
Hu Xiaomeng, Chen Chuyi Tencent Research Institute
AI Agents are undoubtedly the most exciting development in large models today, referred to as “the next battlefield of large models,” “the ultimate killer product,” and “Agent-centric, opening the era of a new industrial revolution.” On November 7, the first OpenAI Developer Conference (OpenAI DevDay) ignited the AI Agent. OpenAI released the initial form of AI Agent products, GPTs, and launched corresponding production tools, GPT Builder. Users can generate their own GPT by simply chatting with GPT Builder and describing the desired GPT functions. Custom GPTs are more applicable in daily life, specific tasks, work, or home. To this end, OpenAI has also opened a large number of new APIs (including visual, image DALL·E3, voice), as well as the newly launched Assistants API, allowing developers to more easily develop their own custom GPTs. Bill Gates recently published an article stating that within five years, AI Agents will be widely adopted, and every user will have their own AI Agent. Users will no longer need to use different apps for different functional needs; they will only need to tell their Agent what they want to do in everyday language.[1]

So, what exactly are AI Agents? Why are they so important that the industry pays such high attention, with some scholars even asserting that “if the American Agent Store develops well, it will continue to widen the gap between China and the US in large models”[2]
In the field of computer and artificial intelligence technology, the term agent is generally translated as “intelligent entity,” defined as a software or hardware entity exhibiting one or more intelligent characteristics such as autonomy, reactivity, sociality, proactivity, cognitive ability, and reflectiveness within a certain environment.[3]
OpenAI defines AI Agent as a system driven by a large language model as its brain, possessing the ability to autonomously understand perception, planning, memory, and tool usage, capable of automating the execution of complex tasks.[4]The basic framework of AI Agents is shown in the figure below:
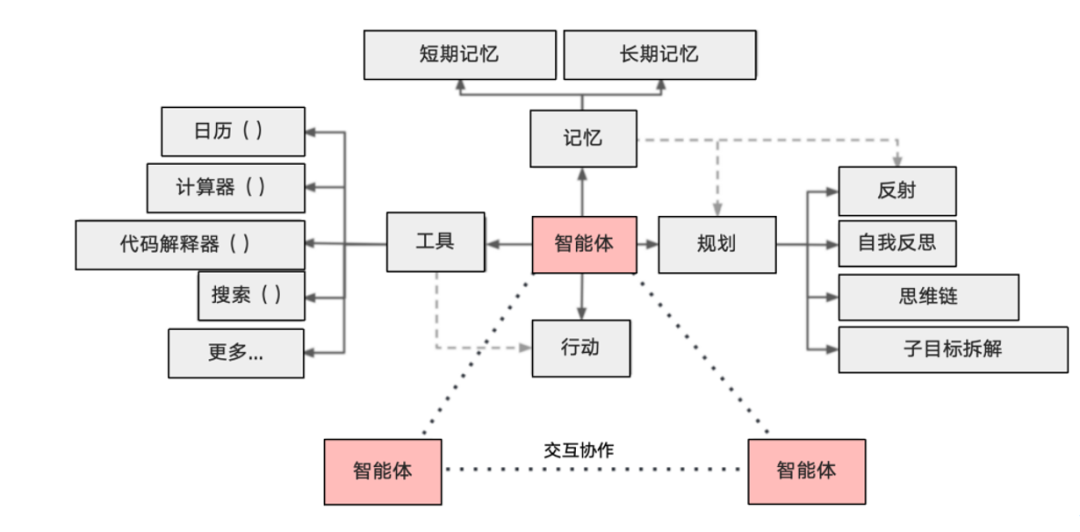
It consists of four main modules:
(1) Memory. The memory module is responsible for storing information, including past interactions, learned knowledge, and even temporary task information. For an intelligent entity, an effective memory mechanism ensures that it can call upon past experiences and knowledge when facing new or complex situations. For example, a chatbot with memory functionality can remember user preferences or previous conversation content, providing a more personalized and coherent communication experience. It is divided into short-term memory and long-term memory: a. Short-term memory, all contextual learning uses short-term memory; b. Long-term memory provides the ability for the intelligent entity to retain and recall (infinitely) information over a long time, usually through external vector databases and rapid retrieval, such as a large amount of data and knowledge accumulated in a specific industry. With long-term memory, much data can be accumulated, making the intelligent entity more powerful, with advantages in industry depth, personalization, and professional capabilities.
(2) Planning. The planning module has two stages: pre-planning and post-reflection. In the pre-planning stage, it involves predicting future actions and decision-making. For example, when executing complex tasks, the intelligent entity breaks down large goals into smaller, manageable sub-goals, allowing it to efficiently plan a series of steps or actions to achieve the desired outcome. In the post-reflection stage, the intelligent entity can check and improve the shortcomings in the planning process, reflect on errors, and learn lessons to improve, forming and adding to long-term memory, helping the intelligent entity avoid mistakes and update its understanding of the world.
(3) Tool use. The tool use module refers to the ability of the intelligent entity to utilize external resources or tools to perform tasks. For instance, learning to call external APIs to obtain additional information missing from the model weights, including current information, code execution capabilities, and access to proprietary information sources, to compensate for the weaknesses of LLMs. For example, the training data of LLMs is not updated in real-time; in this case, tools can be used to access the internet for the latest information or specific software to analyze large amounts of data. There are already many digital and intelligent tools on the market, and intelligent entities can use tools more smoothly and efficiently than humans, completing complex tasks and producing high-quality results through different API calls or tool usage, which also represents an important feature and advantage of intelligent entities.
(4) Action. The action module is the part where the intelligent entity actually executes decisions or responses. Faced with different tasks, the intelligent entity system has a complete action strategy set, allowing it to choose actions to execute when making decisions, such as well-known memory retrieval, reasoning, learning, programming, etc.
In summary, these four modules work together to enable the intelligent entity to take action and make decisions in a broader context, executing complex tasks in a more intelligent and efficient manner.[6]
AI Agents Will Bring
Wider Human-Machine Integration
The agent based on large models not only allows everyone to have a personalized intelligent assistant with enhanced capabilities but will also change the mode of human-machine collaboration, leading to broader human-machine integration. The intelligent revolution of generative AI has evolved to present three modes of human-machine collaboration:
(1) Embedding mode. Users communicate with AI through language, using prompts to set goals, and then AI assists users in achieving these goals, such as ordinary users inputting prompts into generative AI to create novels, music works, 3D content, etc. In this mode, AI acts as a tool executing commands, while humans take on the role of decision-makers and commanders.
(2) Copilot mode. In this mode, humans and AI act more like partners, participating together in workflows and playing their respective roles. AI intervenes in workflows, providing suggestions and assisting in various stages of the process. For example, in software development, AI can help programmers write code, detect errors, or optimize performance. Humans and AI work together in this process, complementing each other’s abilities. AI acts more like a knowledgeable partner than merely a tool.
In fact, Microsoft first introduced the concept of Copilot in GitHub in 2021. GitHub Copilot is an AI service that assists developers in writing code. In May 2023, Microsoft fully upgraded Copilot with the support of large models, launching Dynamics 365 Copilot, Microsoft 365 Copilot, and Power Platform Copilot, and proposed the idea that “Copilot is a new way of working.” Just as in work, life also needs a “Copilot.” Li Zhifei, founder of “Ask Me Anything,” believes that the best work of large models is to be a “Copilot” for humans.
(3) Agent mode. Humans set goals and provide necessary resources (such as computing power), and then AI independently takes on most of the work, with humans supervising the process and evaluating the final results. In this mode, AI fully reflects the interactive, autonomous, and adaptive characteristics of an agent, approaching independent action, while humans play more of a supervisory and evaluative role.
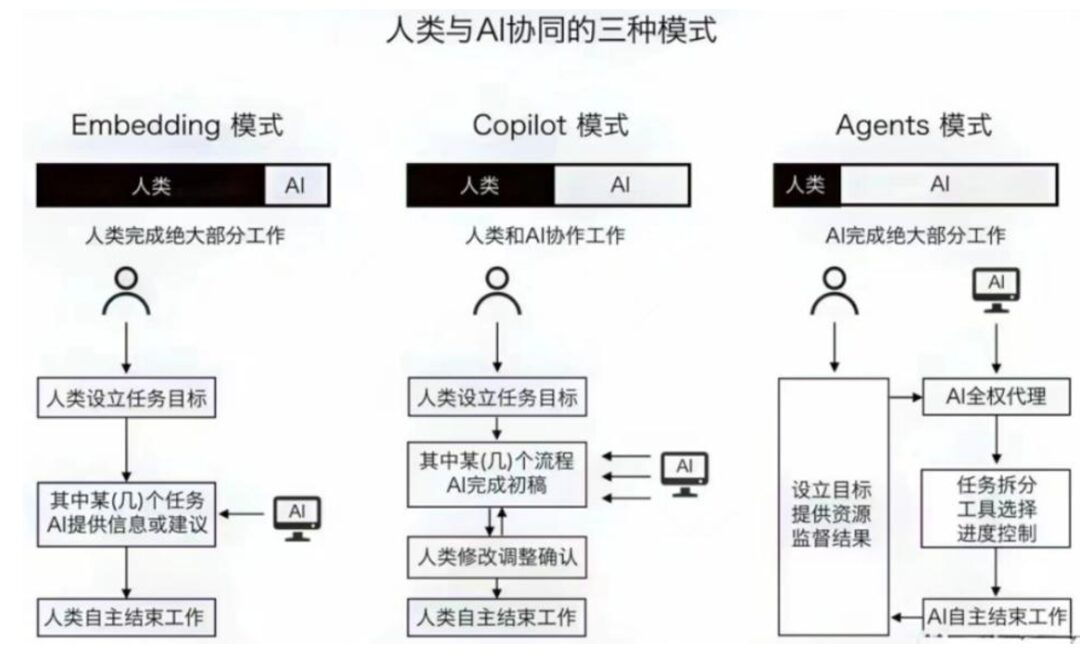
From the previous analysis of the functions of the four main modules of intelligent agents—memory, planning, action, and tool usage—it is evident that the agent mode is undoubtedly more efficient than the embedding mode and copilot mode, and is likely to become the primary mode of human-machine collaboration in the future.
In the human-machine collaboration model based on agents, every ordinary individual has the potential to become a super individual. A super individual possesses their own AI team and automated task workflows, establishing more intelligent and automated collaborative relationships with Agents and other super individuals. Currently, there are many active explorations of one-person companies and super individuals in the industry. On the GitHub platform, there are some automated teams based on Agents—such as the GPTeam project. GPTeam utilizes large models to create multiple intelligent entities assigned with roles and functions, collaborating in multi-agent to achieve predetermined goals. For example, Dev-GPT is a multi-agent collaborative team for automated development and operations, including roles such as product manager Agent, developer Agent, and operations personnel Agent. This multi-agent team can meet and support the normal operation of a startup marketing company, which is essentially a one-person company.
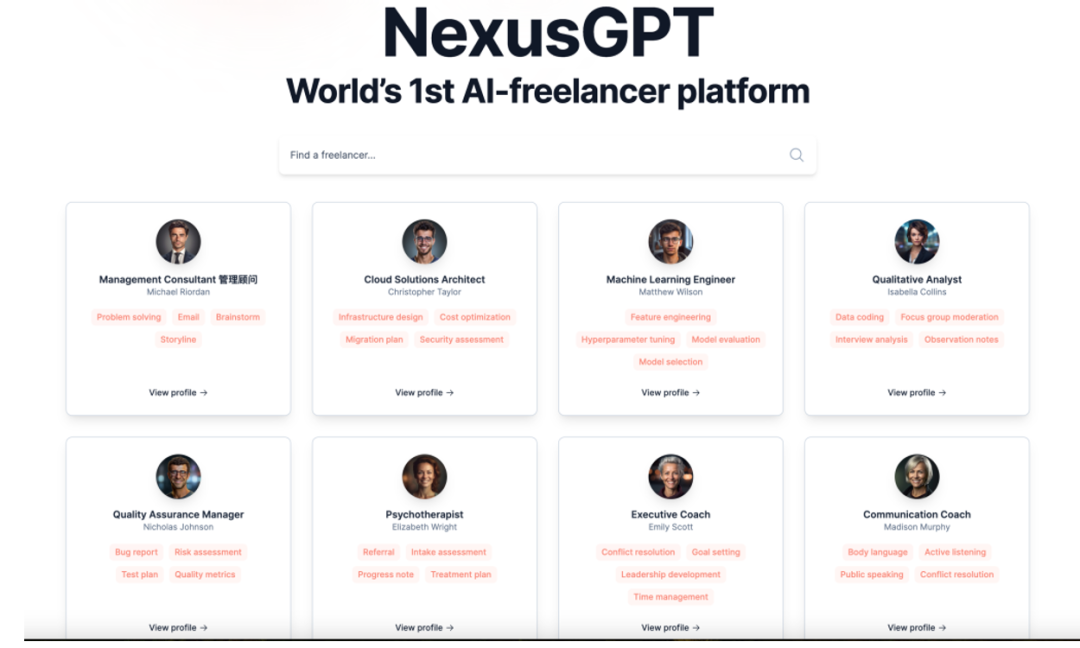
Another example is NexusGPT, claimed to be the world’s first AI freelancer platform.[8]This platform integrates various AI-native data from open-source databases and has over 800 AI intelligent entities with specific skills. On this platform, you can find experts in different fields, such as designers, consultants, sales representatives, etc. Employers can choose an AI intelligent entity to help them complete various tasks at any time on this platform.
AI Agents Will Change The Game of Software
Promote AI Infrastructure
AI Agents are redefining software. Bill Gates believes that AI Agents will completely disrupt the software industry, affecting how we use and write software.[9]
AI Agents will shift the paradigm of software architecture from process-oriented to goal-oriented. Existing software (including apps) fixes processes through a series of predefined instructions, logic, rules, and heuristic algorithms to ensure that the software operation results meet user expectations, meaning users operate step by step according to the instruction logic to achieve goals. This process-oriented software architecture has high reliability and determinism. However, this goal-oriented architecture can only be applied to vertical fields and cannot be universally applied across all fields, making the balance between standardization and customization one of the challenges faced by the SaaS industry.
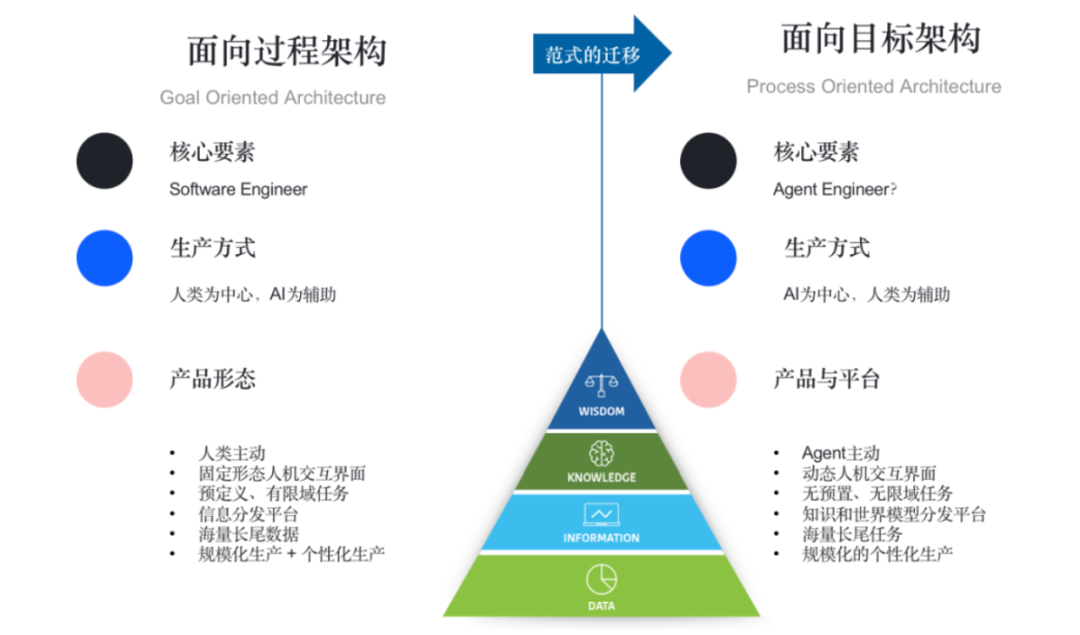
The AI Agent paradigm will gradually shift the function development originally dominated by humans to AI as the main driving force. Based on large models as the technical infrastructure and Agents as the core product form, it will evolve from traditional software’s predefined instructions, logic, rules, and heuristic algorithm task hierarchy to goal-oriented intelligent entities autonomously generating tasks. Consequently, the original architecture could only solve tasks within a limited scope, while future architectures could solve tasks in infinite domains.[11]The future software ecosystem will not only have Agents as the medium interacting with everyone at the top level, but the entire industry’s development—including underlying technology, business models, intermediate components, and even people’s habits and behaviors—will revolve around Agents, marking the dawn of the Agent-Centric era.[12]
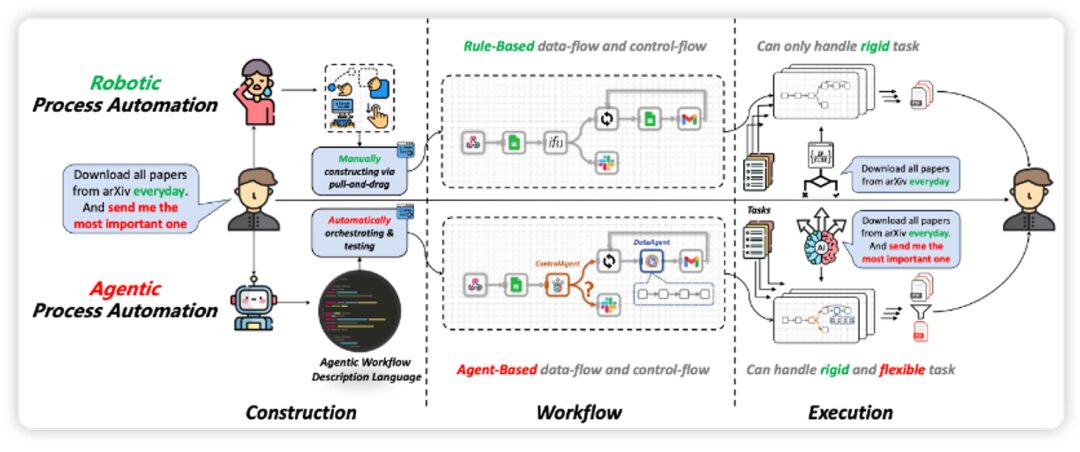
Taking the first “large model + Agent” SaaS product ChatDev intelligent software development platform released by Weibi Intelligence as an example. This platform is like a software development company entirely composed of AI Agents, containing various Agent roles such as CEO, CTO, development manager, product manager, testing specialist, supervisor, etc. Users only need to tell the CEO role Agent their specific needs, and this CEO will organize the entire software development process based on user requirements. The final delivery to the user includes the software product and all the code from the development process, and all processes are automated.[14]This will reduce production costs in the software industry, enhance customization capabilities, and usher in the “3D printing” era of software.
Prospects and Challenges of AI Agents
AI Agents are a significant driving force for artificial intelligence to become infrastructure. Looking back at the history of technological development, the end of technology is to become infrastructure, such as electricity becoming an imperceptible yet essential infrastructure, akin to cloud computing. Of course, this will go through three stages: innovation and development stage—new technologies are invented and begin to be applied; popularization and application stage—as technology matures, it begins to be widely used in various fields, having a profound impact on society and the economy; infrastructure stage—when technology becomes pervasive, it transforms into an infrastructure that has become an indispensable part of people’s daily lives. Almost everyone agrees that artificial intelligence will become the infrastructure of future society. Intelligent entities are promoting the infrastructureization of artificial intelligence. This is not only thanks to the low-cost production advantages of Agent software but also because Agents can adapt to different tasks and environments, learning and optimizing their performance, allowing them to be applied in wide-ranging fields, thereby becoming the foundational support for various industries and social activities.

Agents may evolve in two directions simultaneously. One is intelligent agents that assist humans by executing various tasks, focusing on tool attributes; the other is iterations towards anthropomorphism, capable of making independent decisions, possessing long-term memory, and having certain personality traits, focusing on human-like or superhuman attributes.
From the perspective of technological optimization iterations and realizations, the development of AI Agents also faces some bottlenecks:
First, as seen with OpenAI’s GPTs, issues such as insufficient complex reasoning capabilities and high latency inhibit the true maturity of Agent applications. This is also the direction for future engineering optimization and technological breakthroughs in the industry.
Second, multi-agent development still faces significant challenges. Multi-agent systems represent a very complex academic research direction, and as intelligent agents begin to permeate the mass market, they have become important technological realities. For example, Stanford’s virtual town includes multi-agent research involving 25 agents. However, after the town framework was open-sourced, developer testing revealed that an Agent could cost $20 in tokens per day due to the significant cognitive load of memory and action. This cost exceeds that of many human workers, necessitating dual optimization of the Agent framework and LLM reasoning aspects.
Breaking through the development bottleneck of multi-agents is a crucial prerequisite for establishing an intelligent agent society (Agent Society). Multi-agent collaboration can form the highest form of a technological social system. An intelligent agent society has complex, dynamic, self-organizing, and adaptive characteristics, capable of collaboration, competition, and continuous evolution. In this social system, intelligent agents can execute complex and flexible tasks based on goals and environmental changes, engaging in high-level, multidimensional interactions and collaborations with humans and other intelligent agents. An intelligent agent society not only helps humans explore and expand the physical and virtual worlds but also enhances and extends human capabilities and experiences.
At the same time, these development trends indicate that AI Agents may face challenges in areas such as security and privacy, ethics and responsibility, and economic and social employment impacts.
(1) Security and privacy are key characteristics of intelligent agents, crucial for their stable operation and protection of users and society. These two factors directly affect the trustworthiness and controllability of AI agents. If AI agents have vulnerabilities, suffer attacks, or experience data leaks, it could cause harm to users or society. For instance, shortly after the release of OpenAI’s GPTs, security vulnerabilities led to user-uploaded data being leaked.
(2) Ethics and responsibility are core principles of intelligent agents, determining their values and goals, as well as their respect and protection for users and society. These principles directly influence the credibility and controllability of intelligent agents. If intelligent agents exhibit unfair, opaque, or unreliable behaviors, it may trigger rejection of the technology by users or society. Responsibility attribution is also a key issue for intelligent agents, as unclear or unfair attribution of responsibility in human-agent collaboration could lead to severe consequences.
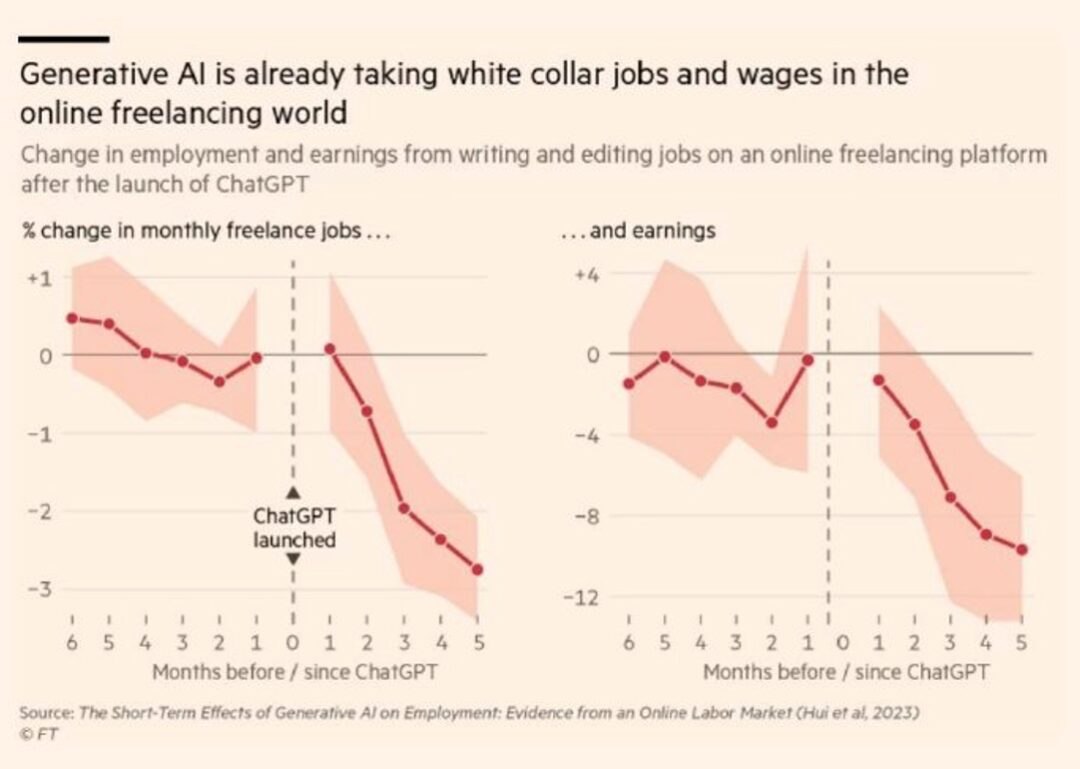
(3) Economic and social employment impacts. One significant challenge in future work will be the competition between humans and intelligent agents. For example, the emergence of AI freelancer platforms like NexusGPT poses a threat to traditional freelancers. In future work collaborations, there will be more and more intelligent agents, and employers may seek to minimize human input based on efficiency and effectiveness considerations. As intelligent agent technology matures, we must proactively consider the long-term impacts of these technological developments on society and individual careers.
[1]https://www.gatesnotes.com/AI-agents
[2]https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/EWvw83Gch_xWmAcT7dVV5A
[3] National Committee for the Approval of Scientific and Technical Terms. “Computer Science and Technology Terms (Third Edition)” [M]. Beijing: Science Press, December 2018.
[4] Translating the concept of AI Agent as “AI proxy” is inaccurate. The term “agent” originates from the Latin verb “agere,” meaning “to do” or “to act,” encompassing a wide range of behaviors and activities. The noun form “agents” evolved from this word, translated as “actors” or “executors,” used to describe entities that perform actions or possess the ability to act.
[5] https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent
[6] https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent
[7] https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/AluYfD6BQOkLo6XpJMyQnQ
[8] https://nexus.snikpic.io/
[9] https://www.gatesnotes.com/AI-agents
[10] https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/X27SWFeZsXmbuFZEow8DLQ
[11] https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/X27SWFeZsXmbuFZEow8DLQ
[12] Tencent Technology. “The Competition for Large Model Capabilities Has Been Determined.” https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/V0fbugryGcs7vox4EkRisg
[13] In the past, RPA could only replace simple, mechanical human work, while some complex processes still relied on human labor, facing two major challenges: writing RPA workflows requires heavy human labor and is costly; complex tasks are very flexible, often involving dynamic decision-making, making it difficult to solidify into rules. In the APA paradigm, the Agent can autonomously complete workflow construction based on human needs and can identify parts of human needs requiring dynamic decision-making, automatically incorporating them into the workflow and taking over the execution of the workflow when it reaches that part to complete the corresponding complex decision.
[14] https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1782631006897855123&wfr=spider&for=pc
[15] https://github.com/e2b-dev/awesome-ai-agents
[16] Hui X, Reshef O, Zhou L. The Short-Term Effects of Generative Artificial Intelligence on Employment: Evidence from an Online Labor Market [J]. Available at SSRN 4527336, 2023.
Recommended Reading
Tong Qi, Hu Xiaomeng: “Interpersonal Relationships in the Era of Large Models: Do Not Walk Gently into the Era of Coexistence with AI”
