Hello, I am Xiao Changhe, a technical expert navigating the world of code.
Today, I want to share an introductory tutorial on Python, mainly covering functions, encapsulation, and recursion. This is a substantial resource that you should definitely bookmark.
1. Basics of Functions and Syntax Standards
Functions are the core building blocks of Python programming, essentially encapsulating and reusing code logic.
Python defines functions using the def keyword, organizing code according to PEP8 coding standards.
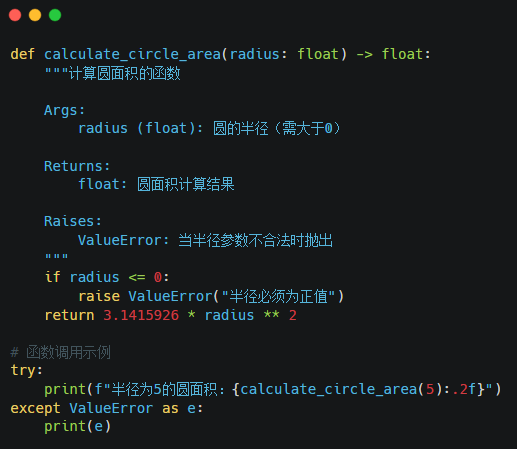
Key Elements Analysis:
1. Type Hinting: Python 3.5+ supports type annotations for parameters and return values.
2. Docstrings: Use triple quotes to write standardized function descriptions.
Exception Handling: Use raise to throw clear error messages.
3. Formatted Output: Use f-strings with format specifiers for precision control.
2. The Art of Encapsulation: Building Modular Code
Good encapsulation should follow the Single Responsibility Principle. We will demonstrate encapsulation techniques using a geometric calculation module:
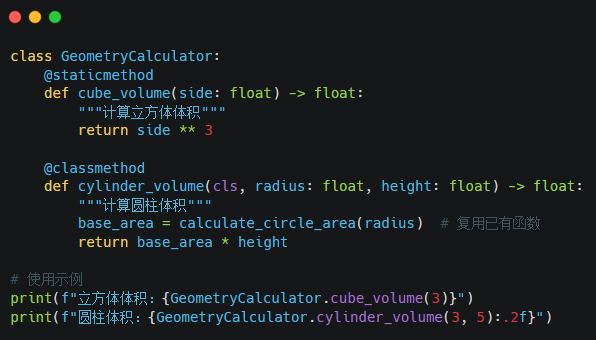
Encapsulation Key Points:
1. Use class methods to organize related functions.
2. Static methods handle independent calculations.
3. Reuse existing functions reasonably.
4. Access control is achieved through naming conventions (a leading underscore indicates protected members).
3. The Secrets and Practice of Recursion
Recursion is a programming paradigm that solves problems through self-calling functions. We will demonstrate recursive applications using directory tree traversal:
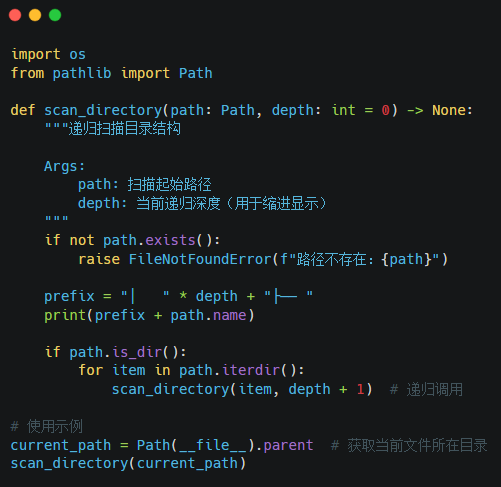
Key Points of Recursive Programming:
1. Base Case: Stop recursion when depth exceeds the threshold.
2. Recursive Step: After processing the current directory item, delve into subdirectories.
3. Tail Recursion Optimization: Although Python does not support TCO, it can be simulated using loop structures.
4. Stack Depth Limit: Use sys.getrecursionlimit() to check the default maximum recursion depth.
4. Comprehensive Application: Image Processing Pipeline
We will build an image processing pipeline combining functions, encapsulation, and recursion:
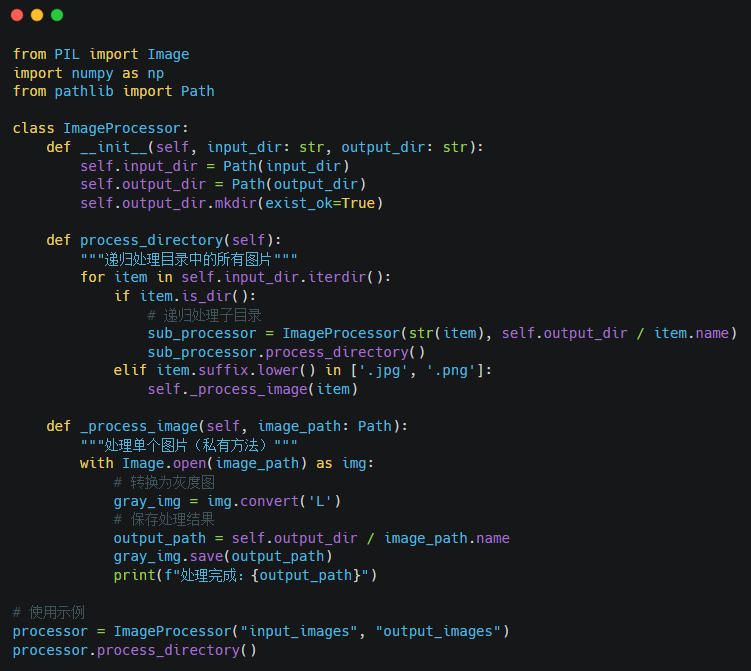
Code Analysis:
1. Class encapsulates processing logic.
2. Recursively traverse the directory tree.
3. Private methods implement specific functions.
4. Use the Pillow library for image processing.
5. Exception handling is implemented through context managers.
5. Alternative Solutions for Recursion Optimization
To address stack overflow issues caused by deep recursion, two optimization strategies are provided:
1. Convert Tail Recursion to Loop:

2. Memoization Recursion Optimization:
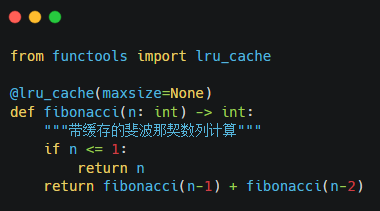
Optimization Strategies:
· Use decorators to cache intermediate results.
· Limit recursion depth.
· Convert recursion to iteration.
· Use divide-and-conquer strategies to reduce time complexity.
6. Summary and Best Practices
1. Function Design Principles:
· Single Responsibility Principle (SRP).
· No more than 5 parameters.
· Consistent return value types.
2. Levels of Encapsulation:
· Function-level encapsulation: handles specific tasks.
· Class-level encapsulation: organizes related operations.
· Module-level encapsulation: builds functional units.
3. Scenarios for Using Recursion:
· Tree structure processing.
· Divide-and-conquer algorithms.
· Implementation of mathematical recurrence formulas.
4. Debugging Techniques:
· Use pdb to set breakpoints.
· Print the recursion call stack.
· Visualize the recursion process.
By breaking down complex problems into function units and effectively utilizing encapsulation and recursion, you can build clear and maintainable Python programs.
However, one thing to note is that excellent code is not written in one go, but is formed through continuous refactoring and optimization.
Finally, I hope this tutorial helps you improve and optimize your coding efficiency. If you have any questions or want more code examples, feel free to reach out to me, Xiao Changhe is always ready to help.
Happy coding!