Have you ever encountered a situation where the photos you painstakingly took suddenly disappear, or important files seem to have “vanished into thin air” from your SD card? The anxiety of data loss is something that everyone who has experienced it understands. Don’t panic! After reading this article, you will know exactly how SD card data recovery works!

1. Why Does Data Loss Occur on SD Cards?
Human Error: Directly removing the card, accidentally deleting files, formatting errors… these actions can damage the index structure of the file system.
Hardware Failure: Oxidation of the metal contacts, chip aging, physical drops, etc., can directly lead to damage to the storage medium.
File System Errors: For example, when the FAT32/exFAT system malfunctions, the kernel may mark the SD card as read-only, causing new data to be lost.
Virus Attacks: Malicious software may hide or encrypt files, or even directly damage the storage structure.
Hot-Swap Risks: Removing the card during data writing or reading can lead to file corruption or loss.
2. Technical Principles of SD Card Data Deletion and Recovery
When you delete a file from the SD card, the system merely marks the storage space as “available,” but the actual data remains in the physical storage area. It’s like tearing up a library card, but the book is still on the shelf. As long as new data does not overwrite the original location, the old file may be “retrieved.”
The Core Logic of Recovery Technology:
Scanning Uncovered Areas: Professional software scans the SD card block by block to find files that have not been overwritten by new data.
Reassembling File Fragments: Even if files are stored in fragments, the software can reassemble the data using file headers, extensions, and other characteristics.
Avoiding Secondary Damage: Writing operations must be stopped during the recovery process; otherwise, new data will overwrite old files, leading to permanent loss.
3. Why Do Deleted Files from SD Cards Not Go to the Recycle Bin?
The Windows Recycle Bin is designed only for local hard drives, while the SD card, as a removable storage device, triggers a physical deletion upon deletion. The system will prompt: “Files will be permanently deleted,” but the actual data remains on the card until overwritten by new data. This is why stopping the use of the SD card immediately after accidental deletion increases the recovery success rate.
4. Summary of SD Card Data Recovery Methods
1. Undo the Last Deletion with a Shortcut Key
Applicable Scenario: Just deleted a file and have not performed any other operations.
Steps: Immediately press Ctrl+Z (Windows) or Command+Z (Mac) to attempt to undo the deletion.
Limitations: Only effective for files deleted in a very short time and if the file manager has not been closed.
2. Professional Data Recovery Software
Applicable Scenario: Various complex scenarios such as SD card deletion, SD card formatting, partition table anomalies, partitions turning RAW, virus attacks, etc.
Recommended Tool: EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard (Chinese version).
Reasons for Recommendation:
Beginner-friendly: The “Scan – Find – Recover” three-step method is easy to use even for beginners.
Powerful Functionality: Covers all scenarios, capable of solving over 90% of daily data loss issues.
Good Compatibility: Supports Windows/Mac systems and can scan various storage devices such as hard drives, USB drives, and SD cards.
Steps:
Step 1. Connect the SD card to the computer via a card reader, ensuring it is recognized, then run the EaseUS Data Recovery software.
Step 2. Select the SD card where data is lost and click “Find Lost Data.” The software will find lost data on the SD card through quick and deep scanning.
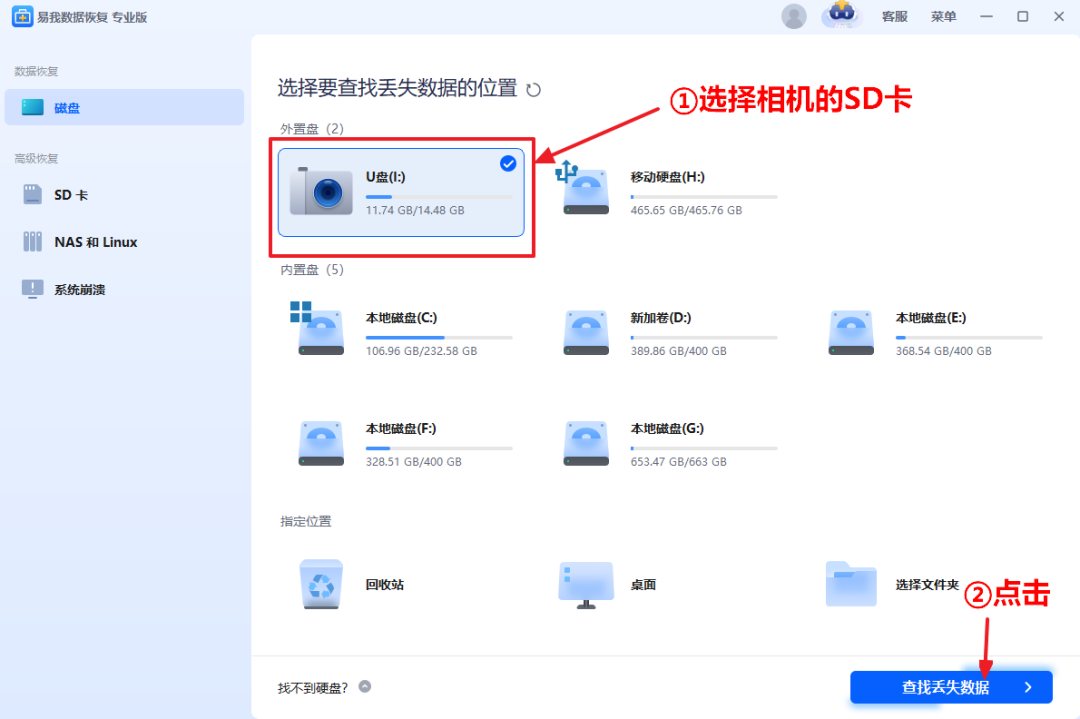
Step 3. During or after the scanning process, you can preview the found files to ensure they are what you need. You can also use the “Filter” and “Search” functions to quickly find the target files.
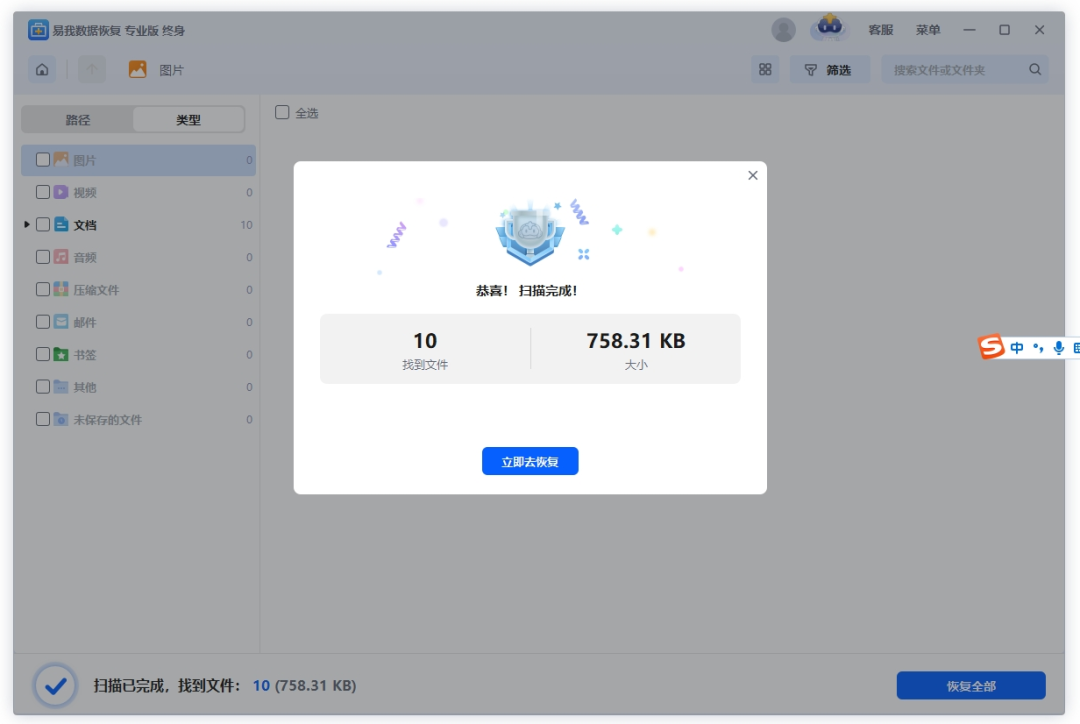
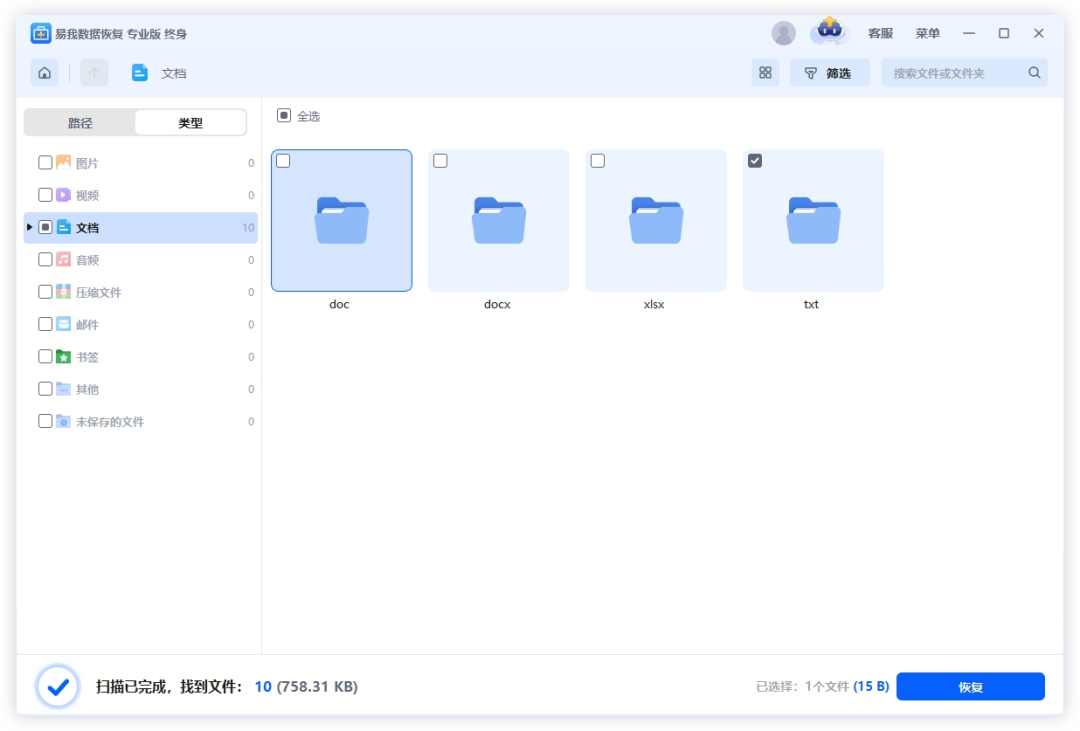
Step 4. Check the files you need to recover from the SD card, perform the “Recover” operation, and then select a target path to save the files. Please save the files on a secure device outside of the SD card.
3. Offline Data Recovery Institutions
Applicable Scenario: SD card has physical damage (e.g., unrecognized, severe scratches).
Steps:
Contact relevant institutions through online consultation or offline stores to inquire about costs.
Mail the SD card to the institution and wait for technicians to inspect and quote.
Data recovery usually takes 3-7 working days, during which the recovered data will be verified.
Precautions:
Choose a legitimate institution to avoid data leakage risks.
Costs can be high (usually starting from 500 yuan), and the recovery success rate is not 100%.
5. Preventing Data Loss: Recommendations for SD Card Usage
Safe Ejection: Click “Safely Remove” in the computer/camera before removing the card to avoid hot-swapping.
Regular Backups: Sync important data to cloud storage or external hard drives to avoid “putting all eggs in one basket.”
Avoid Extreme Environments: Keep away from high temperatures, humidity, and magnetic interference (e.g., near speakers).
Partition Usage: Divide the SD card into “working area” and “backup area” to reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
Timely Replacement of Aging Cards: SD cards have a lifespan; be cautious of bad block accumulation after frequent read/write operations.
6. Conclusion
SD card data recovery is not “mystical” but a technological practice based on storage principles. Stopping writing immediately after accidental deletion, choosing professional tools, and seeking help from offline institutions when necessary can significantly improve recovery success rates. More importantly, developing a “backup first” habit can fundamentally eliminate the anxiety of data loss.