 0x00, 0x08, 0x75, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x00, 0x9B, 0xE2,
0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x00, 0xF6, 0x87, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80,
0x02, 0x00, 0xEC, 0x91, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x01, 0x15, 0x67,
0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x01, 0x49, 0x33, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80,
0x02, 0x00, 0xE7, 0x96, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x00, 0x68, 0x15,
0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x00, 0x3C, 0x41, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80,
0x02, 0x00, 0x66, 0x17, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x00, 0xA5, 0xD8,
0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x01, 0x26, 0x56, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80,
0x02, 0x01, 0x73, 0x09, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x01, 0x64, 0x18,
0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x01, 0x8B, 0xF1, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80,
0x02, 0x01, 0xC6, 0xB6, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x01, 0x7B, 0x01,
0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0x00, 0xCB, 0xB2, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80,
0x02, 0x00, 0x2C, 0x51, 0xAA, 0xAA, 0x04, 0x80, 0x02, 0xFF, 0xE5, 0x99
};
/**
* Initialize a parser
* The first parameter is the data header
* The second parameter is the data header length
* The third parameter is the data tail pointer
* The fourth parameter is the data tail size
* The fifth parameter is the size of a complete frame of data
*/
DataParser *data_parser = parser_init(data_header, sizeof(data_header), NULL, 0, 8);
// Extract the data to be parsed one by one and add it to the parser
for(i = 0; i < sizeof(data); i++)
{
// Parse data, returning RESULT_TRUE indicates successful parsing of a set of data
if(parser_put_data(data_parser, data[i]) == RESULT_TRUE)
{
printf("Successfully parsed a frame of data...\n");
/* Extract parsed data one by one */
printf("The first data is: 0x%x\n", parser_get_data(data_parser, 0));
printf("The second data is: 0x%x\n", parser_get_data(data_parser, 1));
printf("The third data is: 0x%x\n\n\n", parser_get_data(data_parser, 2));
}
}
// When the parser is no longer needed, it should be released to free memory and avoid memory leaks
parser_release(data_parser);
return 0;
}Test results are as follows:
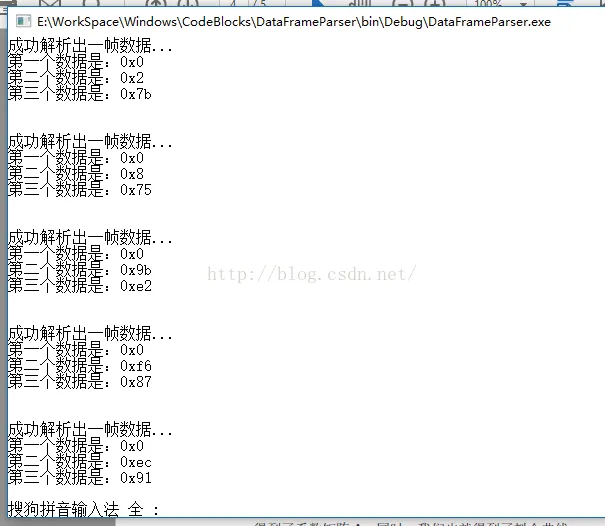
As can be seen from the above, the parsing results are consistent with the target.
GitHub link:
https://github.com/528787067/DataFrameParser


Some screenshots of electronic books

【Complete Set of Hardware Learning Materials Collection】
