Introduction
Hello everyone! Today, I bring you a super detailed tutorial for beginners in Python. Whether you are a complete novice or a developer looking to review the basics, this article will help you. Python, as one of the most popular programming languages today, is known for its simple and understandable syntax and powerful features. Let’s start this journey of learning Python!
1. Introduction to Python
Python was created by Guido van Rossum in 1991 and is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language. It has the following characteristics:
-
Easy to Learn: The syntax is close to natural language, and the code is highly readable.
-
Cross-Platform: Runs on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
-
Rich Libraries: Has a large standard library and many third-party libraries.
-
Wide Applications: Used in web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, automation, etc.
2. Installing Python
1. Download Python
Visit the official Python website to download the latest version (currently the 3.x series).
2. Installation Steps
-
Windows: Run the downloaded installer and check “Add Python to PATH”.
-
Mac: Use the installer or install via Homebrew.
-
Linux: Usually comes pre-installed or can be installed using a package manager.
3. Verify Installation
Open the terminal/command line and enter:

If the Python version number is displayed, the installation was successful!
3. Your First Python Program
Let’s start with the classic “Hello, World!”:

Save this code as<span>hello.py</span>, then run it in the terminal:

Congratulations! You just ran your first Python program!
4. Basic Python Syntax
1. Variables and Data Types
Python is a dynamically typed language, so you do not need to declare variable types:
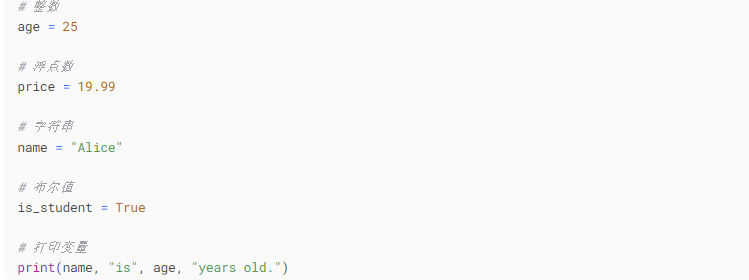
2. Basic Data Types
-
Numbers: int (integer), float (floating point)
-
Strings (str): Enclosed in single or double quotes
-
Booleans (bool): True or False
-
Lists (list): Ordered mutable collection
<span>[1, 2, 3]</span> -
Tuples (tuple): Ordered immutable collection
<span>(1, 2, 3)</span> -
Dictionaries (dict): Collection of key-value pairs
<span>{"name": "Alice", "age": 25}</span> -
Sets (set): Unordered collection of unique elements
<span>{1, 2, 3}</span>
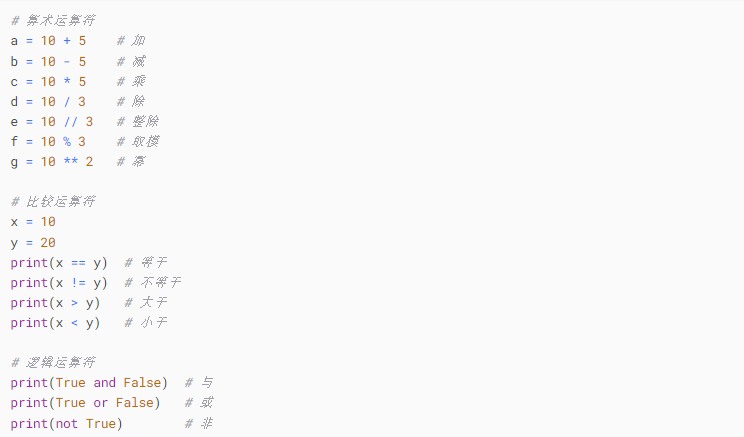
3. Operators
5. Control Flow
1. Conditional Statements

2. Loop Statements
For Loop:
 While Loop:
While Loop:
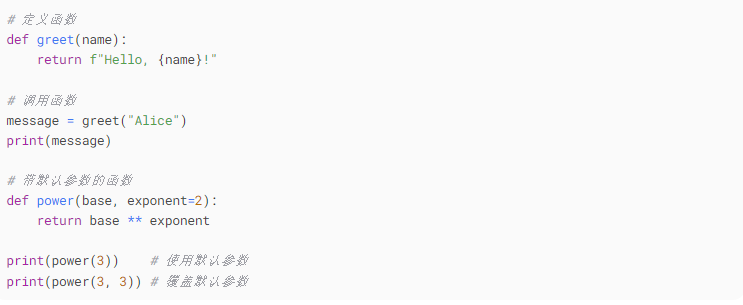
6. Functions
A function is a reusable block of code:
7. Data Structures
1. Lists

2. Dictionaries

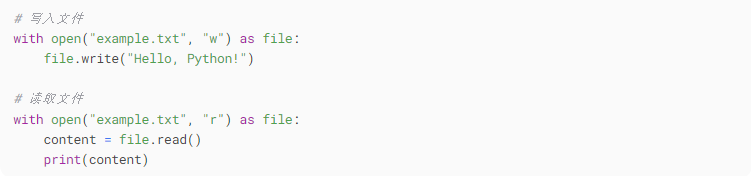
8. File Operations
9. Exception Handling

10. Object-Oriented Programming
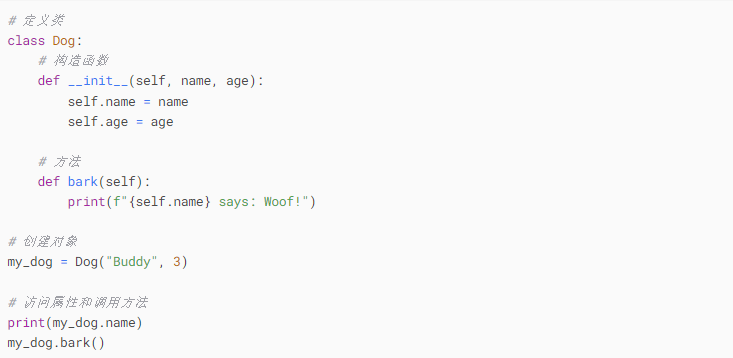
Conclusion
Congratulations on completing your study of the basics of Python! This is just the tip of the iceberg in the world of Python, but it has already laid a solid foundation for you.