
Insulation resistance refers to the ability of electrical equipment’s insulation material to isolate current, which is an important indicator in safety testing of equipment. It can determine whether the insulator is intact, and identify defects such as moisture, insulation degradation, and insulation breakdown. Therefore, before using electrical equipment, it is essential to use an insulation tester to check if the insulation resistance meets the requirements.


Professional Question Mark?
What is a universal insulation tester? How does it work? What are its functions? How does it empower professionals and related fields? How should we choose the instrument?
1. CEM Quick Knowledge
1
Universal Insulation Tester
The universal insulation tester integrates the functions of a multimeter and insulation testing, and can measure AC and DC voltage, current, resistance, capacitance, frequency, batteries, diodes, and other electrical values. It can also conduct insulation resistance tests on conductors, electrical components, circuits, and devices to verify the quality of electrical equipment, ensure compliance with regulations and standards, determine changes in equipment performance over time, and identify causes of failures, widely used in power plants, substations, industrial production lines, petrochemical, and other fields.
2
Testing Principle
The working principle of the universal insulation tester for measuring insulation resistance is based on Ohm’s law, which describes the relationship between resistance, current, and voltage. When the insulation resistance meter applies a high-voltage DC power supply, the insulation material in the tested equipment or circuit forms an equivalent series resistance. This series resistance can be calculated by measuring the tiny leakage current flowing through the tested equipment or circuit during the test.

3
Why Measure Insulation Resistance
1) Enhance Safety:
By performing insulation tests on disconnected live wires, grounding conductors, and ungrounded wires, the risks of electric shock, fires, and other hazardous accidents caused by short circuits can be eliminated, ensuring public and personal safety.
2) Extend Equipment Lifespan:
Periodic maintenance testing can provide data for analysis, while also predicting potential system failures, minimizing the chances of equipment malfunction or failure, and maximizing production efficiency. Additionally, insulation testing is needed to determine the cause of failures when they occur.
3) Compliance with National Standards:
Whether for production materials or electrical equipment, insulation preventive tests must be conducted according to relevant national standards to verify the quality of produced electrical equipment and ensure compliance with regulations and safety standards.
4
Selection Points
1) Voltage Level:
When selecting a universal insulation tester, its rated voltage should match the working voltage of the electrical equipment or circuit being tested. Generally, for measuring the insulation resistance of low-voltage electrical equipment, a 500V insulation resistance meter should be used; for electrical equipment rated above 500V, a 1000V or 2500V insulation resistance meter should be selected. For special equipment, such as insulators, busbars, and isolators, a higher voltage insulation resistance meter may be required, such as 2500-5000V.
Refer to the national standard GB 50150-2015 for the relationship between equipment voltage levels and insulation resistance meter selection.
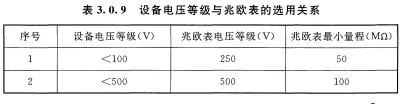
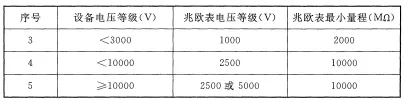
2) Measurement Range:
When selecting an instrument, ensure that its measurement range covers and appropriately exceeds the required insulation resistance values to minimize errors. Additionally, for insulation meters that do not start from zero (e.g., starting from 1MΩ or 2MΩ), they are generally not suitable for measuring the insulation resistance of low-voltage electrical equipment, as these devices may have small insulation resistance values that cannot be read on the meter, leading to misjudgment.
3) Safety Rating:
The CAT safety rating indicates the safety of the equipment in different circuit environments. Ensure that the selected insulation resistance meter’s CAT rating meets the actual measurement environment’s needs.
5
Safe Operation
1) Before Testing
-
Work on de-energized circuits whenever possible, using appropriate lockout/tagout procedures;
-
Assume that the tested circuit is energized, using appropriate personal protective equipment and safety tools;
-
Remove all jewelry and stand on rubber insulating mats.
2) During Testing
-
Do not connect the insulation multimeter to live conductors or energized equipment;
-
Disconnect the tested device using open circuit fuses, switches, or circuit breakers, and lock out and tag the tested device;
-
Disconnect branch wires, grounding wires, and all other equipment from the tested unit;
-
Discharge the capacitance of the carrier before and after testing.
6
Why Can’t the Digital Insulation Resistance Meter Apply Voltage During Testing?
The digital insulation resistance tester is designed with automatic discharge; when the insulation resistance value of the test target is very low, it will not apply voltage. Only when the resistance exceeds a certain value will the corresponding voltage (generally, for 1000V, the measurable insulation resistance value should not be less than 1MΩ) be applied. This design is safer and more convenient for users. When we find that the voltage cannot be applied, it is likely that the insulation condition is already poor.
7
Precautions
1) Do not connect the insulation tester to live conductors or energized equipment;
2) Ensure disconnection of conductor capacitance before and after testing;
3) Some equipment may have a discharge function;
4) Check for leakage current in fuses, switches, and circuit breakers in de-energized circuits. Leakage current may cause contradictory or erroneous test readings;
5) Do not use insulation testers in environments with hazardous or explosive gases, as the instrument may produce arcs if insulation performance is compromised;
6) Wear insulated rubber gloves when connecting test leads.
2. Product Recommendations

1
Product Overview
DT-6508B is a professional color-screen universal insulation tester designed, developed, and produced by CEM Huashengchang, featuring TRMS measurement and insulation testing functions. It has a 3.5-inch color TFT LCD display, fast A/D sampling, precise measurements, dual-injection molded housing, 2-meter drop resistance, safety, and durability. Bluetooth communication allows for convenient on-site recording and transmission of measurement scenarios and data. It provides high-precision measurement, with data logging and trend recording capabilities, and can connect with CEM’s professional APP and PC software, widely used in electricity, electrical, mechanical equipment, maintenance, and acceptance fields.
2
Product Parameters
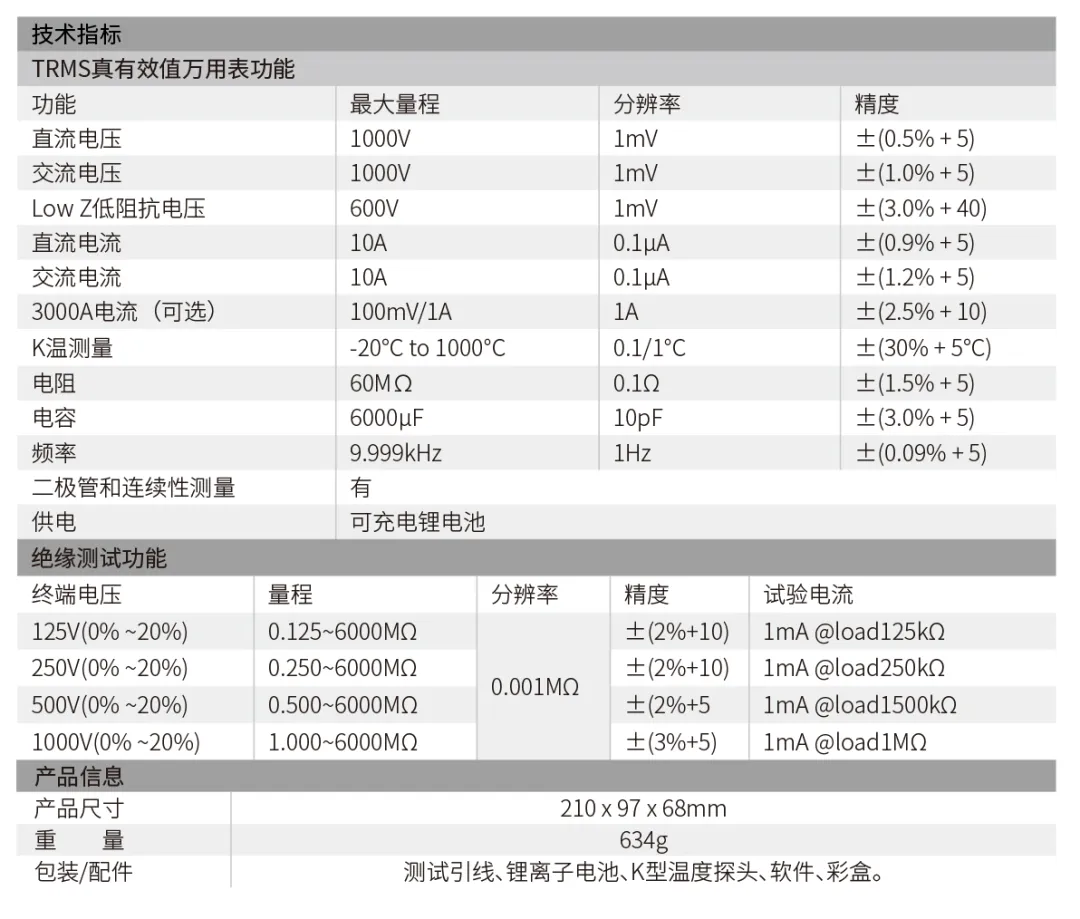
3
Product Advantages
1) 6000 display counts, easy to observe test data and images;
2) Low-pass filter function for precise measurement of variable frequency motor power indicators (VFD frequency testing);
3) Insulation resistance testing range: 0.001MΩ-6000MΩ;
4) Insulation voltage testing range: 125V, 250V, 500V, 1000V;
5) 1kHz AC voltage and current frequency bandwidth design;
6) AC, true RMS measurement for more accurate readings;
7) Polarization index ratio testing;
8) Trend capture function for timely review of historical test data;
9) Peak capture function, up to 500us;
10) High voltage and overload indicators;
11) K-type temperature measurement;
12) Full calibration with PC;
13) CAT III 1000V, CAT IV 600V safety rating design;
14) 3000A flexible clamp head testing (optional).
4
Product Applications
1) Electrical Equipment Insulation Testing:
Using an insulation tester to test the insulation performance of transformers, generators, switch cabinets, and other electrical equipment to ensure their safe and reliable operation.
2) Wire and Cable Insulation Testing:
Testing the insulation of various specifications and types of wires and cables to check compliance with standard requirements and predict their service life.
3) Line Fault Detection:
Conducting insulation tests on various parts of the line can quickly locate fault points in the circuit, improving fault elimination efficiency.
4) Maintenance and Repair:
Regularly testing various equipment and lines to timely detect potential issues and perform repairs, extending equipment lifespan and enhancing system stability.
