Slow internet speed has almost become the most frequent complaint received by broadband service providers. Research shows that most consumers currently experience WiFi speeds that are only about 50% of their router’s bandwidth limit.

The reason WiFi speeds do not meet expectations is related to these six factors.
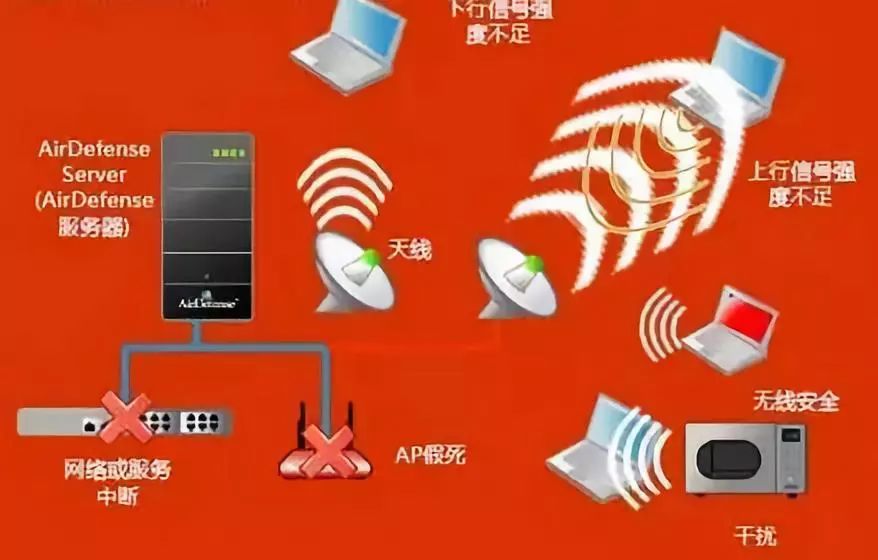
1. WiFi Signal Congestion
When users access the internet via WiFi, it is like tuning into a radio station, using a fixed frequency wireless band. Therefore, the number of similar signal transmitting and receiving devices in the surrounding area greatly affects the WiFi experience.
“If you live in a central apartment building in the city, where there are hundreds of wireless networks, this is almost the worst WiFi usage environment.”
Even if your phone shows full WiFi signal bars, the actual WiFi signal may still be very slow. Devices such as mobile phones, cordless phones, microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and even wireless baby monitors can all affect WiFi signal quality.
2. Devices Cannot Simultaneously Send and Receive Data
Since WiFi signals cannot send and receive data simultaneously, this access method tends to produce more data latency compared to other methods. Moreover, many people using the same WiFi channel simultaneously can significantly affect WiFi signal strength.
Additionally, if you are in a well-signaled area, your router will continuously search for the best network channel, which can also cause network latency, a problem that cannot be resolved by broadband providers.

3. Inherent Defects
No matter how much WiFi technology improves in the future, wireless connections will still struggle to surpass existing wired internet access methods. WiFi will not completely replace wired internet connections; it is merely a more convenient networking solution.
4. Background Processes
If WiFi speed does not improve after ruling out all the above factors, check if your software is automatically syncing data and photos, as this can greatly affect your WiFi speed. Moreover, many of these applications run silently in the background, and many users may not even remember their existence.

5. Router Placement
The placement of your wireless router has a significant impact on signal strength. For example, if you place your router next to a concrete wall, its signal strength will be greatly reduced. Ideally, the best placement for the router is on the ceiling in the center of the room (although many consumers may not have such conditions).
6. Differences in Connected Devices
If your iPhone 4’s WiFi connection speed is slower than that of the iPhone X, do not be surprised, as the WiFi connection speed is also greatly related to the processing speed of the connected device.
1. Upgrade your router to one that supports both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies. However, it should be noted that the 5GHz frequency signal has poorer wall penetration than 2.4GHz, and many older devices do not support this WiFi frequency.
2. Use a channel viewer to check the WiFi channel usage in your area, and then select a less congested channel to use.
3. If you have an idle wireless router, consider using it to extend or amplify the indoor WiFi signal strength.
4. If your router has options for high power and low power usage plans, typically the low power usage plan will provide better WiFi signal strength.
More News
Eating hair in the noodles leads to a complaint: “Go ahead and sue me!” A young man received 1016 yuan in compensation after suing!
Huazhu claims, “One in ten Chinese people are guests,” but what about hotel record leaks?!
The last stand! Only 100 hours left until discharge, and they are still fighting on the front lines against floods.
Source:Practical Life Tips
Supervised by: Chen Zhichun
Edited by:Guan Kailiang, Li Ang
Intern: Si Yiwen

Still suspecting that Lao Wang shared it~
