Skip to content
Cisco Certification | Huawei Certification | IT Technology | Network Engineer
👇3000 people technical exchange QQ group, remark 【official account】 for faster access
In today’s information society, network communication has become the backbone of global information exchange. The TCP/IP model, as the core protocol of internet communication, not only reflects the inevitable choice of technological development but also demonstrates a profound understanding of the demand for reliable and efficient communication.
The reason why the TCP/IP model has become the mainstream standard of network communication today is due to its unique advantages and the logic of historical development. This model originated from the U.S. Department of Defense’s research program, designed to achieve interconnectivity between networks and maintain communication stability and reliability in harsh environments. After decades of development and refinement, TCP/IP has gradually become the most widely adopted network communication protocol.
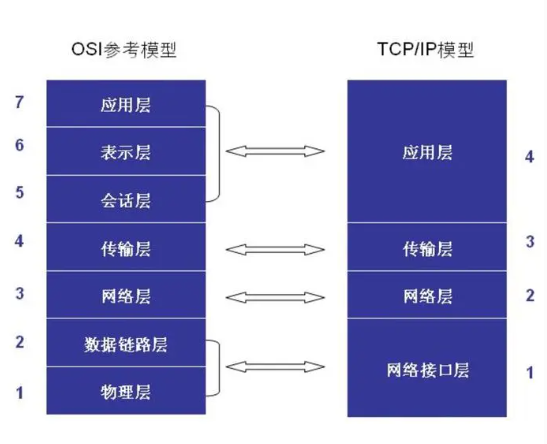
Structurally, the TCP/IP model is divided into four layers: the network interface layer, the internet layer, the transport layer, and the application layer. This layered design not only clearly delineates the responsibilities of network communication but also provides a framework for the integration of various network technologies. Each layer performs specific functions, working together to build a solid foundation for complex network communication.
The network interface layer interfaces with the physical network, providing a unified interface for the upper layers, making the differences between different physical networks transparent to the upper layers, thus achieving compatibility and integration of network technologies. The internet layer is responsible for handling the transmission and routing of data packets, ensuring that data can traverse complex network environments to reach its destination. Among these, the IP protocol, as the core of the internet layer, achieves global network interconnectivity through standardized address allocation and routing mechanisms.
The transport layer is a crucial part of the TCP/IP model, primarily tasked with providing end-to-end data transmission services. The two most well-known protocols at this layer are TCP and UDP. The TCP protocol is known for its reliability, establishing a connection through a three-way handshake, ensuring accurate data transmission through serialized data streams and acknowledgment retransmission mechanisms. Meanwhile, the UDP protocol is favored for its efficiency, suitable for applications that require high real-time performance. The existence of these two protocols meets the dual demands of data transmission speed and quality in different application scenarios.
The application layer is the direct interface where users interact with the network. It handles specific application details, such as protocols like HTTP, FTP, SMTP, etc., all built on this layer, providing users with a rich variety of network services.
In addition to its scientific structure, the widespread application of the TCP/IP model is also due to its excellent scalability and flexibility. With the continuous emergence of new technologies, the TCP/IP model can adapt to new network demands through extensions and upgrades, such as the emergence of IPv6 to address the exhaustion of network addresses, showcasing the TCP/IP model’s strong vitality in adapting to the times.
The TCP/IP model has become the mainstream of current network communication, benefiting from its scientific layered design, adaptability to different network environments, and future-oriented scalability. It not only ensures the flow and exchange of data globally but also promotes the rapid development of information technology and the prosperity of the internet.
For course consultation, add: HCIE666CCIE
↑ Or scan the QR code above ↑
What technical points and content do you want to see?
You can leave a message below to let us know!