
Source: WeChat Official Account “Wireless Deep Sea”
 “Cloud is a concept that has permeated every corner of our lives. During the 2021 Spring Festival, many people celebrated the holiday in place, and family ties could only be conveyed through video, referred to as “cloud reunion“. Some cat lovers, unable to keep cats themselves, could only drool over cat videos shot by others online, termed “cloud cat appreciation“. Even more cleverly, there is the term “cloud backup“. Note that this backup is not related to cars, but rather refers to a goddess’s management and utilization of resources: connecting numerous backups into a “cloud” that can be dispatched at any time and shared with other goddesses. While the above may sound humorous, it hints that the “cloud” in everyone’s mind should be associated with terms like networking, bandwidth, and sharing. Now, let’s take a look at some serious applications of the “cloud”.Cloud Storage: Personal services also known as cloud disks or online disks, allow private files to be stored in the “cloud”, enabling synchronization across multiple devices such as phones, tablets, and computers, ensuring they are never lost and are easy to share.Cloud Office: This refers to enterprises conducting document editing, storage, collaboration, communication, mobile office, and workflow entirely in the “cloud”, with local devices only serving as displays without storing any information.Cloud Gaming: Users enjoy playing games on their phones, while the games actually run in the “cloud”; the phone merely acts as a display, receiving game visuals transmitted over the network. From these examples, we can see that the “cloud” generally has the following characteristics:Networking: The “cloud” must be accessed via a network, and the required bandwidth and latency are significant.Capability: The “cloud” functions like an all-powerful supercomputer, capable of storage, computation, and analysis.Sharing: This supercomputer is shared among multiple users (enterprises), with each user renting resources as needed, paying only for what they use.The cloud has become a new way to access resources. What is Cloud Computing? Gordon Moore, the founder of Intel, once said: “The number of transistors on an integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years“. In other words, the performance of processors doubles every two years. Such rapid development has led to decreasing hardware costs, allowing individual enterprises to afford large numbers of servers. For many large enterprises, the hardware resources required during peak business periods are substantial, but the average load is not high; however, servers must be configured according to maximum demand, leading to inflexible allocation and resource waste. If these idle server capabilities could be integrated into a resource pool and rented out to other companies, it would not only turn waste into treasure but could also open up new business models. In other words, instead of each company buying their own servers and incurring high costs with low utilization and troublesome scaling, I could buy a large number of servers, form a big pool, and rent them out as needed. Wouldn’t that be great? This shift from individual purchases to centralized buying and renting by others led to the birth of cloud computing. Thus, in 2006, Google officially proposed the concept of “cloud computing” at a search engine conference. Amazon, being proactive, launched its commercial “Elastic Compute Cloud” service five months before Google introduced the concept. These two landmark events officially heralded the arrival of the cloud computing era, marking a new phase in the development of the internet. How is Cloud Computing Achieved? Cloud computing has several basic characteristics:Resource Pooling: Service providers do not directly rent out physical servers but virtualize the CPUs, memory, hard drives, and network cards of multiple servers into three categories of resource pools: computing, storage, and networking, which are then divided into smaller, flexible combinations for rental to users. Each user’s resources are physically distributed across multiple servers and shared among multiple users, while logically they are independent and isolated.Service Quantification: The three major resources of computing, storage, and networking are rented out at a granular level, and users must clearly understand how much they have used. This way, both parties can trust each other and achieve a win-win situation.Rapid Elasticity: The capacity available to each user is no longer limited by physical servers; if demand increases, it automatically scales up quickly, and if demand decreases, some resources are released. This service is like a balloon, with capacity that can stretch and contract freely, demonstrating elasticity.Self-Service: Users can directly apply for server rentals, system installations, or activate cloud office, cloud storage, cloud gaming, and other services, with automatic activation and self-checkout, similar to an unmanned supermarket, eliminating inefficient communication with customer service.Broadband Access: The network is the only bridge between users and the cloud, with various services built on frequent data uploads and downloads, making bandwidth and latency crucial; some services also require ultra-high reliability in transmission. The first four characteristics must be built on the foundation of virtualization. The traditional virtualization concept involves virtualizing the CPU, memory, hard drive, and network card resources of a single physical server into a resource pool, which is then divided into multiple virtual servers. However, this resource pool is limited by the capacity of a single physical server.
“Cloud is a concept that has permeated every corner of our lives. During the 2021 Spring Festival, many people celebrated the holiday in place, and family ties could only be conveyed through video, referred to as “cloud reunion“. Some cat lovers, unable to keep cats themselves, could only drool over cat videos shot by others online, termed “cloud cat appreciation“. Even more cleverly, there is the term “cloud backup“. Note that this backup is not related to cars, but rather refers to a goddess’s management and utilization of resources: connecting numerous backups into a “cloud” that can be dispatched at any time and shared with other goddesses. While the above may sound humorous, it hints that the “cloud” in everyone’s mind should be associated with terms like networking, bandwidth, and sharing. Now, let’s take a look at some serious applications of the “cloud”.Cloud Storage: Personal services also known as cloud disks or online disks, allow private files to be stored in the “cloud”, enabling synchronization across multiple devices such as phones, tablets, and computers, ensuring they are never lost and are easy to share.Cloud Office: This refers to enterprises conducting document editing, storage, collaboration, communication, mobile office, and workflow entirely in the “cloud”, with local devices only serving as displays without storing any information.Cloud Gaming: Users enjoy playing games on their phones, while the games actually run in the “cloud”; the phone merely acts as a display, receiving game visuals transmitted over the network. From these examples, we can see that the “cloud” generally has the following characteristics:Networking: The “cloud” must be accessed via a network, and the required bandwidth and latency are significant.Capability: The “cloud” functions like an all-powerful supercomputer, capable of storage, computation, and analysis.Sharing: This supercomputer is shared among multiple users (enterprises), with each user renting resources as needed, paying only for what they use.The cloud has become a new way to access resources. What is Cloud Computing? Gordon Moore, the founder of Intel, once said: “The number of transistors on an integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years“. In other words, the performance of processors doubles every two years. Such rapid development has led to decreasing hardware costs, allowing individual enterprises to afford large numbers of servers. For many large enterprises, the hardware resources required during peak business periods are substantial, but the average load is not high; however, servers must be configured according to maximum demand, leading to inflexible allocation and resource waste. If these idle server capabilities could be integrated into a resource pool and rented out to other companies, it would not only turn waste into treasure but could also open up new business models. In other words, instead of each company buying their own servers and incurring high costs with low utilization and troublesome scaling, I could buy a large number of servers, form a big pool, and rent them out as needed. Wouldn’t that be great? This shift from individual purchases to centralized buying and renting by others led to the birth of cloud computing. Thus, in 2006, Google officially proposed the concept of “cloud computing” at a search engine conference. Amazon, being proactive, launched its commercial “Elastic Compute Cloud” service five months before Google introduced the concept. These two landmark events officially heralded the arrival of the cloud computing era, marking a new phase in the development of the internet. How is Cloud Computing Achieved? Cloud computing has several basic characteristics:Resource Pooling: Service providers do not directly rent out physical servers but virtualize the CPUs, memory, hard drives, and network cards of multiple servers into three categories of resource pools: computing, storage, and networking, which are then divided into smaller, flexible combinations for rental to users. Each user’s resources are physically distributed across multiple servers and shared among multiple users, while logically they are independent and isolated.Service Quantification: The three major resources of computing, storage, and networking are rented out at a granular level, and users must clearly understand how much they have used. This way, both parties can trust each other and achieve a win-win situation.Rapid Elasticity: The capacity available to each user is no longer limited by physical servers; if demand increases, it automatically scales up quickly, and if demand decreases, some resources are released. This service is like a balloon, with capacity that can stretch and contract freely, demonstrating elasticity.Self-Service: Users can directly apply for server rentals, system installations, or activate cloud office, cloud storage, cloud gaming, and other services, with automatic activation and self-checkout, similar to an unmanned supermarket, eliminating inefficient communication with customer service.Broadband Access: The network is the only bridge between users and the cloud, with various services built on frequent data uploads and downloads, making bandwidth and latency crucial; some services also require ultra-high reliability in transmission. The first four characteristics must be built on the foundation of virtualization. The traditional virtualization concept involves virtualizing the CPU, memory, hard drive, and network card resources of a single physical server into a resource pool, which is then divided into multiple virtual servers. However, this resource pool is limited by the capacity of a single physical server.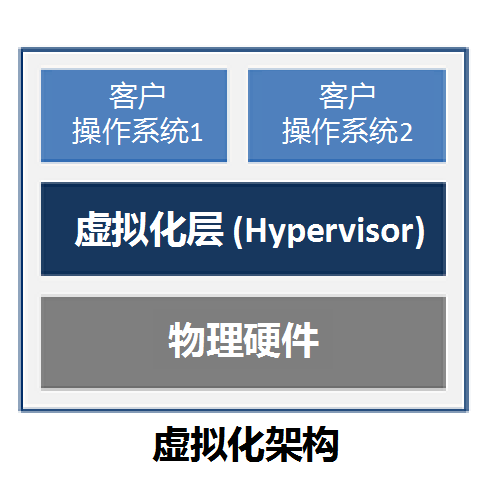 If a large number of servers can be gathered to form a super-large resource pool, and more servers can be added at any time to expand, it creates the “supercomputer” mentioned at the beginning. This requires a “cloud operating system” that can “integrate the fragmented into the whole“. It can consolidate dispersed physical resources into a virtual resource pool and schedule them across devices for upper-layer applications to use.
If a large number of servers can be gathered to form a super-large resource pool, and more servers can be added at any time to expand, it creates the “supercomputer” mentioned at the beginning. This requires a “cloud operating system” that can “integrate the fragmented into the whole“. It can consolidate dispersed physical resources into a virtual resource pool and schedule them across devices for upper-layer applications to use.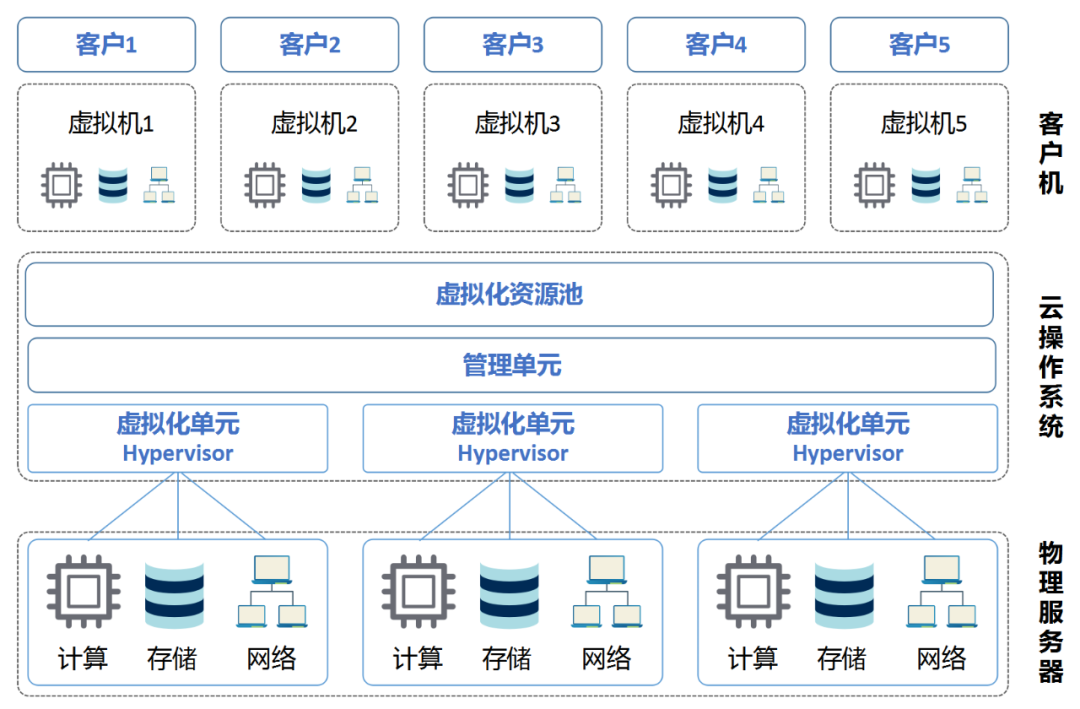 As shown in the figure, the cloud operating system mainly consists of virtualization units and management units. Virtualization refers to the previously mentioned Hypervisor, which is responsible for virtualizing and abstracting the physical resources of each server. The management unit integrates the resources of each server after virtualization, forming a large virtualized resource pool and allocating it for upper-layer applications to use. What Services Can Cloud Computing Provide? With a virtualized resource pool, how do service providers rent out resources? Resource rental is essentially a service. Different user needs require different service levels, so let’s categorize the services provided by cloud computing into three levels.
As shown in the figure, the cloud operating system mainly consists of virtualization units and management units. Virtualization refers to the previously mentioned Hypervisor, which is responsible for virtualizing and abstracting the physical resources of each server. The management unit integrates the resources of each server after virtualization, forming a large virtualized resource pool and allocating it for upper-layer applications to use. What Services Can Cloud Computing Provide? With a virtualized resource pool, how do service providers rent out resources? Resource rental is essentially a service. Different user needs require different service levels, so let’s categorize the services provided by cloud computing into three levels.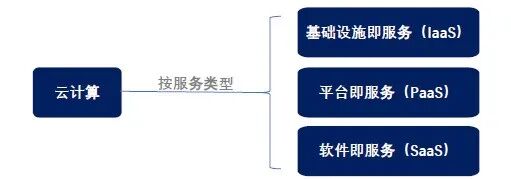 Level One: Simply renting out the three major resources after virtualization: computing, storage, and networking, and combining these resources into virtual servers. Users are entirely responsible for what systems they install, what software they develop, and what businesses they run on them. This level of service is called IaaS, which stands for Infrastructure as a Service, also known as “basic cloud”. This is like directly renting out land; users can build whatever they want on it, plant flowers, vegetables, or keep pets, entirely at their discretion.Level Two: Directly renting out virtual servers without any software, which offers maximum flexibility but may be too challenging for some users. Therefore, we enhance the service by installing the operating system, database, software development environment, etc., essentially helping users set up their development platform. This level of service is called PaaS, which stands for Platform as a Service, meaning “platform as a service”. Continuing the previous analogy, this time we do not directly rent out land; we help users build the house, connect water, electricity, and gas, leaving the decoration and room arrangement to the users.Level Three: For some users, they may not have the time, energy, or ambition to develop software, preferring to use ready-made solutions. Therefore, we provide comprehensive service by pre-installing various software on the cloud platform; users simply log in to their accounts whenever they want to use it. This level of service is called SaaS, which stands for Software as a Service, meaning “software as a service”. Continuing the previous analogy, we do not just rent out land; we not only build the house, connect water, electricity, and gas, but also decorate it beautifully and furnish it with appliances, so users can just move in with their bags.
Level One: Simply renting out the three major resources after virtualization: computing, storage, and networking, and combining these resources into virtual servers. Users are entirely responsible for what systems they install, what software they develop, and what businesses they run on them. This level of service is called IaaS, which stands for Infrastructure as a Service, also known as “basic cloud”. This is like directly renting out land; users can build whatever they want on it, plant flowers, vegetables, or keep pets, entirely at their discretion.Level Two: Directly renting out virtual servers without any software, which offers maximum flexibility but may be too challenging for some users. Therefore, we enhance the service by installing the operating system, database, software development environment, etc., essentially helping users set up their development platform. This level of service is called PaaS, which stands for Platform as a Service, meaning “platform as a service”. Continuing the previous analogy, this time we do not directly rent out land; we help users build the house, connect water, electricity, and gas, leaving the decoration and room arrangement to the users.Level Three: For some users, they may not have the time, energy, or ambition to develop software, preferring to use ready-made solutions. Therefore, we provide comprehensive service by pre-installing various software on the cloud platform; users simply log in to their accounts whenever they want to use it. This level of service is called SaaS, which stands for Software as a Service, meaning “software as a service”. Continuing the previous analogy, we do not just rent out land; we not only build the house, connect water, electricity, and gas, but also decorate it beautifully and furnish it with appliances, so users can just move in with their bags.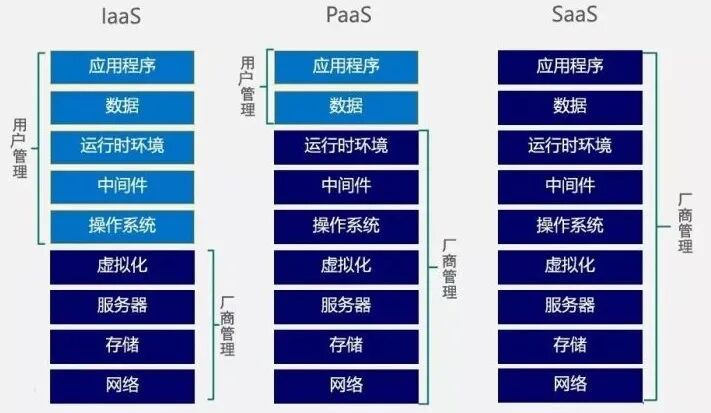 Images from WeChat Official Account “Fresh Date Classroom” Corresponding to these three levels of service, cloud service providers do increasingly more, while users have to worry less. So, beyond the specific applications mentioned at the beginning of this article, what else can the “cloud” do? From the following tables, it is evident that it covers almost everything.
Images from WeChat Official Account “Fresh Date Classroom” Corresponding to these three levels of service, cloud service providers do increasingly more, while users have to worry less. So, beyond the specific applications mentioned at the beginning of this article, what else can the “cloud” do? From the following tables, it is evident that it covers almost everything.
 Tables from WeChat Official Account “Fresh Date Classroom” Indeed, there is nothing that cannot be done; only what cannot be imagined. Besides the most basic IaaS, the vast majority of complex and difficult platforms and software have professional solutions that can be packaged as PaaS and SaaS services on the cloud, allowing ordinary users to simply pay to rent them. Cloud services are just that straightforward. Just as you do not need to build a dam to store water, divert water, or purify it; you just pay, and when you turn on the tap, water is available; you also do not need to burn coal to generate electricity or build a power grid; you just pay to use electricity. It can be said that the “cloud” has become the water and electricity of the information age. Well, that concludes this issue’s content. I hope it is helpful to everyone.— END —
Tables from WeChat Official Account “Fresh Date Classroom” Indeed, there is nothing that cannot be done; only what cannot be imagined. Besides the most basic IaaS, the vast majority of complex and difficult platforms and software have professional solutions that can be packaged as PaaS and SaaS services on the cloud, allowing ordinary users to simply pay to rent them. Cloud services are just that straightforward. Just as you do not need to build a dam to store water, divert water, or purify it; you just pay, and when you turn on the tap, water is available; you also do not need to burn coal to generate electricity or build a power grid; you just pay to use electricity. It can be said that the “cloud” has become the water and electricity of the information age. Well, that concludes this issue’s content. I hope it is helpful to everyone.— END —

Editor: Lemon
