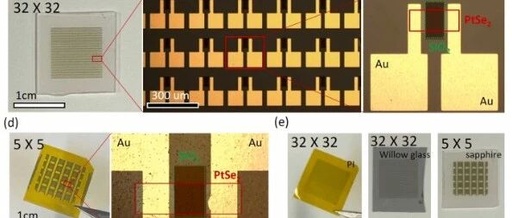
Significant Advances in Edge Computing: Humanity’s First AI Integration into Microelectromechanical Systems
To participate in the Meet 35 conference, please click ↑ To achieve edge computing (computations close to the data source) on devices such as 5G networks and the Internet of Things, it is necessary to deploy sufficient computing power on micro devices. To realize this idea, future efforts will focus on utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) … Read more