 On April 19, the world’s first humanoid robot half marathon was held in Beijing. On the 21.0975-kilometer track, for the first time, “humans and robots ran together,” with 20 robot teams from universities, research institutions, and companies participating. Among them were the 1.8-meter tall, long-striding “Tiangong,” the 82-centimeter tall, agile “Xiao Hai,” and the “Xingzhe No. 2,” which has a battery life of six hours.Liang Jiang, deputy director of the Beijing Economic and Technological Development Area Management Committee, stated that previously humanoid robots were mostly tested in closed environments like laboratories, while this marathon serves as a systematic test of humanoid robots’ adaptability to complex scenarios. Through this “extreme test,” people are concerned about how robots can achieve the technological leap from short-distance walking to marathon racing.
On April 19, the world’s first humanoid robot half marathon was held in Beijing. On the 21.0975-kilometer track, for the first time, “humans and robots ran together,” with 20 robot teams from universities, research institutions, and companies participating. Among them were the 1.8-meter tall, long-striding “Tiangong,” the 82-centimeter tall, agile “Xiao Hai,” and the “Xingzhe No. 2,” which has a battery life of six hours.Liang Jiang, deputy director of the Beijing Economic and Technological Development Area Management Committee, stated that previously humanoid robots were mostly tested in closed environments like laboratories, while this marathon serves as a systematic test of humanoid robots’ adaptability to complex scenarios. Through this “extreme test,” people are concerned about how robots can achieve the technological leap from short-distance walking to marathon racing.
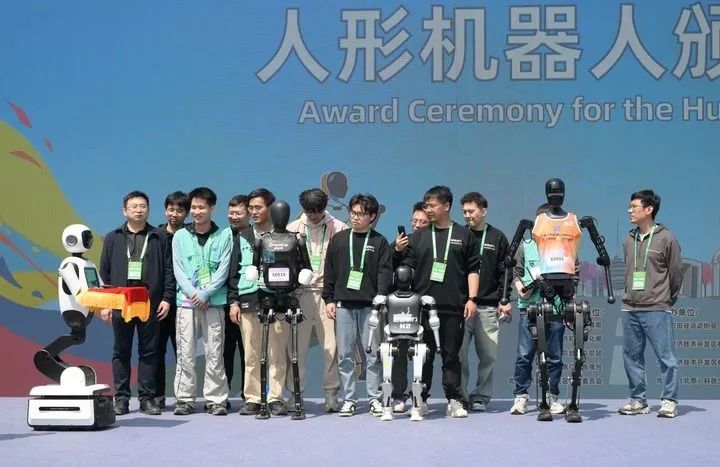

On April 19, 2025, a robot lifted a medal at the humanoid robot award ceremony, approaching the winning robot contestants and technical teams. On that day, the 2025 Beijing Yizhuang Half Marathon and Humanoid Robot Half Marathon took place. (Photo by Xinhua News Agency reporter Li He)Previously, during the Spring Festival Gala of the Year of the Snake, more than ten Yushu robots dressed in floral cotton jackets took the stage, dancing along with human performers, attracting widespread attention. People exclaimed that humanoid robots have entered the lives of ordinary people.Investment in humanoid robots is heating up. More than ten local governments, including Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen, have established industrial funds exceeding 100 million yuan. The number of companies engaged in embodied intelligence is increasing, and the scale of financing is continuously rising.Creating a machine that resembles a human has long been a dream of humanity. From the ancient text “Liezi: Tangwen” recording the creation of “puppets” to the simple combination of “humanoid” shells and mechanical devices in the early 20th century, from various robots in Chinese and foreign science fiction works to the birth of the world’s first humanoid robot WABOT-1 at Waseda University in Japan in 1973, humanity’s exploration of humanoid robots has never ceased. Over the past half-century, this industry has experienced ups and downs, with various humanoid robots launched by countries around the world, but overall development has been slow.Now, why has the development of humanoid robots suddenly accelerated?(1) Robots Frequently Attract Attention“Every few steps, you can encounter a humanoid robot.” In late March, several guests attending the Zhongguancun Forum Annual Meeting expressed, “It feels like being on a sci-fi movie set” and “we have entered the future society ahead of time.”
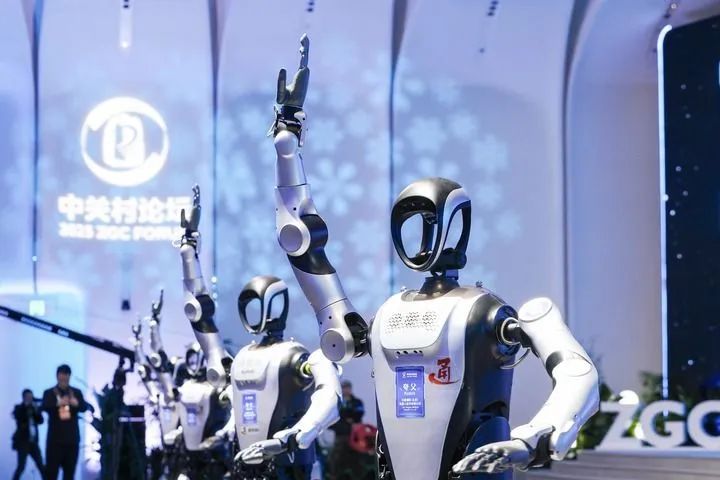

On March 27, 2025, the humanoid robot “Kua Fu” performed at the opening ceremony of the 2025 Zhongguancun Forum Annual Meeting. (Image provided by the interviewed company)Nearly a hundred humanoid robots from more than ten companies took part in the forum, actively engaging in welcoming, communication, hosting, and performance scenarios:At the opening ceremony, the “Kua Fu” performing Tai Chi stands 1.7 meters tall and weighs 55 kilograms, created by Leju Technology Co., Ltd. in collaboration with the Beijing General Artificial Intelligence Research Institute. It also serves as a welcoming robot, answering public inquiries, providing explanations, and guiding services, and can even lead people when asked for directions.The “Tsinghua Huoshen Team” T1 robot, which won the championship at this year’s Robot Football World Cup in Germany, undertakes four tasks: performing group push-ups and standing up in one second at the opening ceremony, playing football and performing stunts in the exhibition hall, guiding as a welcoming robot, and hosting sub-forums.
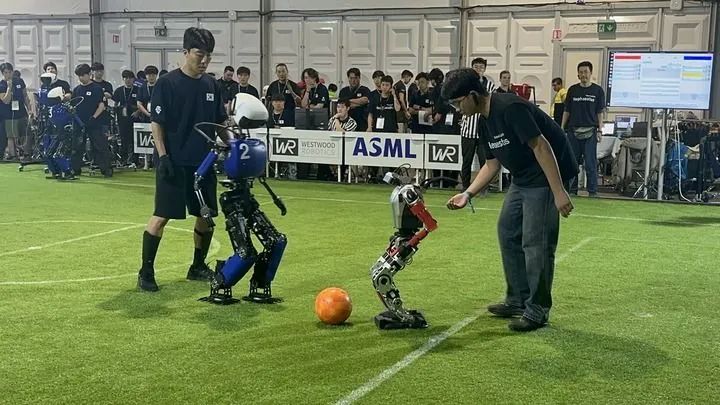

Scene from the 2024 Robot Football World Cup. (Provided by Professor Zhao Mingguo of Tsinghua University)Since the Spring Festival, social media has frequently featured viral videos of humanoid robots showcasing skills such as front flips, back flips, and riding bicycles, refreshing people’s perceptions of embodied intelligence with high-difficulty actions and human-like interactions.Embodied intelligence is a new term that has entered the public eye in recent years. It emphasizes the close integration of intelligent systems with the body, achieving intelligent behavior through interaction between the body and the environment. In contrast, the concept of disembodied intelligence refers to chatbots that lack a physical body and rely entirely on computation and data processing to achieve intelligent behavior.Humanoid robots are one of the typical applications of embodied intelligence. At this year’s National Two Sessions, the government work report clearly stated the establishment of a growth mechanism for future industrial investment, nurturing future industries including embodied intelligence. Some factories, universities, research institutions, and artificial intelligence companies are taking the lead in using humanoid robots.Since the beginning of this year, companies like UBTECH and Leju have announced that their robots have entered automotive factories for training.In a recent video released by UBTECH, two 1.72-meter tall Walker S1 robots stand face to face in the Zeekr automotive factory, nodding to each other simultaneously, then opening their arms to collaboratively transport a material box measuring 1.2 meters long, 50 centimeters wide, and 40 centimeters high. Nearby, another robot uses its “dexterous hand” to place parts into the box.
Some factories, universities, research institutions, and artificial intelligence companies are taking the lead in using humanoid robots.Since the beginning of this year, companies like UBTECH and Leju have announced that their robots have entered automotive factories for training.In a recent video released by UBTECH, two 1.72-meter tall Walker S1 robots stand face to face in the Zeekr automotive factory, nodding to each other simultaneously, then opening their arms to collaboratively transport a material box measuring 1.2 meters long, 50 centimeters wide, and 40 centimeters high. Nearby, another robot uses its “dexterous hand” to place parts into the box.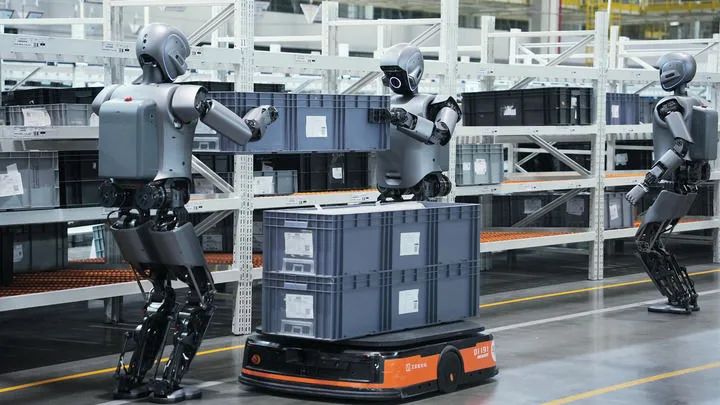 In February 2025, the UBTECH industrial humanoid robot Walker S1 collaborated to transport large boxes in the Zeekr automotive factory. (Image provided by the interviewed company)Leju’s founder, Leng Xiaokun, stated that the company’s robot “Kua Fu” is undergoing training for two tasks in several automotive factories—transporting boxes and sorting spare parts.“The robot’s work efficiency is about 70% of that of skilled workers,” said Leng Xiaokun, adding that robots are not yet capable of performing complex tasks like precision screw fastening, but are suitable for heavy, generalized, and highly repetitive tasks, such as transporting boxes of various sizes, colors, weights, and dimensions, and sorting different shapes of spare parts.“In our research at automotive factories last year, we found that automation equipment has taken on over 80% of the work, but in the ‘last mile,’ such as the final production line in assembly workshops, human labor is still relied upon, as existing mechanical arms and wheeled robots cannot complete these tasks. Thus, humanoid robots are a suitable solution,” Leng Xiaokun said.In March, Dongfeng Liuzhou announced the procurement and deployment of 20 UBTECH humanoid robots, planning to complete delivery in the first half of the year, marking the first batch of humanoid robots entering automotive factories.“Industrial manufacturing is what we value most, as it can genuinely help customers solve practical problems,” said UBTECH founder Zhou Jian, adding that the company’s goal this year is to produce about 1,000 humanoid robots, entering real scenarios to collect more data in preparation for further development.Recently, UBTECH also partnered with the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center to release a full-size research-grade humanoid robot “Tiangong Walker” priced below 300,000 yuan.Yushu Technology, which has no plans to send robots into factories, has recently launched products on e-commerce platforms like JD.com and AliExpress. Yushu’s products fall into two categories: quadruped robotic dogs aimed at end consumers and humanoid robots aimed at developers.Yushu’s products have been selling hot overseas. Recently, at the Mobile World Congress in Spain and the NVIDIA Developer Conference in the United States, Yushu’s robot sales banners attracted attention. Yushu’s marketing director Huang Jiawei stated that last year, Yushu humanoid robots were sold to over 100 countries and regions, with core users being universities, research institutions, and AI technology companies, where users conduct secondary development on Yushu hardware.
In February 2025, the UBTECH industrial humanoid robot Walker S1 collaborated to transport large boxes in the Zeekr automotive factory. (Image provided by the interviewed company)Leju’s founder, Leng Xiaokun, stated that the company’s robot “Kua Fu” is undergoing training for two tasks in several automotive factories—transporting boxes and sorting spare parts.“The robot’s work efficiency is about 70% of that of skilled workers,” said Leng Xiaokun, adding that robots are not yet capable of performing complex tasks like precision screw fastening, but are suitable for heavy, generalized, and highly repetitive tasks, such as transporting boxes of various sizes, colors, weights, and dimensions, and sorting different shapes of spare parts.“In our research at automotive factories last year, we found that automation equipment has taken on over 80% of the work, but in the ‘last mile,’ such as the final production line in assembly workshops, human labor is still relied upon, as existing mechanical arms and wheeled robots cannot complete these tasks. Thus, humanoid robots are a suitable solution,” Leng Xiaokun said.In March, Dongfeng Liuzhou announced the procurement and deployment of 20 UBTECH humanoid robots, planning to complete delivery in the first half of the year, marking the first batch of humanoid robots entering automotive factories.“Industrial manufacturing is what we value most, as it can genuinely help customers solve practical problems,” said UBTECH founder Zhou Jian, adding that the company’s goal this year is to produce about 1,000 humanoid robots, entering real scenarios to collect more data in preparation for further development.Recently, UBTECH also partnered with the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center to release a full-size research-grade humanoid robot “Tiangong Walker” priced below 300,000 yuan.Yushu Technology, which has no plans to send robots into factories, has recently launched products on e-commerce platforms like JD.com and AliExpress. Yushu’s products fall into two categories: quadruped robotic dogs aimed at end consumers and humanoid robots aimed at developers.Yushu’s products have been selling hot overseas. Recently, at the Mobile World Congress in Spain and the NVIDIA Developer Conference in the United States, Yushu’s robot sales banners attracted attention. Yushu’s marketing director Huang Jiawei stated that last year, Yushu humanoid robots were sold to over 100 countries and regions, with core users being universities, research institutions, and AI technology companies, where users conduct secondary development on Yushu hardware.
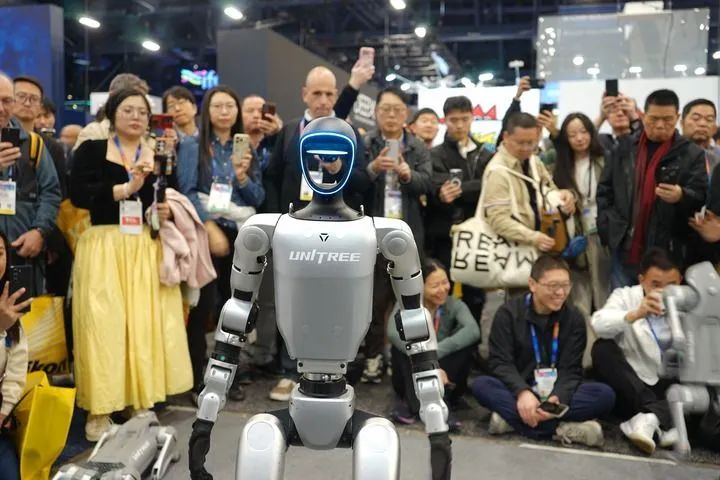

On January 8, 2025, at the Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas, people watched robot demonstrations at the Yushu Technology booth. (Photo by Xinhua News Agency, Zeng Hui)Nearly 30 universities in China have purchased Yushu humanoid robots for teaching and research. Zeng Lingdong, a teacher at the Engineering Technology Training Center of Shanghai University, stated that they are developing three aspects around the robot, including achieving walking, running, and jumping in complex environments, training the robot to perceive the environment for positioning and navigation, and enhancing the robot’s autonomous decision-making and cognitive intelligence.In addition to entering factories, universities, and research fields, humanoid robots are also entering specialized industries. For example, the Southern Power Grid Guangdong Electric Power Company is leading the development of a special humanoid robot for power, capable of withstanding extreme cold at -40°C and high temperatures of 80°C, which has been put into use to accurately locate faults in deep mountains and forests.Across the country, the industrial layout around humanoid robots is accelerating. It is understood that currently, more than ten local governments, including Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Chongqing, have established or are preparing to establish industrial funds, focusing on robot bodies, industrial chain components, and innovative applications in the industrial chain. More than ten companies in Beijing and Shenzhen have released humanoid robot products, with companies in Shanghai, Hangzhou, and Guangzhou also competing to launch their products.In the investment community, the heat around robot companies is increasing. According to data service provider IT Juzi, over 50 companies in the embodied intelligence sector received more than 6 billion yuan in financing in the first three months of this year.(2) What Has Driven the Acceleration?In 1973, Waseda University in Japan launched the world’s first full-size humanoid robot, WABOT-1, which was wrapped in wires, took 45 seconds to take a step, and could only walk 10 centimeters at a time, being heavy and slow.In the early 2000s, Honda released a humanoid robot called ASIMO, resembling a space astronaut, capable of climbing stairs and understanding voice commands. In 2013, Boston Dynamics released the humanoid robot Atlas, which could run on a treadmill and perform jumps, spins, and rolls, designed for disaster sites to replace humans in tasks like turning valves and transporting items in hazardous areas.Despite significant technological advancements, Honda announced in 2018 that it would cease development of the ASIMO robot. Although Boston Dynamics’ Atlas robot received high praise for its motion control capabilities, its high price and maintenance difficulties limited its practical application, leading to multiple sales of Boston Dynamics.
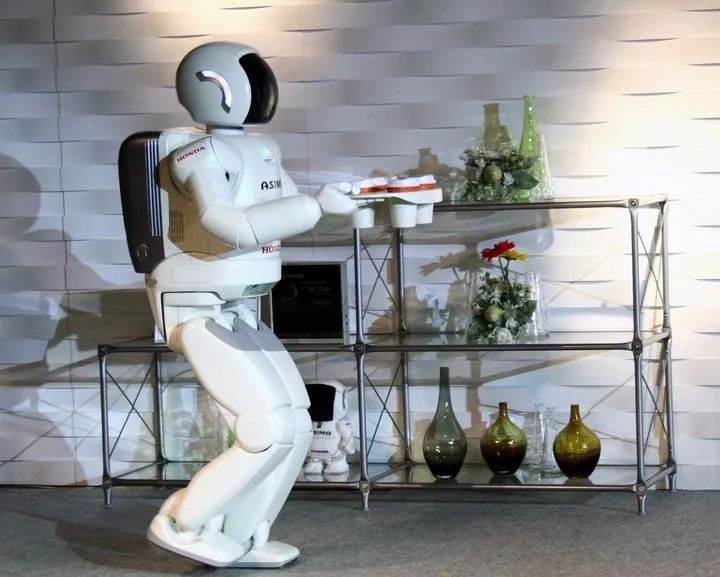

On October 22, 2007, Honda’s robot ASIMO served drinks to guests at the National Museum of Nature and Science in Tokyo, Japan. (Photo by Xinhua News Agency, Qian Zheng)After that, the humanoid robot industry fell into a period of silence. Until recent years, humanoid robots have suddenly accelerated in development. Why?“For a long time, robot development was based on programming. The emergence of AI large models in 2022, which can simulate the human brain and possess generalization and transfer capabilities, has driven the development of this new species of humanoid robots,” explained Wang Tianmiao, honorary director of the Robotics Institute at Beihang University, who developed the first generation of medical robots in the 1990s.Xiong Rong, director of the Humanoid Robot Innovation Center in Zhejiang and a professor at Zhejiang University, stated that traditional robot research paradigms rely on mathematical modeling of human movement mechanics and seek optimal solutions to achieve functionality. This approach heavily depends on the experience of human experts, leading to limitations in generalization capabilities and difficulty in achieving intelligent reasoning.“In the past, when we applied artificial intelligence technology, we mainly focused on developing functions at the perception level, such as voice interaction and visual recognition, which limited robots to executing specific tasks of pre-set programs,” Xiong pointed out. “With the development of the new generation of artificial intelligence technology, we can now use large-scale data collection and neural network training to enable robots to acquire more implicit knowledge, opening new paths for research.”Empowering robots with artificial intelligence is also a consensus in the industry.According to Zhang Jin, president of Shenyang Siasun Robot Automation Co., Ltd., the greatest driving force behind the recent push for humanoid robots is the new generation of artificial intelligence. He entered the Shenyang Institute of Automation at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in the early 1990s, focusing on robot research, and his company was the first to go public in the industry.Zhang Jin stated that their company also attempted to develop humanoid robots, and while walking and limb movements are not technical difficulties, the biggest problem is that the humanoid robots produced lack a “brain.”Experts explain that previously humanoid robots resembled “puppets on strings,” relying on “pre-programmed” or single-function AI, limiting their application scenarios. The emergence of large models has allowed robots to accelerate their intelligence, enabling them to truly understand their environment, make autonomous decisions, and interact, thus opening up a wide range of applications.Many experts mentioned an event that occurred in 2022: Tesla officially released the humanoid robot Optimus. Musk showcased videos of Optimus transporting boxes and grabbing metal rods in an automotive factory, stating that it would be mass-produced, with costs potentially dropping to between $20,000 and $30,000.
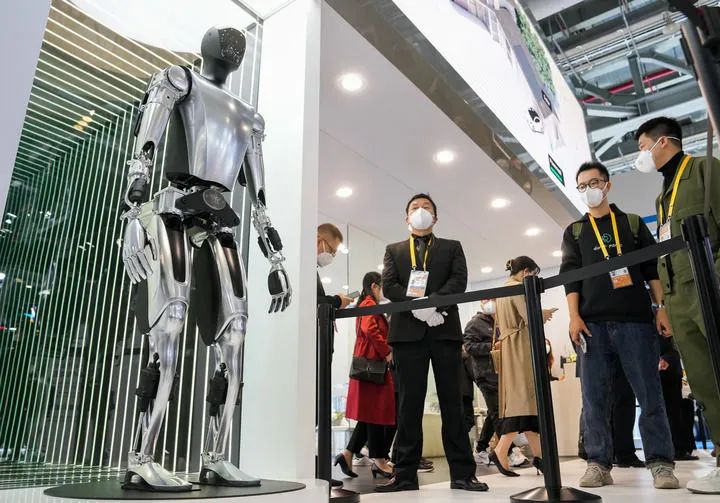

On November 5, 2022, Tesla’s humanoid robot was photographed at the automotive exhibition area of the fifth China International Import Expo. (Photo by Xinhua News Agency, Ding Ting)“When Optimus receives a command, it does not execute it according to traditional programming or follow a fixed motion trajectory; it can understand commands, make autonomous decisions, and decompose them into multiple actions to achieve this, elevating the application of robots to a new level and showing everyone the development direction of humanoid robots,” Zhang Jin said.Zhao Mingguo, director of the Robot Control Laboratory at Tsinghua University’s Department of Automation, stated that he has been researching humanoid robots since 2001 and has always been troubled by the high costs of robots, including reducers, drivers, and motors. With Tesla’s entry into the field, it has brought new ideas to the industry by producing products and building an industrial chain, integrating original automotive suppliers into the robot field.Humanoid robots generally consist of three parts: the brain, the cerebellum, and the body. What challenges are there in their development?For example, to have a humanoid robot pour a cup of water:The “brain” breaks down this command into multiple tasks such as “What is a cup? Where to grip the cup? Where is the water? How to get there? How much water to pour? Is it cold or hot?” In this process, the “brain” performs a large number of calculations for recognition, perception, judgment, and decision-making; any oversight in any link can lead to command failure.Meanwhile, actions like walking, grabbing, pouring, and handing over, including how to navigate around an obstructing stool or step over a kitchen threshold, rely on the “cerebellum” for guidance. During movement, if a pet suddenly appears, it must feedback information to the “brain” to replan the path.Some products that have emerged this year reflect the advancements in technologies like the “cerebellum” and “brain.”The performance of Yushu robots at the Spring Festival Gala has been regarded by many industry insiders as showcasing a “developed cerebellum,” demonstrating a high level of motion control. This is because the characteristics of the “cerebellum” rely heavily on data collected around the robot’s hardware, requiring a high degree of compatibility with the hardware.In March, the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center released the world’s first “one brain, multiple capabilities” and “one brain, multiple machines” general embodied intelligence platform “Hui Si Kai Wu.”“Embodied intelligence is still in its early stages of intelligence, and the industry urgently needs a general intelligent platform with multi-body compatibility, multi-scenario adaptability, and strong generalization capabilities,” said Xiong Youjun, general manager of the innovation center. “Hui Si Kai Wu” aims to fill the important gap of a general software system for the embodied intelligence industry, helping humanoid robots transition from executing single tasks to making autonomous decisions and executing tasks in complex environments.Currently, the biggest bottleneck limiting the development of humanoid robots remains the “brain.” The industry generally believes that research on the general embodied intelligence large model, referred to as the robot’s “brain,” has only just begun.Zhang Weinan, deputy director of the School of Computing at Harbin Institute of Technology and executive dean of the School of Artificial Intelligence, and his team have long been engaged in research on robot brains. He stated that there have not yet been any breakthrough products in the field of robot “brains” comparable to large models, both domestically and internationally.“From the core of intelligence, that is, the software part of the brain, the biggest problem currently faced is data; there is a lack of high-quality, large-scale data for cross-scenario applications,” Zhang Weinan said.In terms of hardware, Zhang Weinan indicated that dedicated computing chips for the robot brain still need further research and popularization.Xu Huazhe, co-founder of Xinghai Map Artificial Intelligence and assistant professor at Tsinghua University’s School of Interdisciplinary Information, focuses on the capabilities of the robot “brain,” which is the foundational large model for embodied intelligence.“A true foundational large model for embodied intelligence must enable robots to possess long-sequence action execution capabilities, the ability to follow language instructions, and have high dexterity and generalization capabilities,” he often uses the example of a robot cooking to describe the level he envisions the “brain” could achieve.“I want the robot to cook a dish called squirrel mandarin fish, as the operational difficulty is high—dealing with a live fish that is slippery and slimy, with granular scales. It must not only handle the live fish but also be able to cut, deep fry, stir-fry, pour sauce, and plate. If a robot can accomplish this, it proves its level of intelligence is very high,” Xu Huazhe said, considering this his “lifetime goal.” Recently, with continuous influx of capital and talent into this field, Xu Huazhe has become more optimistic. However, he still believes it will take at least ten to twenty years to enjoy a dish cooked by a robot.Recently, videos of humanoid robots pouring tea and threading needles through grapes have been widely circulated on social media, leading many to believe that soon they will be able to buy a robot as a housekeeper.When reporters asked several industry experts about when humanoid robots would enter households, their attitudes were generally cautious, stating that just because humanoid robots can perform some complex actions does not mean they can enter homes; there is a significant gap between being able to move and being able to perform tasks.“The explosive growth of embodied intelligence relies on software large models, data synthesis training, and chip computing power,” Wang Tianmiao said. He estimates that in two to three years, various applications of embodied intelligence will emerge, and humanoid robots may become mainstream after 2035.“It is currently very difficult for humanoid robots to enter household scenarios,” Xiong Rong believes, suggesting that they may begin to land in specific scenarios in three to five years, but achieving general applicability will require seven to ten years.Zhang Rui, founder of Beijing Iron Man Technology Co., Ltd., whose team was selected to participate in the Chinese astronaut humanoid robot project in 2021, candidly stated, “Compared to going to space, it is even more challenging for humanoid robots to enter households to complete tasks, and the timeline will be longer.”Zhang Rui explained that homes are complex environments with elderly, children, and pets, and different floor types such as carpets, tiles, and concrete have varying levels of flatness, leading to different friction forces and risks of tipping. A piece of steel weighing over 100 pounds can cause harm whether it falls on a person or a pet. “From this perspective, humanoid robots entering homes cannot simply be a stacking of existing mechanical and electronic structures; they need to be made with new materials that chemically change to form a new generation of muscles and bones,” he said.In Leng Xiaokun’s view, future humanoid robots entering households must be as affordable as home appliances and as intelligent as a PhD.“Many people have already seen the trend of them becoming as cheap as home appliances, as the body and ‘cerebellum’ technology are already available; reducing costs is just a matter of time. However, making robots as intelligent as a PhD and applying AI intelligence to the body is the research challenge,” Leng Xiaokun said.(3) Advantages of Chinese ManufacturingIn an industrial park at the junction of the Lingang and Fengxian districts in southeastern Shanghai, the first phase factory of Shanghai Zhiyuan New Technology Co., Ltd. is located here, also known in the industry as Shanghai’s first mass production factory for humanoid robots.The reason it is called a “mass production factory” is that in January of this year, Zhiyuan’s 1,000th general embodied robot rolled off the production line, including 731 biped humanoid robots “Expedition A2” and “Lingxi X1,” as well as 269 wheeled general robots.Reporters observed that the factory is divided into two floors: the first floor is for production and assembly, while the second floor is for complete machine testing. Unlike many highly automated factories without human workers, most processes here involve engineers or technicians.“Just as humans have over 200 bones, the A2 has over 400 components throughout its body,” said Yao Maoqing, a partner and president of the embodied business department at Zhiyuan. The robot is not complete just by being assembled; that is only the beginning. To avoid instability or falling later, it must undergo numerous itemized tests, such as deep squats with a single leg bearing 30 kilograms, requiring over 2,000 tests.Yao Maoqing stated that the factory began production in July last year, and the current hundred-plus workers mainly come from the artificial intelligence and automotive industries, all possessing certain experience and professional capabilities in quality systems, production operations, and supply chain management, ensuring the safety of every robot that stands up and walks steadily.A recent report by Morgan Stanley titled “Humanoid Robots 100: Mapping the Value Chain of Humanoid Robots” shows that among the top 100 listed companies, Asia accounts for 73%, with China accounting for 56%.“China continues to make the most impressive progress in the field of humanoid robots, with startups benefiting from mature supply chains, local application opportunities, and strong national support,” the Morgan Stanley report stated.In addition to startups in humanoid robots, there are two types of companies entering the research and development of humanoid robots: one type is leading technology companies like Huawei and iFlytek, which approach from the perspective of artificial intelligence to provide “intelligence” for robots; the other type is new energy vehicle companies like Xpeng and Xiaomi, which mainly leverage the transferable aspects of humanoid robots and smart cars in the supply chains of batteries, chips, and sensors, as well as similarities in the application of autonomous driving technology and AI models.“Although humanoid robots first appeared abroad, the most likely place for true industrialization to take place is in China, as China has a very complete industrial chain, with all the core components and technologies being researched by teams,” Zhang Jin stated, noting that leading companies will emerge in every key area, some focusing on the “brain,” others excelling in bipedal locomotion, arms, etc., collectively forming a complete and healthy industrial ecosystem.Xiaopeng Motors founder He Xiaopeng stated that the company has been researching humanoid robots for over five years, currently focusing on developing the physical world large model required for the “brain.” Currently, humanoid robots are close to the initial stage of autonomous driving L2, with hopes of achieving mass production and commercially viable L3 capabilities as soon as possible.A report from Dongwu Securities suggests that the humanoid robot industry in 2025 could be comparable to the electric vehicle industry in 2014. With the start of domestic mass production, a ten-year development cycle is about to begin.“An important characteristic of the development of China’s electric vehicle industry is the integration with the supply chain of consumer electronics. The development of the embodied intelligence industry, represented by humanoid robots, is drawing on this experience,” said Li Zesheng, a professor at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology and initiator of the Dongguan Songshan Lake Robot Industry Base.“China has the potential to replicate the disruptive impact of the electric vehicle industry in the field of humanoid robots. However, this time, the disruptive impact may far exceed a single industry and could change the nature of labor itself,” said analyst Rick Knutson from a semiconductor research consulting firm in the United States, as quoted in a report by the Consumer News and Business Channel.China’s robot industry has developed for decades, accumulating a wealth of technology and customers in industrial and service sectors, laying a foundation for the development of humanoid robots.Last year, China’s industrial robot market sales exceeded 290,000 units, with the highest application levels in the automotive and electronics industries. Medical robots, vacuum robots, and companion robots have also entered hospitals and homes in large numbers.
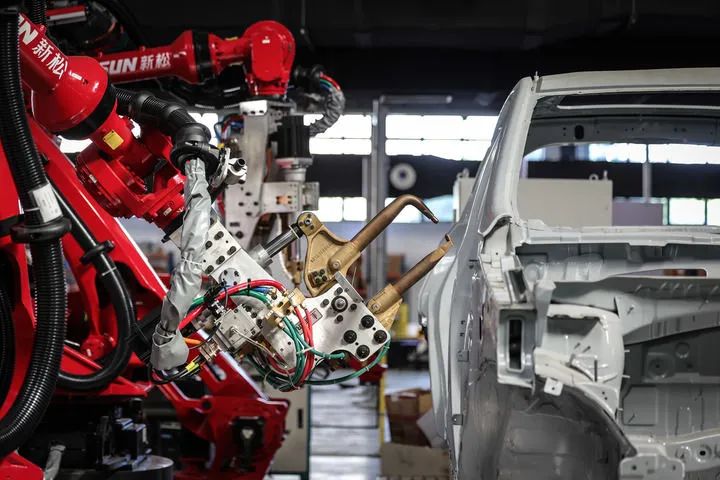

On June 3, 2024, a spot welding robot was photographed. Robots are widely used in industry, capable of handling heavy, dangerous, or complex tasks, improving production efficiency and economic benefits. (Photo by Xinhua News Agency, Pan Yulong)Wu Fengli, founder of Guangdong Tuosida Technology Co., Ltd., which specializes in industrial robots, stated that they are closely monitoring the development of humanoid robots and are making corresponding technological preparations. “Our confidence in developing humanoid robots in the future lies in the fact that we already have over 200,000 manufacturing clients, and the humanoid robot products we develop can be applied to existing clients immediately.”Zhang Jin also stated that Siasun has focused on industrial robots for over 20 years, accumulating rich industrial knowledge and experience. Once there are numerous application scenarios for humanoid robots in the industrial field, Siasun’s current humanoid robot team can quickly follow up.It is widely believed that the engineer dividend is one of China’s significant advantages in developing humanoid robots.China has continuously invested in higher education for over 40 years, cultivating the largest and most complete engineering workforce in the world. A report from the Development Research Center of the State Council shows that the total number of engineers in China increased from 5.21 million in 2000 to 17.653 million in 2020, characterized by youthfulness. According to a report from the Chinese Academy of Engineering in 2021, the total number of engineering graduates in China each year exceeds one-third of the total number of engineering graduates worldwide.High-quality talent cultivated by university robotics programs provides a talent reserve for the development of the humanoid robot industry. In the 1980s, some universities established research institutions for robots based on automation, mechanical engineering, and computer science. For example, in 1986, Harbin Institute of Technology established the Robotics Research Institute, which later developed into the National Key Laboratory of Robotics Technology and Systems.With the rise of artificial intelligence and the robotics industry, the Ministry of Education approved “Robotics Engineering” as an undergraduate major in 2016, and now over 300 universities offer undergraduate programs in robotics engineering.On the policy level, both the national and local governments have clear positioning for the development of the humanoid robot industry and are accelerating deployment.The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the “Guiding Opinions on the Innovative Development of Humanoid Robots” in 2023, stating that humanoid robots are expected to become a disruptive product following computers, smartphones, and new energy vehicles.Last year, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and six other departments issued the “Implementation Opinions on Promoting the Innovative Development of Future Industries,” placing humanoid robots at the top of the “Innovative Flagship Products” column.Locally, cities like Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Hangzhou have introduced policies to support the robotics or embodied intelligence industries.The path for humanoid robots toward the future is becoming increasingly clear, requiring collaborative efforts to accelerate the arrival of technological breakthroughs. Artificial intelligence combined with advanced manufacturing is positioning China at the forefront of the global robotics technology revolution.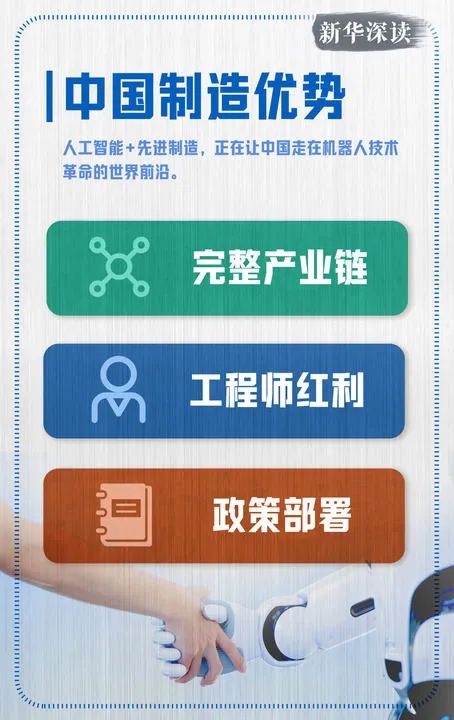 (4) Aspirations and Cautions for the FutureIn which fields will humanoid robots be applied first?The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology’s guiding opinions propose three areas: serving specialized field needs; creating typical manufacturing scenarios; and accelerating promotion in people’s livelihoods and key industries.Experts indicate that humanoid robots are needed for operations in harsh conditions and dangerous scenarios, such as civil explosives and rescue operations, as they can reduce the risk of work.While the automotive, 3C, and other manufacturing industries are important scenarios for enhancing the operational and task execution capabilities of humanoid robots, currently, humanoid robots entering factories are still performing simple tasks, with efficiency not matching that of ordinary workers.For example, the head of Agility Robotics in the United States stated that handling in factories is the most suitable application scenario for humanoid robots, but their robot Digit currently can only work continuously for 1.5 hours on a single charge, requiring 1.5 hours of charging afterward, which determines that the current working efficiency of humanoid robots is far below that of workers.Industry insiders generally believe that for humanoid robots to enter broader real applications, they must first enter “vocational skills training schools.”The data collection center of Shanghai Zhiyuan Robotics is such a school. In a space of about 4,000 square meters, daily life scenarios such as restaurants, tea shops, and homes are set up, with hundreds of data collectors wearing VR glasses and holding controllers, “hand-in-hand” teaching robots to perform household tasks—folding clothes, clearing dishes, pouring tea, serving meals, cleaning tables, and supermarket checkout—each action requiring the robot to repeat hundreds of times.
(4) Aspirations and Cautions for the FutureIn which fields will humanoid robots be applied first?The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology’s guiding opinions propose three areas: serving specialized field needs; creating typical manufacturing scenarios; and accelerating promotion in people’s livelihoods and key industries.Experts indicate that humanoid robots are needed for operations in harsh conditions and dangerous scenarios, such as civil explosives and rescue operations, as they can reduce the risk of work.While the automotive, 3C, and other manufacturing industries are important scenarios for enhancing the operational and task execution capabilities of humanoid robots, currently, humanoid robots entering factories are still performing simple tasks, with efficiency not matching that of ordinary workers.For example, the head of Agility Robotics in the United States stated that handling in factories is the most suitable application scenario for humanoid robots, but their robot Digit currently can only work continuously for 1.5 hours on a single charge, requiring 1.5 hours of charging afterward, which determines that the current working efficiency of humanoid robots is far below that of workers.Industry insiders generally believe that for humanoid robots to enter broader real applications, they must first enter “vocational skills training schools.”The data collection center of Shanghai Zhiyuan Robotics is such a school. In a space of about 4,000 square meters, daily life scenarios such as restaurants, tea shops, and homes are set up, with hundreds of data collectors wearing VR glasses and holding controllers, “hand-in-hand” teaching robots to perform household tasks—folding clothes, clearing dishes, pouring tea, serving meals, cleaning tables, and supermarket checkout—each action requiring the robot to repeat hundreds of times.
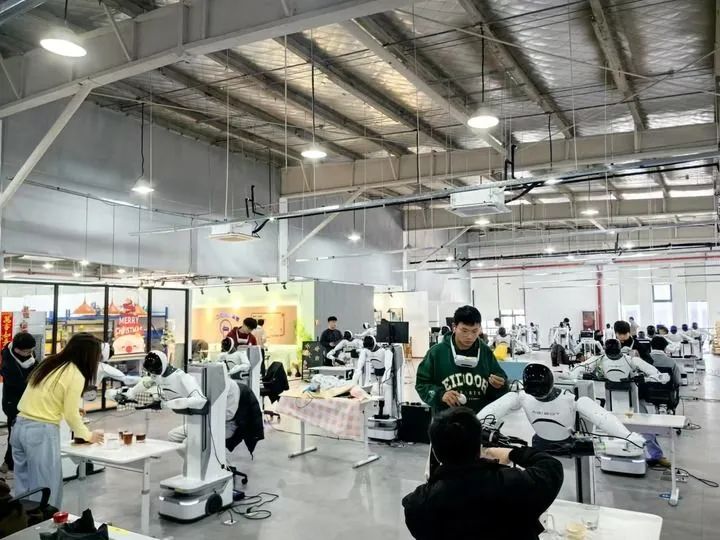

On February 18, 2025, at the data collection center of Zhiyuan New Technology Co., Ltd., data collectors “teach” robots to learn various skills. (Photo by Xinhua News Agency, Gong Wen)For example, the seemingly simple task of pouring water requires the robot to understand from high-quality data whether to pour into cup A or cup B, and how to respond calmly when the cup is temporarily moved, rather than becoming a disruptive or incompetent “idiot.”Peng Zhihui, co-founder of Zhiyuan, explained that unlike the text, images, and videos needed for large language models, robots need to interact with tangible objects in the three-dimensional world, and this data cannot be obtained from the internet; it can only be collected through significant investment in human and material resources to gather vast amounts of real robot interaction data. Over half of Zhiyuan’s R&D team is focused on research related to the “brain” and “cerebellum,” which, while challenging, must be overcome.In addition to training grounds established by robot companies like Zhiyuan, national and local co-built humanoid robot innovation centers in Beijing and Shanghai have also set up humanoid robot “technical schools.”Leng Xiaokun believes that these training grounds abstract real production and life scenarios, allowing robots to complete tasks through manual operation, collecting multi-dimensional data, and then inputting this data into the embodied intelligence model, or the “brain,” for training. Once mature, the model will be deployed to robots, enabling them to acquire new skills. This is the core work for the development of humanoid robots in the next two to three years.Many people worry about being “replaced by humanoid robots.” However, the actual situation is more complex. A factory manager told reporters that they hired about 900 people two years ago, 450 last year, and only a little over 300 this year, with job vacancies still existing. Many people prefer to deliver food rather than work in factories. Therefore, it is not a matter of “robots taking jobs from humans”; rather, there are indeed some jobs that lack workers.Xiong Rong stated that if humanoid robots are widely applied, it means they can replace humans in dangerous, repetitive, and tedious jobs, potentially solving the future labor shortage problem in society.However, while humanoid robots will bring great convenience to human work and life in the future, they may also challenge the existing social order and pose ethical risks. Experts warn that this concerns not only technology and business but also the future of humanity.People worry that robots may lose control at any time, that human rights may be infringed upon unknowingly, and that the behavior of robots may not be traceable or accountable.Wang Tiantian, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering and an expert in robotics and industrial automation, believes that the solutions to these issues directly determine the public’s acceptance of robots and their technology. Therefore, how to constrain the behavior of robots and guide their actions and public decisions to align with basic human values should be a concern for robot designers, manufacturers, users, and social managers alike.More than 80 years ago, science fiction writer Isaac Asimov proposed the “Three Laws of Robotics” to explore the relationship between robots and humans: robots must not harm humans or allow humans to come to harm; robots must obey human commands unless such commands conflict with the first law; and robots must protect themselves as long as it does not conflict with the first or second laws.“The three laws proposed by Asimov are a rule-based decision-making approach, but ethical issues in reality often involve conflicts within the same principle, which are much more complex than Asimov’s three laws,” said Liu Zhe, a professor at Peking University. He participated in drafting the “Prospective Standardization of Robot Ethics in China (2019),” which aims to lay the foundation for the future formulation of ethical standards for robots and ethical legal governance.Liu Zhe believes that although humanoid robots are far from possessing autonomy comparable to humans, their autonomy will bring multiple ethical challenges to human society, requiring more social resources and attention to be invested in research.He emphasized that the decision-making of intelligent robots is currently a “black box,” relying on algorithms and data to make decisions and take actions based on specific environmental changes. Therefore, all global ethical documents related to intelligent robots must propose reasons for the “transparency” and “explainability” of robot systems. In ethical governance, ethical considerations must not only be integrated into the design of robots but also require a socially consensual ethical framework.“When robots possess emotional interaction capabilities, it may trigger a series of ethical issues,” Zhang Weinan said, emphasizing the need to establish ethical norms to further clarify the tool attributes of robots.Humanoid robots represent not only a technological breakthrough but also a profound impact on human self-perception.This human-robot dance has just begun, and its rhythm will concern the future of civilization.Source: Xinhua DailyOriginal title: “The Acceleration of Humanoid Robot Evolution”Reporters: Xiong Zhengyan, Yao Yujie, Gong Wen, Yang Siqi, Zheng Keyi, Ma Xiaocheng, Guo YujingPoster design: Luan Ruohui



