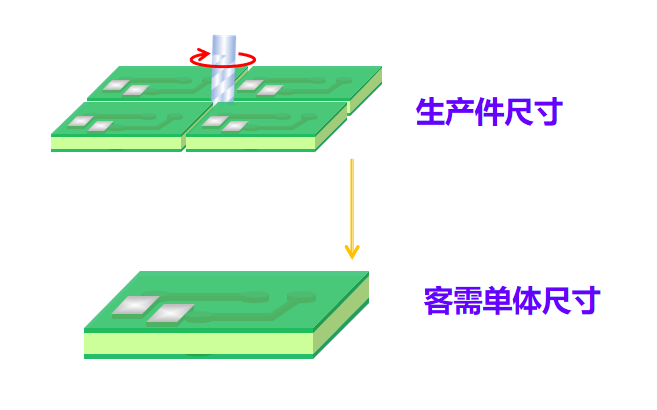
In the electronic devices we encounter daily, whether smartphones, computers, or smart home devices, there is an essential component – the PCB, also known as the Printed Circuit Board. The PCB routing, as a crucial part of the PCB manufacturing process, plays a vital role. Today, let’s talk about this somewhat mysterious “PCB routing” and what it actually is.




Want to know more
Quickly scan the code to follow