MCU (Microcontroller Unit), DSP (Digital Signal Processor), and FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) are three common types of processors in embedded systems, and they have the following main differences:
MCU is a microcomputer that integrates basic components such as a Central Processing Unit (CPU), memory, input/output interfaces, and timers. It is typically used in control applications such as home appliances, automotive control systems, and embedded sensors.
DSP is a processor specifically designed for digital signal processing (such as audio, video, image processing, etc.). It possesses high-speed and efficient digital signal computation capabilities and is widely used in communications, audio processing, radar, and other fields.
FPGA is a programmable logic device that can be programmed according to user requirements to implement various digital logic circuits. It is often used in applications that require customized hardware acceleration, such as high-performance computing, signal processing, and image processing.
MCUs typically have a fixed hardware structure with relatively fixed functions, lacking flexibility.
DSPs have specialized instruction sets and hardware accelerators for efficiently processing digital signals, but they are not as flexible as FPGAs.
FPGAs offer high programmability and can implement various complex digital circuits as needed, providing significant flexibility.
MCUs generally have lower clock frequencies and computational capabilities, making them suitable for low-power, low-complexity applications.
DSPs usually have higher clock frequencies and dedicated hardware units for digital signal processing, suitable for applications requiring high-performance digital signal processing.
The performance of FPGAs depends on their hardware resources and design, allowing for the implementation of very high-performance digital logic circuits, suitable for high-performance applications requiring customized hardware acceleration.
MCUs typically have lower power consumption, making them suitable for applications that require long-term operation and low power.
DSPs have relatively higher power consumption because they often need to process large amounts of digital signal data.
FPGAs have higher power consumption, but compared to ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits), they offer better flexibility and programmability.
In summary, the choice between MCU, DSP, or FPGA depends on the application requirements. If a control application is needed, choose MCU; if high-performance digital signal processing is needed, choose DSP; if customized hardware acceleration or higher flexibility is required, choose FPGA.
— End —
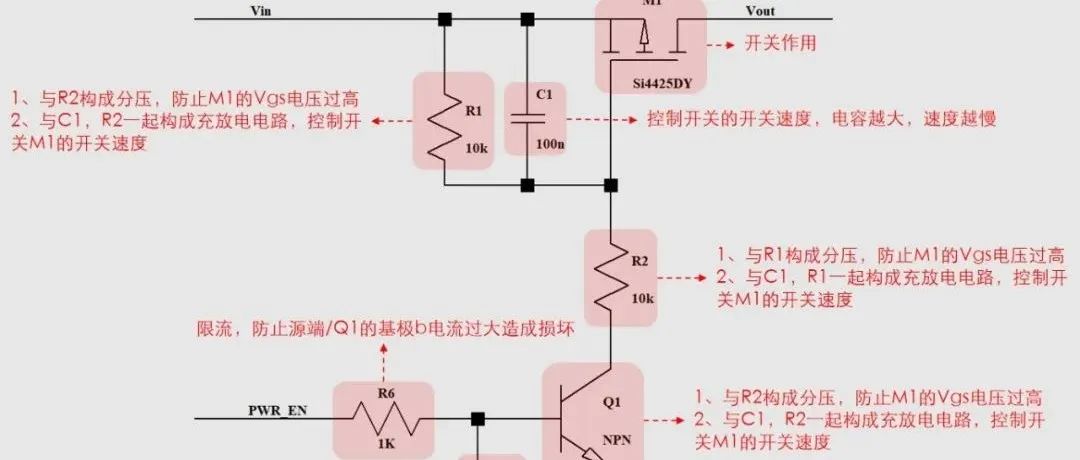
Must-read for hardware engineers: Common PMOS switch circuit issues!
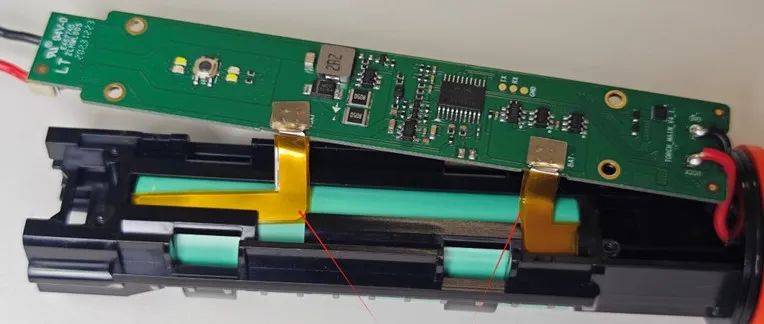
Disassembling the multifunctional flashlight that comes with Xiaomi’s SU7 car: Is it worth 199 yuan?