
In the next five years, with the rapid advancement of 5G network construction, edge computing and distributed cloud will experience a comprehensive explosion.
Author | Su YiEditor | Zi QiAs the most complex communication technology in human history, 5G is also considered a core variable driving the transformation of human social production and lifestyle.
Industry estimates suggest that by 2023, 5G will account for about one-fifth of all global mobile data traffic, with the number of 5G users reaching 1 billion.This is very similar to the 4G era; since the launch of LTE technology in 2010, its explosive growth has far exceeded previous expectations, occupying 50% of global mobile traffic by 2017, and it continues to maintain a high growth trend.China and the United States have become the two poles of innovation in the global mobile internet era, directly related to the strong user demand and the level of LTE network penetration in both countries.
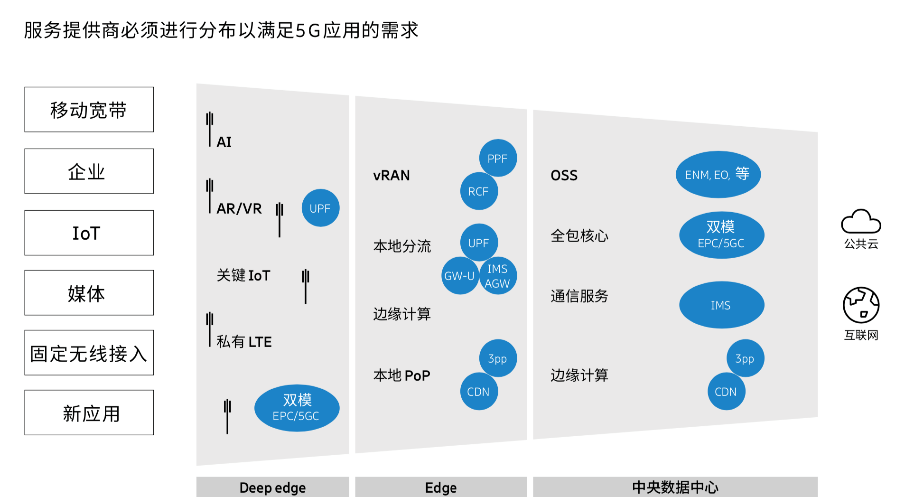
However, with the popularization of smart manufacturing, vehicle-road collaboration, and new intelligent devices such as AR/VR, the industry has found that distributed cloud technology and edge computing are equally crucial.For example, deploying computing and storage resources in the most effective yet cost-efficient locations.While operators promote 5G network construction, they also need to comprehensively consider the integration of edge computing with communication networks and vertical industry networks to better meet actual customer needs.
1
Hundreds of Billions of Dollars in New Market Potential
Over the past decade, cloud computing has rapidly developed and gained popularity, with telecom operators, internet companies, and many technology firms entering this field.
If we consider only cost, centralized cloud deployment is usually the first approach.However, for many specific enterprises and applications, even in the 5G era, better edge computing and distributed cloud technology support is still needed.
For instance, in the industrial Internet of Things, the requirements for reliability, anti-interference, and indoor coverage are extremely high, posing a significant challenge to the traditional single communication base station model.

In the mass consumer market, new intelligent terminals such as AR/VR need to send enhanced data like videos and 3D models to smart devices, especially closely integrating with real physical scenes, which requires high bandwidth and low latency, directly determining a strong user experience.Therefore, content delivery network (CDN) functionality needs to be placed in distributed sites at the edge, keeping the closest distance to users and applications.
In fact, many data-intensive applications in the future will require broader distribution to optimize bandwidth consumption and ensure low latency requirements, which also demands the reliability and availability of edge computing, bringing data processing closer to the source rather than external data centers or clouds, thus shortening latency.
For smart manufacturing enterprises, edge computing can also save investment costs, adopt more targeted service solutions, reduce network traffic and big data bottlenecks, and provide better security and data protection features.
From this perspective, as 5G network service providers, telecom operators must also focus on optimizing specific networks, enhancing edge computing capabilities closer to customers and applications, deploying more computing and storage resources, and providing the most suitable latency, bandwidth, and rate solutions.
At the same time, for operators themselves, developing edge computing can further optimize 4G and 5G networks, enhance the flexibility of end-to-end network architecture, shorten service launch times, and save overall network bandwidth investment, eliminating the need to transmit data over long distances across the entire network, significantly improving network operational efficiency.
The rapid growth of user demand and the technological evolution of edge computing present a certain incremental market for operators.Ericsson’s survey on the potential of global operators’ 5G business indicates:From 2020 to 2024, the global revenue potential for operators’ 5G business will surge from $14 billion to $129 billion.Among them, distributed cloud is suitable for customers with strict requirements for scalability, security, availability, low latency, and bandwidth, this portion of revenue will account for 25%.Equivalent to a new market potential of over $30 billion.
It can be anticipated that in the next five years, with the rapid advancement of 5G network construction, edge computing and distributed cloud will experience a comprehensive explosion, bringing enormous innovation space to social intelligent production and consumer life.
2
Opportunities and Challenges Faced by Operators
In the 5G era, the resources and capabilities that operators possess give them a natural advantage in the expansion of edge computing and distributed cloud business.
First, in the 5G era of the Internet of Everything, edge computing and distributed cloud business do not exist in isolation; they will still be closely connected with public clouds and external big data, with the three main characteristics of 5G networks being high speed, low latency, and wide connectivity, which remain the fundamental network infrastructure.This gives operators a natural advantage of a complete solution with “one network” in the 5G era.
Second, applications in fields such as industrial IoT and autonomous driving require extremely high reliability and stability.Operators can provide solutions that meet the stringent operational requirements of telecom-grade services, which is something many traditional enterprise solution providers find difficult to achieve.
Third, operators have rich capabilities and experience in distributed cloud computing, cloud computing, network, and service orchestration.However, many third parties and ordinary developers often lack understanding of the characteristics of telecom networks, providing operators with the opportunity to configure, launch, and debug various computing services and network types in a unified manner, offering users low-threshold integrated API development interfaces.This makes it easy for industry clients to get started, as simple as using public cloud services.
Currently, operators can meet customer needs in different application scenarios through three methods: collaborating with various industries to promote ecosystem development to provide solutions, driving ecosystem development themselves, and leveraging existing ecosystems of hyperscale cloud providers.
However, for a new type of business expansion, operators still face many practical challenges in developing edge computing:
For example, how to efficiently manage and operate edge computing business.Edge computing networks may have hundreds or thousands of edge locations, such as central offices, wireless base stations, or enterprise sites, which will pose significant challenges for management and operation.
At the same time, most current NFV infrastructures are built for larger data center deployments.Therefore, for edge deployments to succeed, maintaining a competitive total cost of ownership (TCO) for edge sites is crucial, while also meeting the requirements for small server size, low power consumption, and the ability to reuse existing sites and network assets.
This is a race between market opportunity windows and technological solutions.
3
Six Advantages of Ericsson’s Edge NFVI Solution
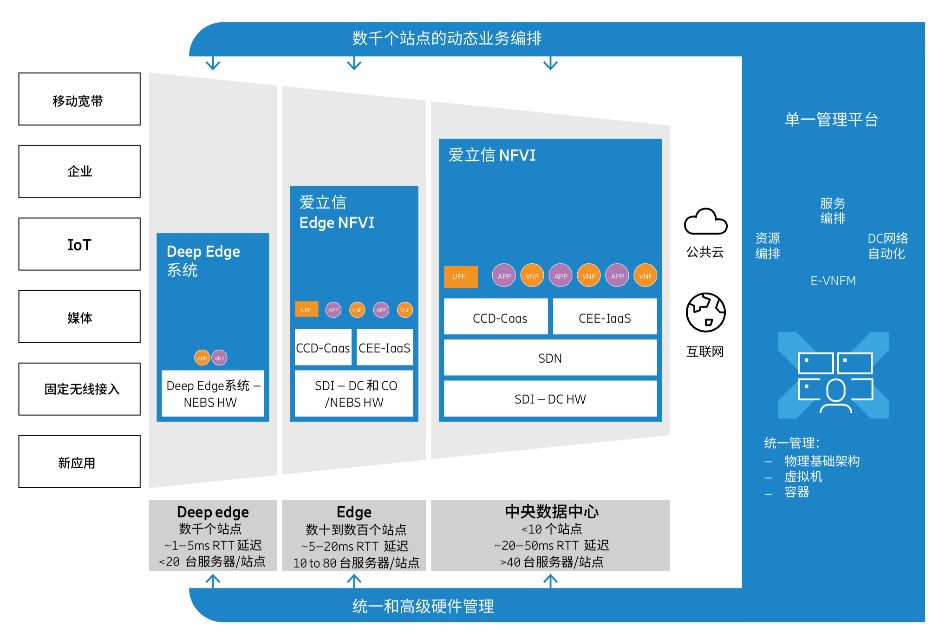
In response to the new market opportunities and practical challenges faced by telecom operators in the 5G era, Ericsson has launched an end-to-end distributed edge solution—Edge NFVI—designed to meet various industry needs across the entire network.
Compared to traditional edge computing solutions, Ericsson’s Edge NFVI solution has six main advantages:
1. Compact yet Powerful
Ericsson Edge NFVI offers multiple solution options; operators can choose either the Compute Sled Unit 02 or Compute Rack Unit 02 (validated for data center environments), or the new short-format Compute Sled Unit – Short format (CSU-S), which is a universal 1.5U server with a depth of only 350 mm, suitable for installation in space-constrained edge sites.
By requiring fewer servers, it saves hardware investment, significantly reducing costs.The smaller form factor also saves space, allowing installation not only in existing central sites but also in Ericsson’s wireless base stations located at the edge.

2. Rapid Deployment
Ericsson Edge NFVI uses the same system validation methods as those used for deploying Ericsson NFVI in central data centers, thus it is pre-integrated and pre-tested, retaining flexibility in hardware selection and requiring very little configuration work to get started, reducing risk and deployment time.VNF and applications certified by Ericsson are also available for distributed deployment across networks.
3. Unified End-to-End Management
The Edge NFVI compact solution uses the same software stack as the fully functional NFVI solution and supports the same pre-integrated hardware components.Dynamic service orchestration and management of thousands of edge sites are mature and powerful, providing automated end-to-end service orchestration across central data centers and distributed sites, managed through dashboards for a large number of sites.Automated workflows for common operational tasks (such as upgrades, reboots, or adding/removing devices) will be developed using a one-click approach.
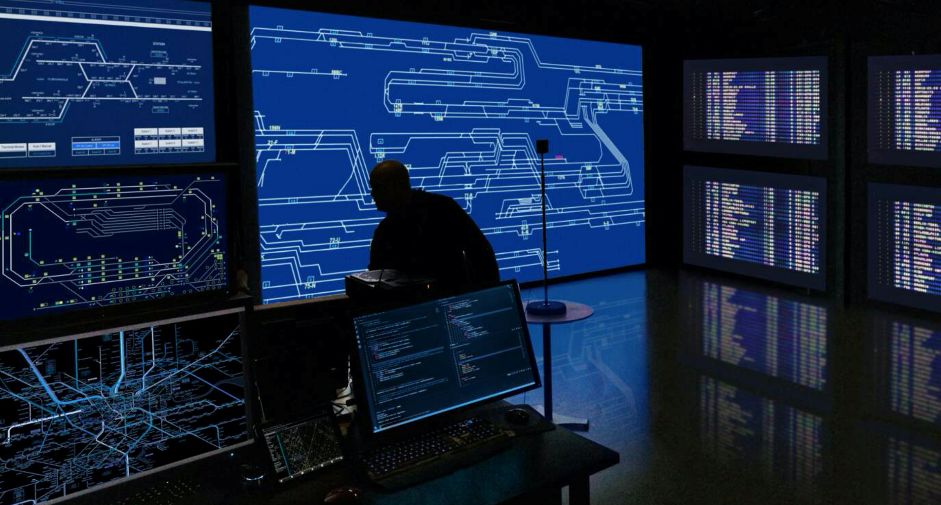

4. Telecom-grade Reliability
By adopting market-validated and telecom-grade system verification designs, Ericsson Edge NFVI can be rapidly deployed in demanding telecom environments.The entire platform integrates security measures, and the effectiveness of these measures is verified at the system level.The performance of the entire system has been optimized end-to-end, with Ericsson providing system support and version release management for the entire solution.Both virtual machines and containers achieve high reliability and automatic fault recovery.
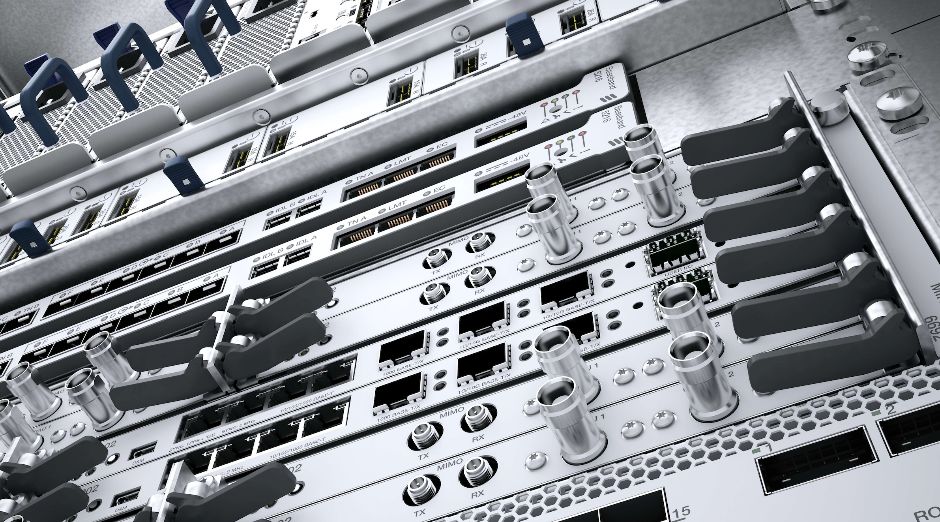

5. Efficiently Mixing Virtual Machines and Container Environments
In the foreseeable future, virtual machines and containers will coexist.While most VNFs today are based on virtual machines, 5G VNFs and new edge applications will be based on containers.To meet both needs, Ericsson Edge NFVI provides a universal MANO platform to manage virtual machines and containers running on the same platform.
6. Open Industry Development Ecosystem
Ericsson simplifies network assets and functions (network slicing, mobile network connections, anchor points, and infrastructure resources) through a user-centric approach that hides complexity, such as simple parameterization of open network slicing and adoption of industry-standard technologies like Kubernetes and ONAP.It collaborates closely with developers and industry solutions on API definitions and use cases to facilitate applications, such as within AECC.Developers do not need to learn new telecom-specific APIs.
 According to “Yi Observation”, Ericsson’s Edge NFVI solution deeply matches the diverse needs of operators to meet industry customers’ edge computing and distributed cloud technology requirements, and possesses an open and scalable industry ecosystem, as well as providing telecom-grade reliability. For operators and industry customers, Ericsson’s Edge NFVI solution is not only compact and powerful, easy to deploy and manage, but also addresses core pain points and differentiated demands while saving investment, making it the preferred solution for deploying edge computing in the 5G era.
According to “Yi Observation”, Ericsson’s Edge NFVI solution deeply matches the diverse needs of operators to meet industry customers’ edge computing and distributed cloud technology requirements, and possesses an open and scalable industry ecosystem, as well as providing telecom-grade reliability. For operators and industry customers, Ericsson’s Edge NFVI solution is not only compact and powerful, easy to deploy and manage, but also addresses core pain points and differentiated demands while saving investment, making it the preferred solution for deploying edge computing in the 5G era.
End


Long press to recognize and follow
Founder of “Yi Observation” Su Yi
Former Chief Editor of Sohu Technology Communications
Search “Yi Observation” on Toutiao, Tencent News, and Sohu Search
Search “Su Yi” on Baijiahao, Weibo, and Douyin for more
丨Smart Hardware丨Communications丨New Retail丨Artificial Intelligence丨
丨Smart Internet of Vehicles丨Smart Home丨
For reprints and cooperation, contact WeChat: yiguancha_01