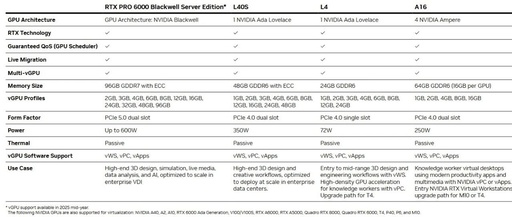
NVIDIA GPU in Virtualization
NVIDIA Virtual GPU (vGPU) software unleashes powerful GPU performance for enterprise data centers, as well as public and private clouds. Installed on a server equipped with an NVIDIA GPU, NVIDIA vGPU software can create virtual GPUs that can be shared among multiple virtual machines running on any device, anywhere. IT departments achieve standardized infrastructure in … Read more